We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
4v94
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | ||
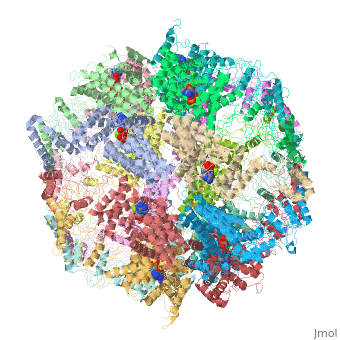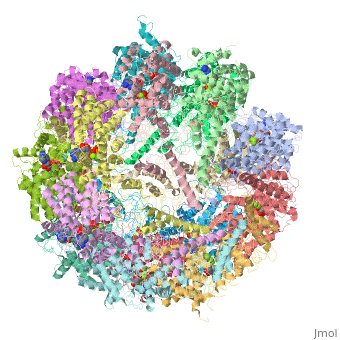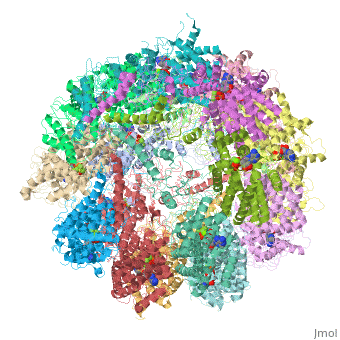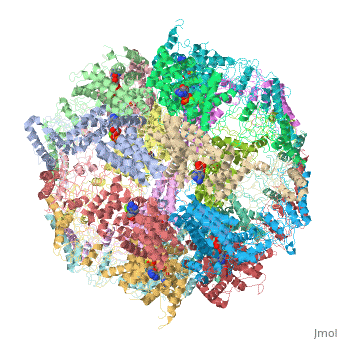
==Molecular architecture of the eukaryotic chaperonin TRiC/CCT derived by a combination of chemical crosslinking and mass-spectrometry, XL-MS== | ==Molecular architecture of the eukaryotic chaperonin TRiC/CCT derived by a combination of chemical crosslinking and mass-spectrometry, XL-MS== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='4v94' size='340' side='right' caption='[[4v94]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.80Å' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='4v94' size='340' side='right'caption='[[4v94]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.80Å' scene=''> |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4v94]] is a 32 chain structure with sequence from [ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4v94]] is a 32 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae_S288C Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C]. This structure supersedes the now removed PDB entries [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/send-pdb?obs=1&id=4d8q 4d8q] and [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/send-pdb?obs=1&id=4d8r 4d8r]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4V94 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4V94 FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ADP:ADENOSINE-5-DIPHOSPHATE'>ADP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=BEF:BERYLLIUM+TRIFLUORIDE+ION'>BEF</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene> | + | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ADP:ADENOSINE-5-DIPHOSPHATE'>ADP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=BEF:BERYLLIUM+TRIFLUORIDE+ION'>BEF</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene></td></tr> |
| - | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4v94 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4v94 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/4v94 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4v94 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4v94 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4v94 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | |
</table> | </table> | ||
| - | {{Large structure}} | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [ | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/TCPZ_YEAST TCPZ_YEAST] Molecular chaperone; assists the folding of proteins upon ATP hydrolysis. Known to play a role, in vitro, in the folding of actin and tubulin. In yeast may play a role in mitotic spindle formation. |
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| - | + | TRiC/CCT is a highly conserved and essential chaperonin that uses ATP cycling to facilitate folding of approximately 10% of the eukaryotic proteome. This 1 MDa hetero-oligomeric complex consists of two stacked rings of eight paralogous subunits each. Previously proposed TRiC models differ substantially in their subunit arrangements and ring register. Here, we integrate chemical crosslinking, mass spectrometry, and combinatorial modeling to reveal the definitive subunit arrangement of TRiC. In vivo disulfide mapping provided additional validation for the crosslinking-derived arrangement as the definitive TRiC topology. This subunit arrangement allowed the refinement of a structural model using existing X-ray diffraction data. The structure described here explains all available crosslink experiments, provides a rationale for previously unexplained structural features, and reveals a surprising asymmetry of charges within the chaperonin folding chamber. | |
| - | The | + | The Molecular Architecture of the Eukaryotic Chaperonin TRiC/CCT.,Leitner A, Joachimiak LA, Bracher A, Monkemeyer L, Walzthoeni T, Chen B, Pechmann S, Holmes S, Cong Y, Ma B, Ludtke S, Chiu W, Hartl FU, Aebersold R, Frydman J Structure. 2012 May 9;20(5):814-25. Epub 2012 Apr 12. PMID:22503819<ref>PMID:22503819</ref> |
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="pdbe-citations 4v94" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | <div class="pdbe-citations 4v94" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See Also== | ||
| + | *[[Chaperonin 3D structures|Chaperonin 3D structures]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Aebersold | + | [[Category: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C]] |
| - | [[Category: Bracher | + | [[Category: Aebersold R]] |
| - | [[Category: Chen | + | [[Category: Bracher A]] |
| - | [[Category: Chiu | + | [[Category: Chen B]] |
| - | [[Category: Cong | + | [[Category: Chiu W]] |
| - | [[Category: Frydman | + | [[Category: Cong Y]] |
| - | [[Category: Hartl | + | [[Category: Frydman J]] |
| - | [[Category: Holmes | + | [[Category: Hartl FU]] |
| - | [[Category: Joachimiak | + | [[Category: Holmes S]] |
| - | [[Category: Leitner | + | [[Category: Joachimiak LA]] |
| - | [[Category: Ludtke | + | [[Category: Leitner A]] |
| - | [[Category: Ma | + | [[Category: Ludtke S]] |
| - | [[Category: Monkemeyer | + | [[Category: Ma B]] |
| - | [[Category: Pechmann | + | [[Category: Monkemeyer L]] |
| - | [[Category: Walzthoeni | + | [[Category: Pechmann S]] |
| - | + | [[Category: Walzthoeni T]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 08:13, 29 March 2023
Molecular architecture of the eukaryotic chaperonin TRiC/CCT derived by a combination of chemical crosslinking and mass-spectrometry, XL-MS
| |||||||||||
Categories: Large Structures | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C | Aebersold R | Bracher A | Chen B | Chiu W | Cong Y | Frydman J | Hartl FU | Holmes S | Joachimiak LA | Leitner A | Ludtke S | Ma B | Monkemeyer L | Pechmann S | Walzthoeni T