Structure Determination
Attempts to determine the structure of native SRP20 have been largely unsuccessful due to the low solubility of the protein. This is likely due to the hydrophobic core of the RRM and exposed hydrophobic residues for RNA recognition on the β-sheets. As a solution, researchers removed the SR domain from the C terminus, leaving only the SRP20 RRM and a small arginine rich segment at the C terminus, then fused with a soluble of Streptococcal protein G to the N terminus of the protein, providing the first published structure of the SRP20 RRM via NMR3. However, the solution of the structure via NMR, in addition to fusion with a globular tag, results in multiple possible conformations of the protein, meaning measurements such as bond angles, lengths, and substrate interactions are variable. Further, information concerning structural aspects of the SR domain are still limited to experimental data of protein function with certain mutations or deletions, and by comparison to sister proteins such as 9G8. To date, structure of the SR domain or the protein without the globular tag have not been solved, nor has a crystal structure for any part of the protein been determined.
Splicing Activity
The splicing mechanism for SRp20 follows the normal eukaryotic mechanism, in which five different
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) bring the splice sites together in order to start the reaction (Figure 1). Specifically, SRp20 and other SR proteins interact with the RNA ligand at the
exonic splicing enhancer sequence at the beginning of the 3’ splice site adjacent to the intron being removed. SRp20 facilitates the interaction of the U2 snRNP with the RNA to continue the mechanism (Figure 2).
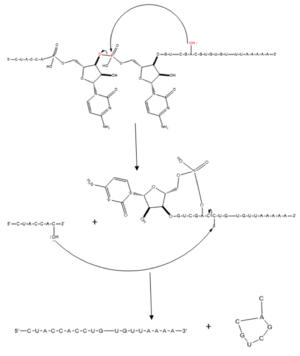
Figure 1. Splicing mechanism for eukaryotes. Free 3’OH nucleophile of adenosine in intron attacks phosphorus of phosphate creating a ring structure intron known as a lariat. The free 2’OH in the 5’ splice site (red) acts as the nucleophile to attack the phosphate of the first nucleotide in the 3’ splice site (red) to release the
lariat intron. The products include the final modified RNA sequence and the lariat which will be recycled.
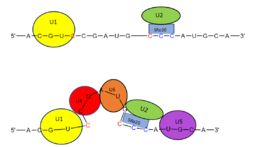
Figure 2. SRp20 works with
U2 snRNP: Five snRNPs are needed in the eukaryotic splicing mechanism to facilitate the reaction. The U2 snRNP must attach to the 3’ splice site to bring together the 5’ and 3’ splice sites (red). SRp20 facilitates binding of U2 to the 3’ splice site by binding to the exonic splicing enhancer sequence (blue) in the RNA at the backbone. U2 must bind before the other snRNPs can bind to continue the mechanism.
Structural Highlights
RNA Recognition Motif
The SRP20 RRM (aa 1-86) a βαββαβ , common of many other RRMs3. For substrate binding, researchers used a 4 base RNA with sequence CAUC, which matches the SRP20 recognition sequence found on corresponding H2A mRNA. The RNA bases each onto an aromatic side chain protruding from one of the SRP20 β-sheets, forming the primary interactions which allow substrate binding to the protein. In particular, C1 on Y13 in β1, stacks on F50 in β3, and F48 of β3 sits in between the sugar rings of C1 and A2. It should also be noted that A2 adopts an irregular conformation when bound to the RRM, something that was observed only for guanine in the 2 position previously3. U3 onto F48 in β3, also W40 and A42 in β2, however when bound, U3 out of line in comparison to the rest of the substrate. C4 partially stacks over , and also forms hydrogen between the C4 amino group and A2 2’ oxygen.
While all 4 bases form a number of hydrophobic stacking interactions, alteration to the last 3 bases of substrate sequence does not significantly impact binding affinity, while C to G mutation of C1 results in a 10-fold decrease in binding affinity. This suggests that C1 interacts specifically with the protein, while positions 2-4 interact nonspecifically3. The Srp20 RRM is able to recognize C1 with high specificity primarily through 4 : from the C1 amino protons to Leu 80 backbone carbonyl oxygen and to Glu 79 side-chain carbonyl oxygen, from C1 N3 to Asn82 amide, and C1 O2 with Ser 81 side chain hydroxyl group.
