Platelet-derived growth factors and receptors
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
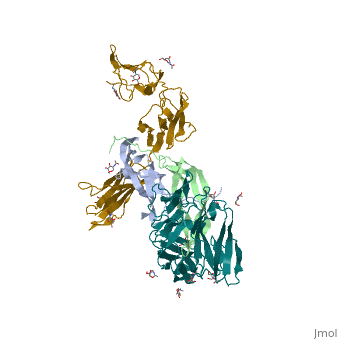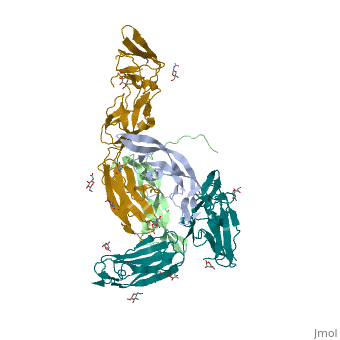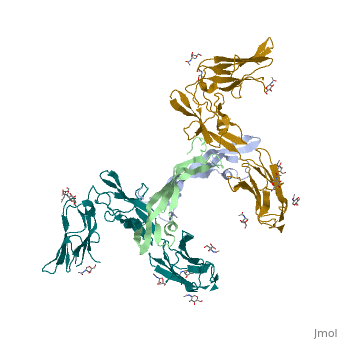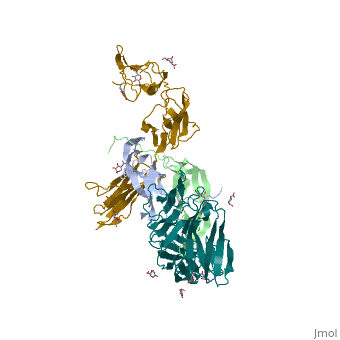
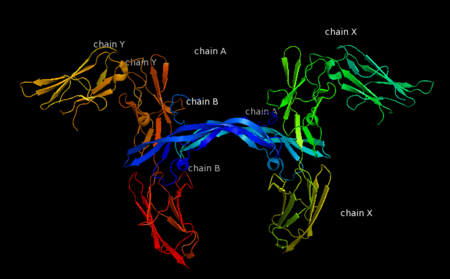
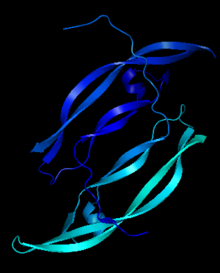
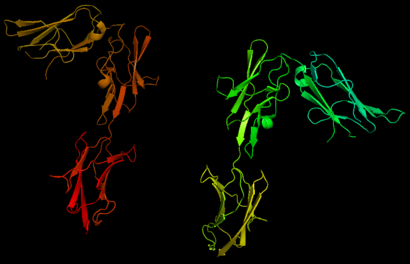
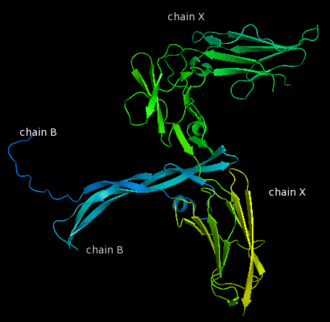
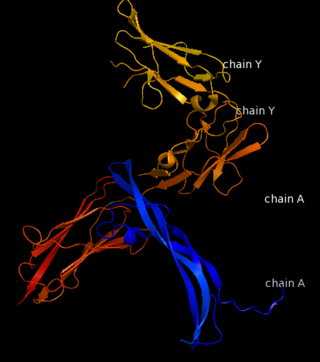
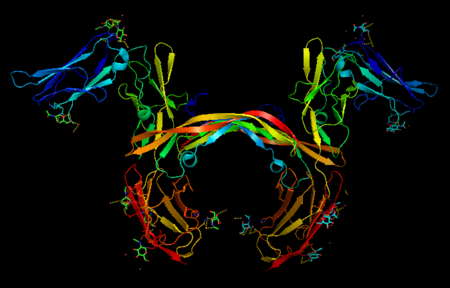
| - | Platelet-derived growth factor receptors, PDGF-R, are cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors for members of the platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs). PDGF (Chains A and B) is a 172 amino acid sequence consisting of one alpha helix and eight beta-pleated sheets. PDGF function as disulfide-linked dimers. PDGFs have a cysteine-knot-fold growth factor domain of ∼100 amino acids involved in receptor-binding and dimerization. The synthesis and processing of PDGFs is highly regulated. There are two forms of PDGF-R, alpha and beta, which are each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor binds to the receptor, PDGF-R homodimerizes or heterodimerizes | + | Platelet-derived growth factor receptors, PDGF-R, are cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors for members of the platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs). PDGF (Chains A and B) is a 172 amino acid sequence consisting of one alpha helix and eight beta-pleated sheets. PDGF function as disulfide-linked dimers. PDGFs have a cysteine-knot-fold growth factor domain of ∼100 amino acids involved in receptor-binding and dimerization. The synthesis and processing of PDGFs is highly regulated. There are two forms of PDGF-R, alpha and beta, which are each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor binds to the receptor, PDGF-R homodimerizes or heterodimerizes<ref>PMID:1315403</ref>. The PDGF-R is a 289 amino acid sequence consisting of two alpha helices and twenty-nine beta-pleated sheets. Together these form the PDGF-R complex. |
[[Image:Labeled PDGF-R_r.png|left|450px]] | [[Image:Labeled PDGF-R_r.png|left|450px]] | ||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | == | + | ==References== |
| - | + | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
<1>Heldin CH, Ostman A, Eriksson A, Siegbahn A, Claesson-Welsh L, Westermark B (March 1992). "Platelet-derived growth factor: isoform-specific signalling via heterodimeric or homodimeric receptor complexes". Kidney Int. 41 (3): 571–4. DOI:10.1038/ki.1992.84. PMID 1315403. | <1>Heldin CH, Ostman A, Eriksson A, Siegbahn A, Claesson-Welsh L, Westermark B (March 1992). "Platelet-derived growth factor: isoform-specific signalling via heterodimeric or homodimeric receptor complexes". Kidney Int. 41 (3): 571–4. DOI:10.1038/ki.1992.84. PMID 1315403. | ||
Revision as of 21:40, 19 January 2018
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Heldin CH, Ostman A, Eriksson A, Siegbahn A, Claesson-Welsh L, Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: isoform-specific signalling via heterodimeric or homodimeric receptor complexes. Kidney Int. 1992 Mar;41(3):571-4. PMID:1315403
<1>Heldin CH, Ostman A, Eriksson A, Siegbahn A, Claesson-Welsh L, Westermark B (March 1992). "Platelet-derived growth factor: isoform-specific signalling via heterodimeric or homodimeric receptor complexes". Kidney Int. 41 (3): 571–4. DOI:10.1038/ki.1992.84. PMID 1315403.
<2>Williams LT (March 1989). "Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor". Science 243 (4898): 1564–70. DOI:10.1126/science.2538922. PMID 2538922.
<3>PDB 3MJG; Shima AHR, Liua H, Fociaa PJ, Chena X, Linb PC, He X. (2010). "Structures of a platelet-derived growth factor/propeptide complex and a platelet-derived growth factor/receptor complex". PNAS 107 (25): 11307–12. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1000806107. PMC 2895058. PMID 20534510.; rendered using PyMOL.
<4> Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Shim, Ann Hye-Ryong and He, Xiaolin. 2010 June 22; 107(25): 11307–11312. Published online 2010 June 2
<5>Heldin CH, Westermark B (April 1989). "Platelet-derived growth factor: three isoforms and two receptor types". Trends Genet. 5 (4): 108–11. DOI:10.1016/0168-9525(89)90040-1. PMID 2543106.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Lisa Tice, Michal Harel, Angel Herraez, Jaime Prilusky, Alexander Berchansky