We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Reverse transcriptase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
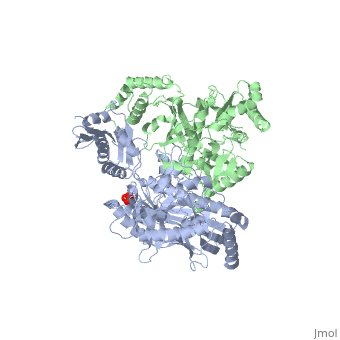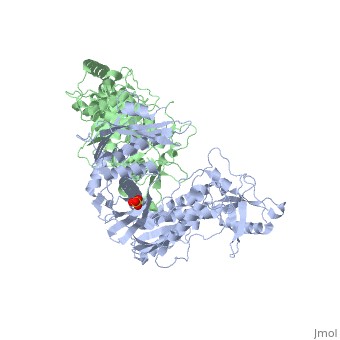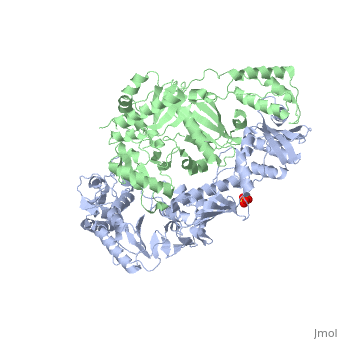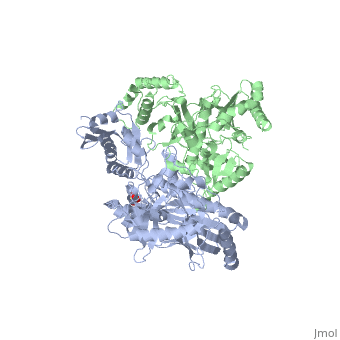
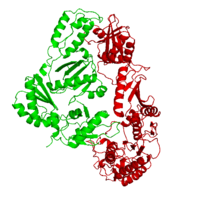
| - | This ''hand-like'' <scene name='Reverse_transcriptase/Chains/2'>heterodimer</scene> protein has an usual length of 1000 residues (560 in Chain A and 440 for B), a third of them involved in alpha helices and almost a quarter involved in beta sheets, showing α+β <scene name='Reverse_transcriptase/Secondary/2'>secondary structure</scene> domains. <scene name='Reverse_transcriptase/Chaina/2'>Chain A</scene> has an usual weight of 66KDa whereas <scene name='Reverse_transcriptase/Chainb/2'>Chain B</scene> is around 51KDa. These monomers are derived from the same gene, but p51 lacks the amino acids of one active site and has a different tertiary structure conformation compared to p66. Because of this, p51 is enzymatically inactive | + | This ''hand-like'' <scene name='Reverse_transcriptase/Chains/2'>heterodimer</scene> protein has an usual length of 1000 residues (560 in Chain A and 440 for B), a third of them involved in alpha helices and almost a quarter involved in beta sheets, showing α+β <scene name='Reverse_transcriptase/Secondary/2'>secondary structure</scene> domains. <scene name='Reverse_transcriptase/Chaina/2'>Chain A</scene> has an usual weight of 66KDa whereas <scene name='Reverse_transcriptase/Chainb/2'>Chain B</scene> is around 51KDa. These monomers are derived from the same gene, but p51 lacks the amino acids of one active site and has a different tertiary structure conformation compared to p66. Because of this, p51 is enzymatically inactive<ref>PMID: 1377403</ref> |
There are five distinct structures within the p66 subchain that are used to describe the functions of RT: the fingers (residues 1–85 and 118–155), the palm (residues 86–117 and 156–236), the thumb (residues 237–318), the connection (319–426), and the RNase H (residues 427-end). The palm contains the main active site (residues 110, 185-186).[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2881421/?tool=pubmed] | There are five distinct structures within the p66 subchain that are used to describe the functions of RT: the fingers (residues 1–85 and 118–155), the palm (residues 86–117 and 156–236), the thumb (residues 237–318), the connection (319–426), and the RNase H (residues 427-end). The palm contains the main active site (residues 110, 185-186).[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2881421/?tool=pubmed] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 27 September 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Reverse transcriptase
Updated on 27-September-2017
See Also
- Reverse Transcriptase at Wikipedia
- Molecule of the Month (09/2002) at RCSB Protein Data Bank
- List of Reverse Transcriptase articles at Proteopedia and at RCSB Protein Data Bank
- Model of Reverse Transcriptase as one of the CBI Molecules on the Molecular Playground
- See Transcription for additional Proteopedia articles on the subject.
- For additional information, see: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- For additional information, see: Transcription and RNA Processing
References
- ↑ Kohlstaedt LA, Wang J, Friedman JM, Rice PA, Steitz TA. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783-90. PMID:1377403 doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1377403 http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1377403
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201200096
- [2] Consurf Server Data Base. Evolutionary conservation profile for Reverse Transcriptase PDB file 1JLB
- [3] Abbondanzieri, E.A. et al. Nature 453, 184-189 (2008) | doi:10.1038/nature06941
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Daniel Moyano-Marino, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Amol Kapoor, Jaime Prilusky, Brian Foley, Lynmarie K Thompson, Eric Martz