Prolyl hydroxylase domain
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' scene='45/459221/Cv/1' caption='Human PHD2 catalytic domain complex with Fe+2 ion (orange), inhibitor and sulfate, [[3ouh]]' pspeed='8'> |
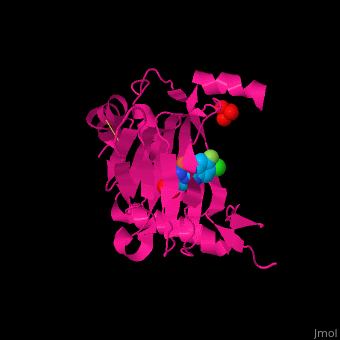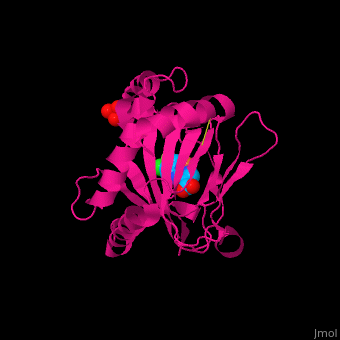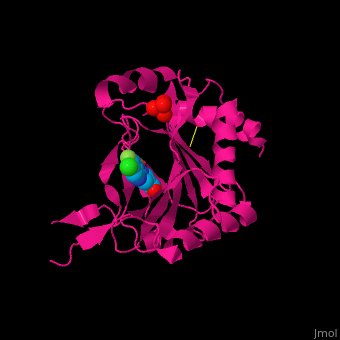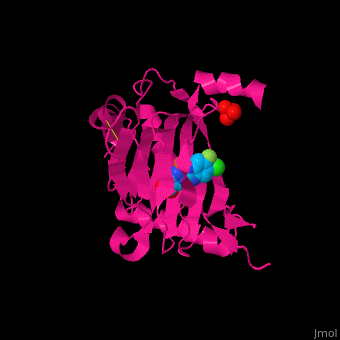
'''Prolyl hydroxylase domain''' (PHD) proteins mediate oxygen-dependent degradation of Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) α subunit. They include PHD1, PHD2 and PHD3. The PHD is a Fe+2/oxogluterate (2OG)-dependent enzyme. [[3ouh]] is the crystallized structure of the enzyme PHD2, an [[oxidoreductase]] that is 237 amino acids long with a molecular weight of 27 kDa. [[3ouh]] is found in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and is a homolog of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EGLN1 EGLN1] found in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caenorhabditis_elegans C. elegans]. | '''Prolyl hydroxylase domain''' (PHD) proteins mediate oxygen-dependent degradation of Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) α subunit. They include PHD1, PHD2 and PHD3. The PHD is a Fe+2/oxogluterate (2OG)-dependent enzyme. [[3ouh]] is the crystallized structure of the enzyme PHD2, an [[oxidoreductase]] that is 237 amino acids long with a molecular weight of 27 kDa. [[3ouh]] is found in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and is a homolog of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EGLN1 EGLN1] found in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caenorhabditis_elegans C. elegans]. | ||
Revision as of 06:51, 16 September 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of prolyl hydroxylase domain
2y33 – hPHD2 catalytic domain + Zn + chloro-iodoisoquinolin-carbonyl glycine – human
2y34 - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + chloro-iodoisoquinolin-carbonyl glycine
3ouh, 3oui - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + inhibitor
3ouj - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + 2OG
3hqr - hPHD2 catalytic domain (mutant) + Mn + HIF 1 α C terminal + oxalylglycine
3hqu - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + HIF 1 α C terminal + chloro-iodoisoquinolin-carbonyl glycine
2hbt, 2hbu - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + chloro-iodoisoquinolin-carbonyl glycine
2g19, 2g1m - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + hydroxy-iodoisoquinolin-carbonyl glycine
4h6j – hPHD Pasb domain (mutant) + aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator (mutant)
References
- ↑ Stolze IP, Mole DR, Ratcliffe PJ. Regulation of HIF: prolyl hydroxylases. Novartis Found Symp. 2006;272:15-25; discussion 25-36. PMID:16686427
- ↑ Rosen M D, Venkatesan H, Peltier H M, Bembenek S D, Kanelakis K C, Zhao L X, Leonard B E, Hocutt F M, Wu X, Palomino H L, Brondtetter T I, Haugh P V, Cagnon L, Yan W, Liotta L A, Young A, Mirzadegan T, Shankley N P, Barrett T D, Rabinowitz M H. Benzimidazole-2-pyrazole HIF Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Inhibitors as Oral Erythropoietin Secretagogues. ACS Medicinal Chemical Letters. 2010 Oct 5.
Created with the participation of Andrew Winslow.