We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
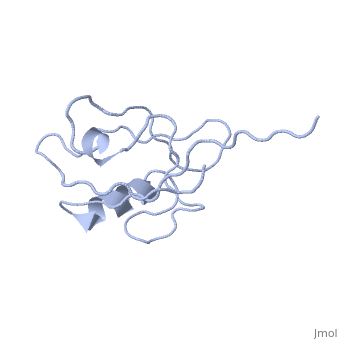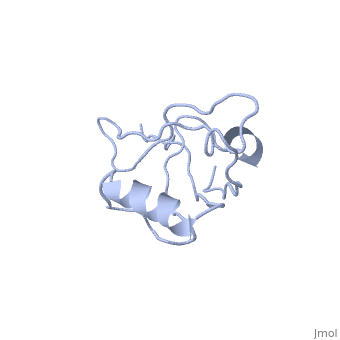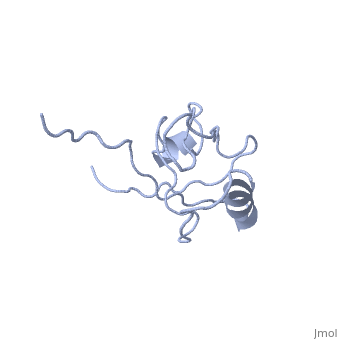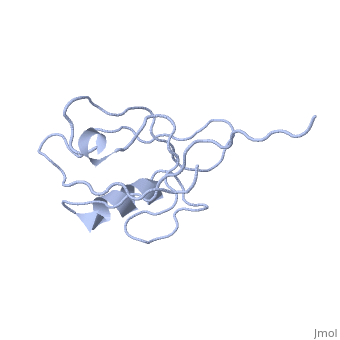
| - | <StructureSection load='4q3h' size='340' side='right' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='4q3h' size='340' side='right' caption='Human NHERF-1 second PDZ domain with CXCR2 peptide chimera (PDB cod [[4q3h]])' scene=''> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factors''' (NHERF) are multifunctional adaptor protein which plays a role in the assembly of signal transduction complexes, linking ion channels and receptors to the actin skeleton<ref>PMID:11141479</ref>. NHERF-1 is the major isoform present in the brain and it regulates the trans-cellular ion transport through the blood-brain barrier membrane | + | '''Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factors''' (NHERF) are multifunctional adaptor protein which plays a role in the assembly of signal transduction complexes, linking ion channels and receptors to the actin skeleton<ref>PMID:11141479</ref>. NHERF-1 is the major isoform present in the brain and it regulates the trans-cellular ion transport through the blood-brain barrier membrane<ref>PMID:26010555</ref>. |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | NHERF interacts with ion transporters and receptors via its PDZ domains and with the merlin, ezrin, radixin and moesin proteins via its c-terminal. | + | NHERF interacts with ion transporters and receptors via its PDZ domains and with the merlin, ezrin, radixin and moesin proteins via its c-terminal. The CXCR2 peptide binds the second PDZ domain hydrophobic cleft<ref>PMID:26010555</ref>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
*Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor 1 | *Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor 1 | ||
| - | ** | + | **[[1g9o]], [[1gq5]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 1 domain – human <br /> |
**[[2m0t]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 1 domain - NMR <br /> | **[[2m0t]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 1 domain - NMR <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1i92]], [[4jl7]], [[4lmm]], [[4mpa]], [[4n6x]] - hNHERF-1 PDZ 1 domain/CFTR C-terminal peptide <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4pqw]] - hNHERF-1 PDZ 1 domain/phospholipase C peptide <br /> | ||
**[[2m0u]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 1 domain + CFTR C-terminal peptide - NMR <br /> | **[[2m0u]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 1 domain + CFTR C-terminal peptide - NMR <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2ozf]] | + | **[[2ozf]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 2 domain <br /> |
| + | **[[4q3h]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 2 domain/CXCR2 peptide <br /> | ||
**[[2jxo]], [[2kjd]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 2 domain - NMR <br /> | **[[2jxo]], [[2kjd]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 2 domain - NMR <br /> | ||
**[[2m0w]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 2 domain + CFTR C-terminal peptide - NMR <br /> | **[[2m0w]] – hNHERF-1 PDZ 2 domain + CFTR C-terminal peptide - NMR <br /> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 38: | ||
**[[2he4]] – hNHERF-2 PDZ 2 domain (mutant)<br /> | **[[2he4]] – hNHERF-2 PDZ 2 domain (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | *Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor 3 | + | *Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor 3 or PDZK1 |
| - | **[[3ngh]] – mNHERF-3 PDZ 1 domain - mouse<br /> | + | **[[3ngh]] – mNHERF-3 PDZ 1 domain/HDL receptor - mouse<br /> |
| - | **[[4f8k]] – mNHERF-3 PDZ 1 domain (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[4f8k]] – mNHERF-3 PDZ 1 domain (mutant)/prostacyclin receptor<br /> |
| - | **[[4q2p]] – hNHERF-3 PDZ 2 domain <br /> | + | **[[4q2p]] – hNHERF-3 PDZ 2 domain/phage peptide <br /> |
| - | **[[3r68]] | + | **[[3r68]] – mNHERF-3 PDZ 3 domain<br /> |
| + | **[[3r69]] – mNHERF-3 PDZ 3 domain/HDL receptor<br /> | ||
**[[3tmh]] – hNHERF-3 PDZ 3 domain + CAMP-dependent protein kinase docking domain + AKAP-10 A-kinase-binding domain<br /> | **[[3tmh]] – hNHERF-3 PDZ 3 domain + CAMP-dependent protein kinase docking domain + AKAP-10 A-kinase-binding domain<br /> | ||
**[[4r2z]] – mNHERF-3 PDZ 4 domain <br /> | **[[4r2z]] – mNHERF-3 PDZ 4 domain <br /> | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 26 December 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor
Updated on 26-December-2017
References
- ↑ Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Wiederhold T, Nielsen GP, James M, Pinney-Michalowski D, Roy JE, Cohen WA, Ramesh V, Louis DN. NHE-RF, a merlin-interacting protein, is primarily expressed in luminal epithelia, proliferative endometrium, and estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 2001 Jan;158(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63944-2. PMID:11141479 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63944-2
- ↑ Song S, Sun X, Li X, Yuan Y, Jiao N. Efficient and Practical Oxidative Bromination and Iodination of Arenes and Heteroarenes with DMSO and Hydrogen Halide: A Mild Protocol for Late-Stage Functionalization. Org Lett. 2015 Jun 19;17(12):2886-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00932. Epub 2015 , May 26. PMID:26010555 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00932
- ↑ Morris K. Targeting the myocardial sodium-hydrogen exchange for treatment of heart failure. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2002 Jun;6(3):291-8. doi: 10.1517/14728222.6.3.291 . PMID:12223070 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1517/14728222.6.3.291
- ↑ Parker MD, Myers EJ, Schelling JR. Na+-H+ exchanger-1 (NHE1) regulation in kidney proximal tubule. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jun;72(11):2061-74. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1848-8. Epub , 2015 Feb 14. PMID:25680790 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1848-8
- ↑ Song S, Sun X, Li X, Yuan Y, Jiao N. Efficient and Practical Oxidative Bromination and Iodination of Arenes and Heteroarenes with DMSO and Hydrogen Halide: A Mild Protocol for Late-Stage Functionalization. Org Lett. 2015 Jun 19;17(12):2886-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00932. Epub 2015 , May 26. PMID:26010555 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00932