We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1072
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
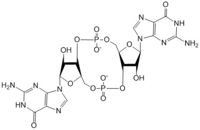
4. The result of this reaction is the C3 alcohol group of each ribose covalently bonded to an α-phosphate forming c-di-GMP. | 4. The result of this reaction is the C3 alcohol group of each ribose covalently bonded to an α-phosphate forming c-di-GMP. | ||
| - | ===CZB Domain=== | + | ===CZB Domain and Zinc Binding Site=== |
The <scene name='69/694239/Zb_domain_residues_19-90/5'>CZB Domain</scene>, residues 19-90, is responsible for regulating the function of DgcZ. The domain contains the allosteric binding site of the enzyme with cooperative binding. Four residues bind zinc with a high affinity even at 10<sup>-16</sup>M concentrations of Zinc in solution. Due to the tightness of Zinc binding, the enzyme has not yet been crystallized in its complete active conformation without the presence of Zinc metal inhibitor. When zinc is bound, DgcZ activity is limited<sup>[1]</sup>. Two Zinc binding sites are located on the CZB domain. | The <scene name='69/694239/Zb_domain_residues_19-90/5'>CZB Domain</scene>, residues 19-90, is responsible for regulating the function of DgcZ. The domain contains the allosteric binding site of the enzyme with cooperative binding. Four residues bind zinc with a high affinity even at 10<sup>-16</sup>M concentrations of Zinc in solution. Due to the tightness of Zinc binding, the enzyme has not yet been crystallized in its complete active conformation without the presence of Zinc metal inhibitor. When zinc is bound, DgcZ activity is limited<sup>[1]</sup>. Two Zinc binding sites are located on the CZB domain. | ||
| - | |||
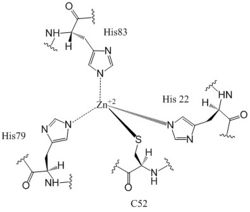
[[Image:Zinc binding site labels.jpg|250 px|left|thumb|Zn<sup>+2</sup> Coordination to amino acid residues on three of the four 𝝰 helices of DgcZ]] | [[Image:Zinc binding site labels.jpg|250 px|left|thumb|Zn<sup>+2</sup> Coordination to amino acid residues on three of the four 𝝰 helices of DgcZ]] | ||
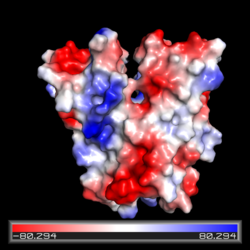
[[Image:Electrostatic map front view CZB.png|250 px|right|thumb|Electrostatic potential map of the CZB domain of Diguanylate Cyclase. Regions of relatively negative charge are in red and regions of relatively positive charge are in blue. Electrically neutral regions are in white]] | [[Image:Electrostatic map front view CZB.png|250 px|right|thumb|Electrostatic potential map of the CZB domain of Diguanylate Cyclase. Regions of relatively negative charge are in red and regions of relatively positive charge are in blue. Electrically neutral regions are in white]] | ||
| - | === Zinc Binding Site === | ||
Most cells possess efficient Zinc uptake systems, as Zinc is a reactive Lewis Acid. Zinc binds incredibly tightly to this enzyme at subfemtomolar concentrations, attributing to why the enzyme has not been crystallized without Zinc present. The Zinc co-purified with the protein. Zinc allosterically inhibits the activity of enzyme DgcZ through two allosteric binding sites located on the CZB domain <sup>[1]</sup>. The inhibition prevents regulation of GGDEF domain function, the location of the active site. The CZB domain is folded into four anti-parallel α-helices as a 2-fold symmetric homodimer, with the N-terminus on the helix 𝝰4. The allosteric binding site includes a <scene name='69/694239/Zinc_binding_domain/4'>3His/1Cys</scene> motif that uses amino acids H22 of 𝝰1, C52 of 𝝰2, and H79 and H83 of 𝝰3, spanning three of the four alpha helices of the CZB domain and coordinating the Zinc residue in a tetrahedral fashion. For clarification, the entirety of 𝝰helix 2 on one monomer of CZB is not successfully crystallized after the Cys52 residue and is not the N-terminal residue. | Most cells possess efficient Zinc uptake systems, as Zinc is a reactive Lewis Acid. Zinc binds incredibly tightly to this enzyme at subfemtomolar concentrations, attributing to why the enzyme has not been crystallized without Zinc present. The Zinc co-purified with the protein. Zinc allosterically inhibits the activity of enzyme DgcZ through two allosteric binding sites located on the CZB domain <sup>[1]</sup>. The inhibition prevents regulation of GGDEF domain function, the location of the active site. The CZB domain is folded into four anti-parallel α-helices as a 2-fold symmetric homodimer, with the N-terminus on the helix 𝝰4. The allosteric binding site includes a <scene name='69/694239/Zinc_binding_domain/4'>3His/1Cys</scene> motif that uses amino acids H22 of 𝝰1, C52 of 𝝰2, and H79 and H83 of 𝝰3, spanning three of the four alpha helices of the CZB domain and coordinating the Zinc residue in a tetrahedral fashion. For clarification, the entirety of 𝝰helix 2 on one monomer of CZB is not successfully crystallized after the Cys52 residue and is not the N-terminal residue. | ||
Revision as of 02:26, 21 April 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Diguanylate Cyclase DgcZ from Escherichia coli
| |||||||||||