We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Poly(A) binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
====Adenosine Stabilization Interaction Patterns==== | ====Adenosine Stabilization Interaction Patterns==== | ||
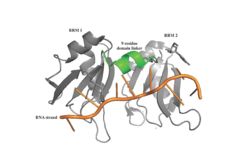
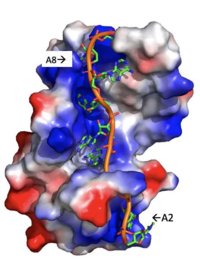
| - | Specifically, there are several significant interaction patterns that stabilize adenosine recognition. RRM 1 and 2 makes significant interactions with the adenosine backbone, shown in Figure 3. Additionally, the adenosine stabilizes itself within the binding by intramolecular stacking interactions between adenosines. Through the extensive <scene name='78/781949/Lys_104_asp_105/1'>interactions with adenosine 2</scene>, the RRM specifies the position of adenosine 2, allowing it to make strong intramolecular stacking interactions with adenosine 1. As a result, adenosine 1 requires less contact with the RRM, as it is mostly stabilized by adenosine 2. Furthermore, some adenosines like adenosine 3 and adenosine 6 are stabilized by being sandwiched between aromatic and alipathic side chains. <scene name='78/781947/Interactions_with_a3/1'>Adenosine-3 sandwiching</scene> occurs between aromatic and alipathic side chains and is specified by Lysine 104, and <scene name='78/781947/Residues_interacting_with_a6/1'>Adenosine-6 sandwiching</scene> occurs similarly, but it is specified doubly by two residues, Trp-86 and Gln-88. | + | Specifically, there are several significant interaction patterns that stabilize adenosine recognition. RRM 1 and 2 makes significant interactions with the adenosine backbone, shown in Figure 3. Additionally, the adenosine stabilizes itself within the binding by intramolecular stacking interactions between adenosines. Through the extensive <scene name='78/781949/Lys_104_asp_105/1'>interactions with adenosine 2</scene>, the RRM specifies the position of adenosine 2, allowing it to make strong intramolecular stacking interactions with adenosine 1. As a result, adenosine 1 requires less contact with the RRM, as it is mostly stabilized by adenosine 2. Furthermore, some adenosines like adenosine 3 and adenosine 6 are stabilized by being sandwiched between aromatic and alipathic side chains. <scene name='78/781947/Interactions_with_a3/1'>Adenosine-3 sandwiching</scene> occurs between aromatic and alipathic side chains and is specified by Lysine 104, and <scene name='78/781947/Residues_interacting_with_a6/1'>Adenosine-6 sandwiching</scene> occurs similarly, but it is specified doubly by two residues, Trp-86 and Gln-88. <ref> Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell, vol. 98, no. 6, 1999, pp. 835–845., doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81517-2. <ref/> |
===Translation Initiation=== | ===Translation Initiation=== | ||
Revision as of 17:31, 29 March 2018
Poly(A) binding protein - Homo sapiens
Structure
| |||||||||||