We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Lactate Dehydrogenase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
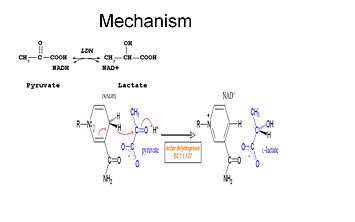
'''L-lactate dehydrogenase''' (L-LDH) catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and NADH+ to L-lactate and NAD+.<br /> | '''L-lactate dehydrogenase''' (L-LDH) catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and NADH+ to L-lactate and NAD+.<br /> | ||
'''H-lactate dehydrogenase''' (H-LDH) catalyzes the interconversion of D-lactate and ferricytochrome c to pyruvate and ferrocytochrome c.<br /> | '''H-lactate dehydrogenase''' (H-LDH) catalyzes the interconversion of D-lactate and ferricytochrome c to pyruvate and ferrocytochrome c.<br /> | ||
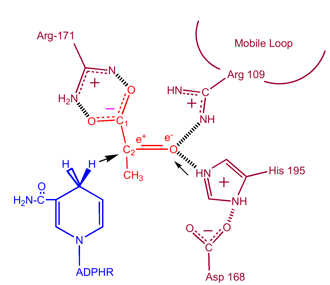
| - | Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) is an important enzyme in humans. It occurs in different regions of the body, each region having a unique conformation of different subunits. LDH is a key enzyme in anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic Respiration is the <scene name='Lactate_Dehydrogenase/Cv/4'>conversion of pyruvate into lactate acid</scene> in the absence oxygen. This pathway is important to glycolysis in two main ways. The first is that if pyruvate were to build up glycoysis and thus the generation of ATP would slow. The second is anaerobic respiration allows for the regeneration of NAD+ from NADH. NAD+ is required when glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase oxidizes glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in glycolysis, which generates NADH. Lactate dehydrogenase is responsible for the anaerobic conversion of NADH to NAD+. <scene name='40/400612/ | + | Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) is an important enzyme in humans. It occurs in different regions of the body, each region having a unique conformation of different subunits. LDH is a key enzyme in anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic Respiration is the <scene name='Lactate_Dehydrogenase/Cv/4'>conversion of pyruvate into lactate acid</scene> in the absence oxygen. This pathway is important to glycolysis in two main ways. The first is that if pyruvate were to build up glycoysis and thus the generation of ATP would slow. The second is anaerobic respiration allows for the regeneration of NAD+ from NADH. NAD+ is required when glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase oxidizes glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in glycolysis, which generates NADH. Lactate dehydrogenase is responsible for the anaerobic conversion of NADH to NAD+. <scene name='40/400612/Cv1/2'>Click here to see the residues which form interactions with pyruvate</scene> in the Lactate Dehydrogenase from ''Cryptosporidium parvum'' ([[4nd4]]). |
==Human Lactate Dehydrogenase== | ==Human Lactate Dehydrogenase== | ||
Revision as of 12:23, 22 January 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of lactate dehydrogenase
Updated on 22-January-2018
Additional Information
For additional information, see Carbohydrate Metabolism
Reference
- 1- http://www.bioc.aecom.yu.edu/labs/calllab/highlights/LDH.htm
- 2- http://www.cheric.org/ippage/e/ipdata/2004/05/file/e200405-701.pdf
- 3- http://resources.metapress.com/pdf-preview.axd?code=ulnhp23038060m21&size=largest
- 4- http://www.u676.org/Documents/Chretien-ClinChimActa-95.pdf
- 5- http://www.jbc.org/content/243/17/4526.full.pdf+html
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Ann Taylor, Jasper Small, David Canner