The semi specific RNA recognition is a mechanism which reduces evolutionary pressure on bound mRNA by increasing the number of possible RNA recognition sequences. As a result, tolerance for possible mutation in the RNA sequence is increased, meaning Srp20 can bind a more diverse range of substrates, or even original substrates that were mutated during replication (eg. H2A mRNA with a point mutation) thereby increasing organism survival chance by reducing the probability of physiological impact as a result of certain mutations.
Tip Associated Protein Binding Domain

Figure 3. SRp20 Domain Representation. Shown are the RRM (green), the TAP binding linker (red line) and SR-rich domain (blue).
In addition to RNA recognition and alternative splicing functions, SRP20 has been shown to associate with Tip Associated Protein (TAP), an mRNA export factor, to promote transport of bound mRNA out of the nucleus for eventual translation3. In particular SRp20 promotes the export of H2A histone mRNA, by binding the CAUC consensus sequence on the mRNA and binding TAP. Previous experiments have shown that Srp20 binding TAP is dependent on presence of both the SRP20RRM and a short arginine rich C-terminal segment after the RRM (aa 1-83 and 84-90 respectively) (Figure 3). Previous research also shows that mutation of any one of the three arginine residues present between residues 84-90 to glutamate prevents TAP binding, indicative of the importance of these arginine residues in TAP association. The structure is only solved to residue 86 so only the is present. The same study also found that transfer of the TAP-binding motif to a non-functional REF2 RRM still allowed for TAP-binding and nuclear export of the target protein, suggesting that not only is the TAP-binding motif transferable, it does not depend on interaction with the host RRM to retain function.
SR Domain
While the RNA-protein interaction occurs at the RRMs, SR domains are typically responsible for the recruitment of other proteins that act in the splicing mechanism. The serines within the SR domain are phosphorylated by kinases within the cell to direct them to pre-mRNA sites (Figure 4).
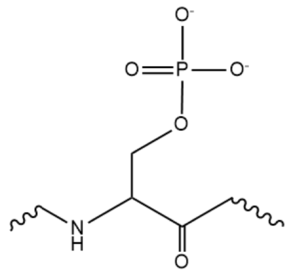
Figure 4. An example of one phosphorylated serine within the RS domain.
Phosphorylation acts as recruiting tools for the SRp20 protein and other SR proteins to promote splicing. However, some SR proteins have shown that phosphorylation actually leads to a decrease in splicing, as in the SRp38 protein undergoing heat shock. Research has recently revealed that serines are dephosphorylated as splicing continues, indicating how far along the mRNA strand is in splicing. Dephosphorylation then serves as a signal to the cell that the mRNA is ready to be exported out of the nucleus. Rephosphorylation then appears to trigger the SR protein to enter back into the nucleus.
The SR domain also appears to modulate mRNA stability, though different SR proteins have been shown to have greater effects. Some SR proteins appears to increase the sensitivity of certain mRNA sequences to degradation; this degradation appears to be controlled by SR domain interactions with the 3’ UTR of the pre-mRNA. These effects are not present without the SR domain of the protein. The destabilizing effect of SRp20 specifically has yet to be studied. (Huang & Steitz 2003).
9G8 and SRP20
9G8 is another SR protein that is 80% similar in amino acid sequence. They are two of the smallest proteins in the SR family and both contain an RRM that promotes export of mRNA through interaction with the TAP protein. The only other protein shown to promote transport through the TAP protein is SF2, one of the first SR proteins discovered (Huang 2003). Both RRMs adopt a βαββαβ mentioned earlier. Both RRMs interact with RNA with limited selectivity and therefore recognize many different RNA sequences. The 9G8 RRM contains an large hydrophobic core on its B-sheet. Observing the 9G8 protein has proved useful in understanding SRp20 less stable protein structure. In fact, the one of the only significant structural difference between the two proteins lies in the loops between a-helix 2 and B-4 where several amino acids are not conserved.
