Biological Function
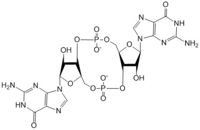
Figure 1: Cyclic-dimeric-GMP. Cyclic-dimeric-GMP is the product of the reaction catalyzed by DgcZ.
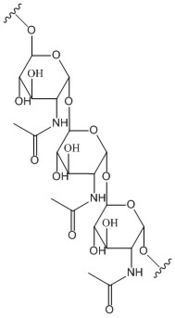
Figure 2: Poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine. Poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine is a carbohydrate formed downstream of c-di-GMP utilized in formation of bacterial bio-films.
Diguanylate cyclases are class 2 transferase enzymes (2.7.7.65) that catalyze the production of cyclic dimeric-guanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP, Figure 1), important to signal transduction as a second messenger[1]. Signal transduction sends messages through cells to induce cellular responses, most commonly through phosphorylation or dephosphoylation of substrate molecules. Escherechia coli (E. coli), a gram-negative bacterium often found in the intestines of mammals, uses diguanylate cyclase (DgcZ) in the synthesis of its biofilm[2]. DgcZ from E. coli acts as a catalyst, synthesizing c-di-GMP from two substrate guanosine triphosphate (GTP) molecules. C-di-GMP is a second messenger in the production of poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine (poly-GlcNAc, Figure 2), a polysaccharide required for E. coli biofilm production[2]. This biofilm allows E. coli to adhere to extracellular surfaces. Only the inactive conformation of the complete DgcZ enzyme has been crystallized to date[3].
![Figure 3: Diagram of DgcZ. DgcZ is shown in its active (left) and inactive (right) conformations. The boxes represent the GGEEF domains of the enzyme, while the cylinders represent the alpha helices of the CZB domains where the Zinc binding sites are located[3]. Binding Zn+2 inactivates the enzyme, disrupting the active conformation of the GGEEF domain by not allowing the GTP molecules to react. The red and blue sections represent the two monomers of the symmetric homodimer.](/wiki/images/thumb/1/10/Conformation_change_2_bold.png/250px-Conformation_change_2_bold.png)
Figure 3: Diagram of DgcZ. DgcZ is shown in its active (left) and inactive (right) conformations. The boxes represent the GGEEF domains of the enzyme, while the cylinders represent the alpha helices of the CZB domains where the Zinc binding sites are located
[3]. Binding Zn
+2 inactivates the enzyme, disrupting the active conformation of the GGEEF domain by not allowing the GTP molecules to react. The red and blue sections represent the two monomers of the symmetric homodimer.
Structural Overview
![Figure 4: Diguanylate cyclase DgcZ from E. Coli. The domains of the enzyme are labeled, as well as the allosteric binding sites and the Zn+2 binding sites on the CZB domains[3].](/wiki/images/thumb/3/38/DgcZ_all_domains_sites_labeled.png/250px-DgcZ_all_domains_sites_labeled.png)
Figure 4: Diguanylate cyclase DgcZ from E. Coli. The domains of the enzyme are labeled, as well as the allosteric binding sites and the Zn
+2 binding sites on the CZB domains
[3].
DgcZ is a dimeric protein with per monomer[4]. The DgcZ protein has symmetry down its central axis. The catalytic glycine-glycine-glutamate-glutamate-phenylalanine (GGEEF) domains are responsible for synthesizing c-di-GMP. The regulatory chemoreceptor Zinc binding (CZB) domains house the two zinc binding sites, one site located on each monomer. DgcZ binds Zinc in the CZB domains with sub-femtomolar (10-16M) affinity. When Zinc is bound, the CZB and GGEEF domains adopt conformations that inhibit DgcZ function, as illustrated in Figure 3[3]. Enzyme DgcZ was co-crystallized with Zinc, fixing the structure in its inactivate conformation. The GGEEF domains are catalytic, containing the active sites for cyclizing GTP into c-di-GMP. The CZB domains are used for ligand-mediated regulation of c-di-GMP production and have an important role in signal transduction of bacteria. CZB and GGEEF domains are found in proteins from many bacterial lineages, including DgcZ homologs[5].
