AppA protein BLUF domain
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
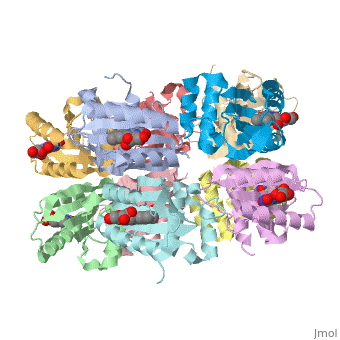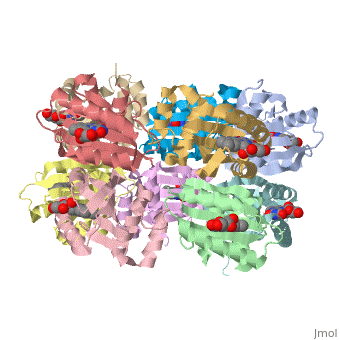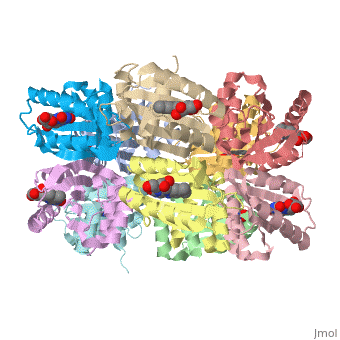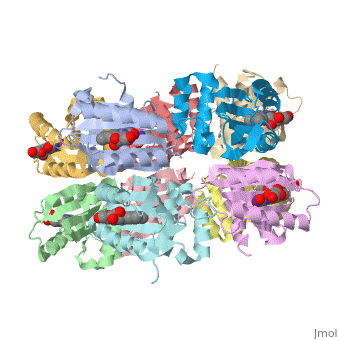
Each monomer is comprised of 5 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_310/Monomer/3'>β-strands</scene> and 4<scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_310/Monomer/2'>α-helices</scene> in the order of β1α1β2β3α2β4β5α3α4. Specifically, the BLUF domain of the monomer contains β1α1β2β3α2β4β5, while the C-terminal domain contains α3α4<ref name="one" />. The C-terminal domain interacts with the end of the β-sheet of the neighbouring monomer. | Each monomer is comprised of 5 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_310/Monomer/3'>β-strands</scene> and 4<scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_310/Monomer/2'>α-helices</scene> in the order of β1α1β2β3α2β4β5α3α4. Specifically, the BLUF domain of the monomer contains β1α1β2β3α2β4β5, while the C-terminal domain contains α3α4<ref name="one" />. The C-terminal domain interacts with the end of the β-sheet of the neighbouring monomer. | ||
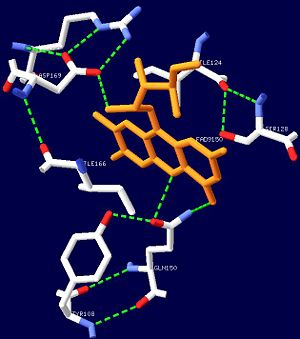
| - | The isoalloxazine ring of FAD is located between <scene name=' | + | The isoalloxazine ring of FAD is located between <scene name='44/447813/Cv/1'>α1 and α2</scene> of the BLUF domain, between <scene name='44/447813/Cv/4'>two highly conserved hydrophobic residues: Ile124 and Ile166</scene><ref name="one" />. FAD forms hydrogen bonds with the following amino acid residues: <scene name='44/447813/Cv/5'>Asn132, Gln150, Arg165 and Asp169</scene> (ses also static image Figure 1)<ref name="one" />. More specifically, the <scene name='44/447813/Cv/6'>side chain of Asn131 binds to O2 of FAD</scene> and <scene name='44/447813/Cv/7'>Asn132 binds to N3 and O4 of FAD</scene>. The <scene name='44/447813/Cv/8'>guanido group of Arg165 contributes to a network between FAD and the apo protein</scene>. The amide N of the Gln150 sidechain interacts with N5 and O4 of FAD through hydrogen bonding, while the amide O of the sidechain is closely linked with the hydroxyl oxygen of the highly conserved Tyr8 residue, forming a <scene name='44/447813/Cv/9'>FAD-Gln150-Tyr108 network</scene><ref name="one" />. This conserved Tyr108 residue is the only residue that has been shown to be essential for light reaction in the BLUF domain containing AppA and Slr1694 proteins<ref name ="seven">PMID: 17042486</ref>. |
==Further Analyses== | ==Further Analyses== | ||
Revision as of 12:37, 24 May 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of BLUF domain protein
Updated on 24-May-2018
2byc - RsBLUF dark structure - Rhodobacter sphaeroides
2iyg, 2iyi - RsBLUF dark structure BLUF domain (mutant)
1x0p - BLUF - Thermosynechococcus elongatus
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 Kita A, Okajima K, Morimoto Y, Ikeuchi M, Miki K. Structure of a cyanobacterial BLUF protein, Tll0078, containing a novel FAD-binding blue light sensor domain. J Mol Biol. 2005 May 27;349(1):1-9. Epub 2005 Apr 9. PMID:15876364 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.067
- ↑ van der Horst MA, Hellingwerf KJ. Photoreceptor proteins, "star actors of modern times": a review of the functional dynamics in the structure of representative members of six different photoreceptor families. Acc Chem Res. 2004 Jan;37(1):13-20. PMID:14730990 doi:10.1021/ar020219d
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Masuda S, Bauer CE. AppA is a blue light photoreceptor that antirepresses photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Cell. 2002 Sep 6;110(5):613-23. PMID:12230978
- ↑ Laan W, van der Horst MA, van Stokkum IH, Hellingwerf KJ. Initial characterization of the primary photochemistry of AppA, a blue-light-using flavin adenine dinucleotide-domain containing transcriptional antirepressor protein from Rhodobacter sphaeroides: a key role for reversible intramolecular proton transfer from the flavin adenine dinucleotide chromophore to a conserved tyrosine? Photochem Photobiol. 2003 Sep;78(3):290-7. PMID:14556317
- ↑ Hasegawa K, Masuda S, Ono TA. Spectroscopic analysis of the dark relaxation process of a photocycle in a sensor of blue light using FAD (BLUF) protein Slr1694 of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005 Jan;46(1):136-46. Epub 2005 Jan 19. PMID:15659451 doi:10.1093/pcp/pci003
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Iseki M, Matsunaga S, Murakami A, Ohno K, Shiga K, Yoshida K, Sugai M, Takahashi T, Hori T, Watanabe M. A blue-light-activated adenylyl cyclase mediates photoavoidance in Euglena gracilis. Nature. 2002 Feb 28;415(6875):1047-51. PMID:11875575 doi:10.1038/4151047a
- ↑ Yuan H, Anderson S, Masuda S, Dragnea V, Moffat K, Bauer C. Crystal structures of the Synechocystis photoreceptor Slr1694 reveal distinct structural states related to signaling. Biochemistry. 2006 Oct 24;45(42):12687-94. PMID:17042486 doi:10.1021/bi061435n
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Amanda Cookhouse, Jaime Prilusky