Aside from the RRM, both proteins have one SR-rich domain although 9G8 includes about 40 more amino acids this domain (Corbo 2013).
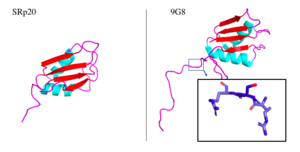
Figure 5. SRp20 and 9G8 proteins. The PDB file for SRp20 (left; PDB file: 2i2y) does not include the SR-rich domain but 9G8 (right; PDB file: 2hvz) does. Boxed image shows an RSR region in the PG8 protein with oxygens highlighted in red. Images taken from PyMol software.jpg
Within the bigger 9G8 protein, there is a zinc knuckle that allows for binding of pyrimidine-rich RNA sequences. This zinc knuckle is not present in SRp20, lending the protein to binding of more purine-rich sequences (Huang 2003).Not only are these two proteins similar, but they also play similar roles in mRNA export out of the nucleus. Both move continuously between the nucleus and cytoplasm which requires phosphorylation of its serine residues located in the SR-rich domain. Serine phosphorylation has been shown to have great importance in the proper functioning of many SR proteins (Figure Shepard & Hertel 2009).
Medical Significance
Cancer
SRp20 has been linked to cancer in many instances, as well as other AS proteins. SRp20 has been seen to activate the AS of the CD44 adhesion molecule. SRp20 facilitates the splicing of exon v9, one important for function of CD44. Loss of function of SRp20 leading to loss of function of CD44 will lead to loss of “stickiness” of cells, a way that cancer cells can spread to other areas of the body. SRp20 can also affect the alternative splicing of oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Expression of the signaling pathway for SRp20 translation is directly triggered by oncogenic signalling pathways. For example, the Wnt pathway that is associated with cancer development also drives further expression of SRp20 and other SR proteins (7). These proteins aid in cell growth and proliferation, in that they increase expression of proteins they are involved in splicing. One study found that silencing SRp20 slowed cell proliferation, further supporting the idea that SRp20 helps with this process (8). Cell cycle regulator proteins FoxM1, Cdc25B, and PLK1 are alternatively spliced by SRp20, specifically regulating the G2/M cycles. These proteins are also associated with regulation of cell apoptosis. When these genes are overexpressed due to overexpressed SRp20, cells will no longer be able to apoptose when they are damaged, and the cell cycle will continue without regulation, causing overactive cell proliferation and eventually cancer. SRp20 has been seen to be overexpressed in ovarian, lung, breast, stomach, skin, bladder, colon, liver, thyroid, and kidney cancer tissue (9). SRp20 also regulates genes associated with cellular senescence, or cellular immortality, which contributes to cancer formation. Specifically, SRp20 alternatively splices the TP53 gene, which generates the p53 senescence protein.
Neurological Disorders
Along with cancer, SRp20 mutations have been linked to Alzheimers, a neurodegenerative disorder. SRp20 is involved in AS of a wide array of RNAs, including that of the TRKB gene to generate TrkB-Shc transcripts that are involved in generation of the disorder. SRp20 also promotes exclusion of exon 10 in the TAU gene, a gene important in establishing microtubules in axons or transport processes.Underexpression of SRp20 results in dysfunction of the TAU gene, less microtubule functionality, and the brain deterioration characteristic of Alzheimers (10, 7).
Other Genetic Disorders
SRp20 and other SR proteins have been shown to prevent R-loops from forming, 3-stranded nucleic acid structures consisting of RNA and DNA. R-loops have been known to promote mutations, recombination, and chromosome rearrangement. One proposed mechanism for R-loop prevention by SRp20 is that SRp20, being a protein involved in RNA metabolism, is a binding partner of the TOP1 protein. Underexpression of TOP1 also promotes R-loop formation. TOP1 has kinase activity that potentially phosphorylates the SR domain of SRp20, which contributes to its function. Underexpression of TOP1 would lead to loss-of-function of SRp20, which could lead to cancer and Alzheimers as mentioned above, as well as cause R-loops to form. R-loops have been associated with disorders such as Down Syndrome (Naro et al. 2015).