Catalytic GGEEF Domains
The of DgcZ are part of the GGDEF family of proteins that are characterized by a conserved sequence, GG[DE][DE]F[6]. The GGEEF domains contain a central five-stranded β-sheet surrounded by five α-helices (Figure 4). The GGEEF domains each possess a catalytic half-site (residues Gly-206, Gly-207, Glu-208, Glu-209, and Phe-210) that, when combined together in a productive conformation, form the entire . Each half-site binds the guanine base of a single GTP molecule via hydrogen bonding to residues . This scene depicts an inactive form of the protein because it was crystallized with zinc bound, destroying the active conformation of GGEEF domains. The ribose of each guanosine triphosphate, and subsequent product c-di-GMP riboses, are held only loosely by the enzyme, while the phosphate groups are not bound to the active site at all[3].
The alpha phosphate is available for attack by the 3 prime hydroxyl group on another GTP. A (Mg+2) stabilizes the negative charges on the phosphate groups. When in the inactive conformation, the C3 of the ribose on one GTP is (9-10 Angstroms) from the alpha phosphate on the other GTP to undergo cyclization. When in the productive conformation, each GTP is held in close proximity with the α-phosphate groups overlapping C3 of the ribose ring. This conformation allows the α-phospate of one GTP to react with the alcohol group attached to C3 of the ribose on the second GTP, resulting in a cyclization of the two molecules into c-di-GMP[3].
Mechanism of Action
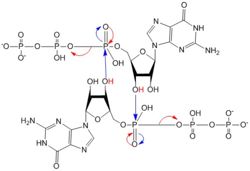
Figure 5: Mechanism of c-di-GMP synthesis. Addition arrows are shown in blue and elimination arrows are shown in red.
Diguanylate cyclases only function efficiently when the two half-sites of the GGEEF domains are in close enough proximity to bind the substrates. The presence of Zinc disrupts the ability of the domains to overlap.
1. The enzyme coordinates the substrate in a conformation to allow deprotonation of the C3 alcohol groups of the ribose. The negatively charged Oxygens on the phosphate groups of GTP are stabilized by Mg2+ ions.
2. The deprotonated oxygen then acts as a nucleophile to attack the α-phosphate of GTP. This initiates an addition-elimination reaction.
3. The β and γ phosphates of GTP are kicked off as leaving groups.
4. The result of this reaction is the C3 alcohol group of each ribose covalently bonded to an α-phosphate forming c-di-GMP[7].
CZB Domains and Zinc Binding Site
The , residues 19-90, are responsible for regulating the function of DgcZ due to the presence of two Zinc binding sites. The CZB domains contain the of the enzyme (Figure 4), which exhibit cooperative binding. Four residues bind Zinc with a high affinity even at 10-16M concentrations of Zinc in solution. Due to the tightness of Zinc binding, the complete enzyme has not yet been crystallized in its active conformation without the presence of Zinc metal inhibitor. When Zinc is bound, DgcZ activity is limited[3].
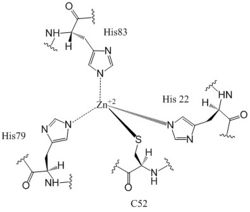
Figure 6: Zn+2 Coordination to amino acid residues. Three of the four 𝝰 helices of the CZB domain of DgcZ coordinate to the Zn
+2 ion for binding.
Most cells possess efficient Zinc uptake systems, as Zinc is a reactive Lewis Acid. Zinc binds incredibly tightly to this enzyme at subfemtomolar concentrations, attributing to why Zinc co-purified with the protein. Zinc allosterically inhibits the activity of enzyme DgcZ through two allosteric binding sites located on the CZB domain [8]. The inhibition prevents regulation of GGDEF domain function, the location of the active site. The CZB domain is folded into four anti-parallel α-helices as a 2-fold symmetric homodimer, with the N-terminus on helix 𝝰4. The allosteric binding site includes a motif that uses amino acids H22 of 𝝰1, C52 of 𝝰2, and H79 and H83 of 𝝰3, spanning three of the four alpha helices of each CZB domain and coordinating the Zinc residue in a tetrahedral fashion (Figure 6). For , the entirety of 𝝰helix 2 on one monomer of CZB is not successfully crystallized after the Cys52 residue and is not the N-terminal residue[3].
