Sandbox Reserved 1319
From Proteopedia
(→Function) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
===Function=== | ===Function=== | ||
| - | GLUT3 is a glucose transporter that serves highly metabolic and oxidative systems. As such, it is the glucose transporter for neurons and is also known as the neuronal glucose transporter. It plays a key role in metabolism in the brain. GLUT3 also acts as the glucose transporter for cells such as sperm and white blood cells. | + | GLUT3 is a glucose transporter that serves highly metabolic and oxidative systems. As such, it is the glucose transporter for neurons and is also known as the neuronal glucose transporter. It plays a key role in metabolism in the brain. GLUT3 also acts as the glucose transporter for cells such as sperm and white blood cells. The protein uses a glucose diffusion gradient to move across membranes. |
===Structure=== | ===Structure=== | ||
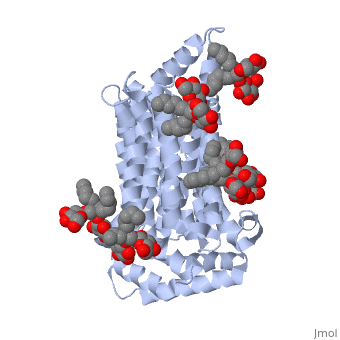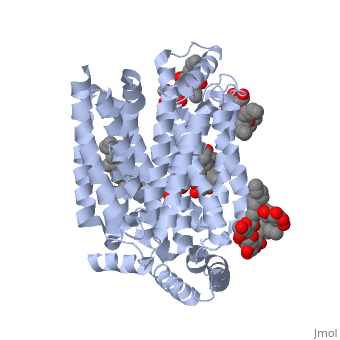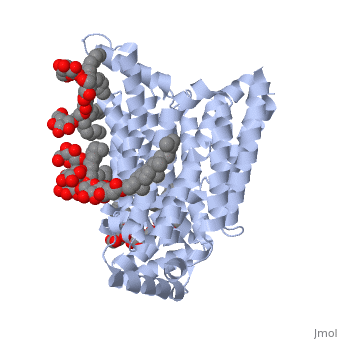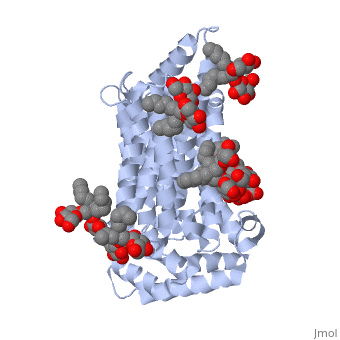
The structure of this protein contains <scene name='77/777639/Alpha_helix_of_glut3/1'>alpha helices</scene> that are composed of two separate chains (alpha helix shown in blue). The structure of GLUT3 also consists of ligands <scene name='77/777639/Y01_ligand/1'>Y01</scene> and <scene name='77/777639/37x_ligand/1'>37X</scene> and is composed of 481 amino acids. It has four different transmembrane segments that are repeated three times (for a total of 12 transmembrane segments). | The structure of this protein contains <scene name='77/777639/Alpha_helix_of_glut3/1'>alpha helices</scene> that are composed of two separate chains (alpha helix shown in blue). The structure of GLUT3 also consists of ligands <scene name='77/777639/Y01_ligand/1'>Y01</scene> and <scene name='77/777639/37x_ligand/1'>37X</scene> and is composed of 481 amino acids. It has four different transmembrane segments that are repeated three times (for a total of 12 transmembrane segments). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Diseases=== | ||
| + | Type 2 Diabetes: Higher glucose concentration affects GLUT expression in white blood cells. The level of transcripts encoding GLUT3 are reduced in diabetic patients, which could impair the immune system and make patients more susceptible to infection. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alzheimer's Disease: Decreased levels of GLUT3 in the brain of Alzheimer's patients leads to hyperphosphorylation of the Tau protein, which can lead to tangles. | ||
Revision as of 21:00, 20 February 2018
Contents |
GLUT3: Glucose Transporter in Mammalian Cells
|
Function
GLUT3 is a glucose transporter that serves highly metabolic and oxidative systems. As such, it is the glucose transporter for neurons and is also known as the neuronal glucose transporter. It plays a key role in metabolism in the brain. GLUT3 also acts as the glucose transporter for cells such as sperm and white blood cells. The protein uses a glucose diffusion gradient to move across membranes.
Structure
The structure of this protein contains that are composed of two separate chains (alpha helix shown in blue). The structure of GLUT3 also consists of ligands and and is composed of 481 amino acids. It has four different transmembrane segments that are repeated three times (for a total of 12 transmembrane segments).
Diseases
Type 2 Diabetes: Higher glucose concentration affects GLUT expression in white blood cells. The level of transcripts encoding GLUT3 are reduced in diabetic patients, which could impair the immune system and make patients more susceptible to infection.
Alzheimer's Disease: Decreased levels of GLUT3 in the brain of Alzheimer's patients leads to hyperphosphorylation of the Tau protein, which can lead to tangles.