User:Alec Bertsch/sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
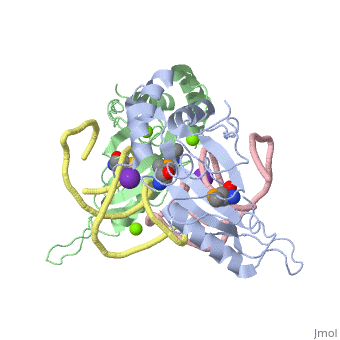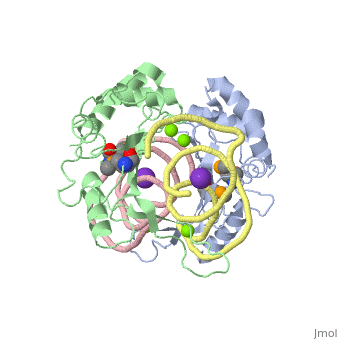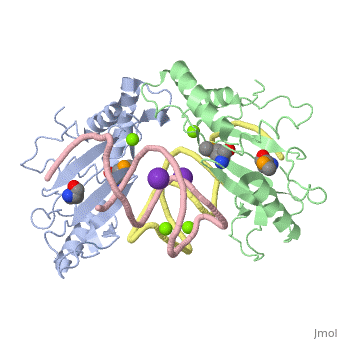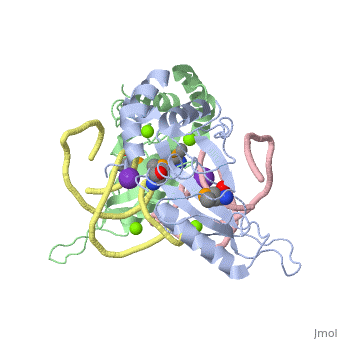
| - | The <scene name='76/769327/Ribosome_l5_protein/2'>L5/5S rRNA complex</scene> makes up the main function and structural component of the large ribosomal sub-unit. | + | The <scene name='76/769327/Ribosome_l5_protein/2'>L5/5S rRNA complex</scene> makes up the main function and structural component of the large ribosomal sub-unit. This image depicts two L5 proteins surrounding two strands of rRNA. |
<scene name='76/769327/Asp4/1'>Asp4</scene> is one of many residues within the L5 protein that have a crucial role in the binding affinity of 5S rRNA.<ref>PMID:1370121</ref> Mutations on these residues have been shown to drastically decrease they probability of the 5S rRNA binding to the L5 protein. Residues like <scene name='76/769327/Asn40/1'>Asn40</scene> directly influence the binding ability of 5S rRNA. Mutations in these residues result it a less stable interaction between the 5S rRNA and L5 protein. <ref>PMID:1370121</ref> | <scene name='76/769327/Asp4/1'>Asp4</scene> is one of many residues within the L5 protein that have a crucial role in the binding affinity of 5S rRNA.<ref>PMID:1370121</ref> Mutations on these residues have been shown to drastically decrease they probability of the 5S rRNA binding to the L5 protein. Residues like <scene name='76/769327/Asn40/1'>Asn40</scene> directly influence the binding ability of 5S rRNA. Mutations in these residues result it a less stable interaction between the 5S rRNA and L5 protein. <ref>PMID:1370121</ref> | ||
The 5S rRNA has many <scene name='76/769327/Conserved_rrna/1'>conserved residues</scene> that contribute to both its structure and function. These residues include C47, U48, C37, C38, A34, and G44. The structural role comes from stacking interactions that occur from the binding of these residues.<ref>DOI:10.1017/S1355838202029953</ref> | The 5S rRNA has many <scene name='76/769327/Conserved_rrna/1'>conserved residues</scene> that contribute to both its structure and function. These residues include C47, U48, C37, C38, A34, and G44. The structural role comes from stacking interactions that occur from the binding of these residues.<ref>DOI:10.1017/S1355838202029953</ref> | ||
Revision as of 12:27, 10 October 2017
L5/5S rRNA Complex
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wise JP, Leonard JC, Patierno SR. Clastogenicity of lead chromate particles in hamster and human cells. Mutat Res. 1992 Jan;278(1):69-79. PMID:1370121
- ↑ Meskauskas A, Dinman JD. Ribosomal protein L5 helps anchor peptidyl-tRNA to the P-site in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA. 2001 Aug;7(8):1084-96. PMID:11497428
- ↑ Korepanov AP, Korobeinikova AV, Shestakov SA, Garber MB, Gongadze GM. Protein L5 is crucial for in vivo assembly of the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit central protuberance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(18):9153-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks676. Epub 2012 Jul, 20. PMID:22821559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks676
- ↑ Barciszewska MZ, Szymanski M, Erdmann VA, Barciszewski J. Structure and functions of 5S rRNA. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(1):191-8. PMID:11440169
- ↑ Pelava A, Schneider C, Watkins NJ. The importance of ribosome production, and the 5S RNP-MDM2 pathway, in health and disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Aug 15;44(4):1086-90. doi: 10.1042/BST20160106. PMID:27528756 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BST20160106
- ↑ Bogdanov AA, Dontsova OA, Dokudovskaya SS, Lavrik IN. Structure and function of 5S rRNA in the ribosome. Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Nov-Dec;73(11-12):869-76. PMID:8722002
- ↑ Wise JP, Leonard JC, Patierno SR. Clastogenicity of lead chromate particles in hamster and human cells. Mutat Res. 1992 Jan;278(1):69-79. PMID:1370121
- ↑ Wise JP, Leonard JC, Patierno SR. Clastogenicity of lead chromate particles in hamster and human cells. Mutat Res. 1992 Jan;278(1):69-79. PMID:1370121
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S1355838202029953