Zahringer et al. mutated Cys52 to Ala through site-directed mutagenesis, resulting in a lack of coordination on α2. The cysteine residue is not essential for Zinc binding, as Zinc still coordinates to the three His residues with the Cys52Ala mutation, but α2 is free to move and expose the Zinc binding pocket. This exposure was found to lower the protein's affinity for zinc, as the mutation of cysteine to alanine increased the activity of the DgcZ. When not coordinated to Zn+2, the CZB domain presumably adopts a conformation that straightens the . This results in a closer association between on the alpha helices in the already of the CZB domain. Increased activity of DgcZ presumably occurs due to this conformational shift, which forces the GGEEF domain into its productive conformation. Until the entire protein is crystallized without Zn+2, this conformational change is merely hypothesized. But, it is known that activity increases without Zinc due to activation of poly-GlcNAc production, biofilm formation, and maximal cyclic di-GMP production.
Other Ligands
c-di-GMP and GTP bind although the function of this binding is unknown. Very weak product inhibition was observed when c-di-GMP bound allosterically but the inhibition was so weak, it is possible the c-di-GMP actually interacts with another as of yet unknown molecule at that site[9].
See Also
3tvk Crystal structure of GGEEF domain from DgcZ
3t9o Crystal structure of CZB domain from DgcZ
Diguanylate cyclase Diguanylate cyclase (DGC) structure and function
4URG Crystal structure of DGC from 'T. maritima' in a pseudo-active form.
4URQ Crystal structure of DGC from 'T. maritima' with an inhibitor site mutant
4URS Crystal structure of DGC from 'T. maritima'
References
1. Hengge, R. (2009). Principles of c-di-GMP signalling in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 263–273. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2109
2. Wang, X., Dubey, A.K., Suzuki, K., Baker, C.S., Babitzke, P., and Romeo, T. (2005). CsrA post-transcriptionally represses pgaABCD, responsible for synthesis of a biofilm polysaccharide adhesin of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 56, 1648–1663. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04648.x
3. Zahringer, Franziska, Egidio Lancanna, Urs Jenal, Tilman Schirmer, and Alex Boehm. "Structure of E. Coli Zinc-Sensory Diguanylate Cyclase DgcZ." Cell Press: Structure 21 (2013): 1149-157.doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.04.026
4. R. Paul, S. Abel, P. Wassmann, A. Beck, H. Heerklotz, U. Jenal Activation of the diguanylate cyclase PleD by phosphorylation-mediated dimerization J. Biol. Chem., 282 (2007), pp. 29170–29177 doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704702200
5. Jenny Draper, K. Karplus, K. Ottemann. Identification of a Chemoreceptor Zinc-Binding Domain Common to Cytoplasmic Bacterial Chemoreceptors. Journal of Bacteriology. Vol. 193, No. 17. 4338-4345. (2011). doi: 10.1128/JB.05140-11
6. Carmen Chan, R. Paul, D. Samoray, N. Amiot, B. Giese, U. Jenal, T. Schirmer. Structural basis of activity and allosteric control of diguanylate cyclases. PNAS. Vol 101. No. 49 17084-17089. (2004). doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406134101
7. Chan, C., Paul, R., Samoray, D., Amiot, N.C., Giese, B., Jenal, U., and Schirmer, T. (2004). Structural basis of activity and allosteric control of diguanylate cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 17084–17089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406134101
8. Vallee, B.L., and Falchuk, K.H. (1993). The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol. Rev. 73, 79–118. PMID: 8419966
9. Boehm, A., Steiner, S., Zaehringer, F., Casanova, A., Hamburger, F., Ritz, D., Keck, W., Ackermann, M., Schirmer, T., and Jenal, U. (2009). Second messenger signalling governs escherichia coli biofilm induction upon ribosomal stress. Mol. Microbiol. 72, 1500–1516. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06739.x.


![Figure 3: Diagram of DgcZ. DgcZ is shown in its active (left) and inactive (right) conformations. The boxes represent the GGEEF domains of the enzyme, while the cylinders represent the alpha helices of the CZB domains where the Zinc binding sites are located[3]. Binding Zn+2 inactivates the enzyme, disrupting the active conformation of the GGEEF domain by not allowing the GTP molecules to react. The red and blue sections represent the two monomers of the symmetric homodimer.](/wiki/images/thumb/1/10/Conformation_change_2_bold.png/250px-Conformation_change_2_bold.png)
![Figure 4: Diguanylate cyclase DgcZ from E. Coli. The domains of the enzyme are labeled, as well as the allosteric binding sites and the Zn+2 binding sites on the CZB domains[3].](/wiki/images/thumb/3/38/DgcZ_all_domains_sites_labeled.png/250px-DgcZ_all_domains_sites_labeled.png)


