Introduction
Alternative RNA splicing is a significant post-transcriptional process that allows diversity of gene expression. Initially, a gene is transcribed into pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA). The pre-mRNA contains introns, which are sequences that are not translated into protein, and exons, which code for proteins. In alternative RNA splicing, exons are either removed or retained in the mRNA in different combinations, creating diverse arrangements of mRNAs from one pre-mRNA. This process is carried out with splicing factors which are proteins that remove introns and exons via spliceosomes [1]. The sequence-specific RNA binding protein SRp20 (gene name SRSF3) is a splicing factor and one of the smallest member of the serine and arginine-rich (SR) protein family that plays a significant role in alternative splicing of exons [1] [2]. It is a highly conserved Homo Sapien protein[3].
Function
SRp20 is a splicing factor involved in regulation of many genes through alternative splicing of exons by associating with cis-elements of RNA[1][4]. It contains an auto-regulatory activity in which it can alternatively splice its own mRNA through including exon 4 thus reducing the length of its protein[5][6][7]. It has been speculated that SRp20 has been linked to termination of transcription by either activating enzymes responsible for degrading the RNA sequence downstream from the cleavage site or promoting the removal of RNA polymerase from the DNA[8]. SRp20 might play a role in export of mature mRNAs by promoting the recruitment of TAP, which is a receptor for mRNA export out of the nucleus5. It has been found that SRp20 and PCBP2, which is a protein that binds to internal ribosome entry site (IRES) RNA sequences in picornavirus, interact with each other to initiate viral translation[9]. Thus, these findings indicate SRp20 playing a role in protein translation. SRp20 is also suggested to allow 3' terminal exon to be recognized by polyadenylation factors[10].
Structure

Figure 1: SRp20 RRM and RS domains are shown
The structure of SRp20 was determined by heteronuclear single quantum coherence (
HSQC) NMR. The structure is composed of one RNA recognition motif (RRM) at the N-terminus and one Arg/Ser (AR) domain at the C-terminus where the Ser residues are phosphorylated
[1]. The RRM of SRp20 demonstrates the β1α1β2β3α2β3 topology seen in other
RRMs. The role of the RRM region is to provide substrate specificity where SRp20 interacts with splicing enhancing sequences in mRNA. There have been no determined 3D structures of the RS domain thus it is unclear what its exact role is. However there have been some speculation that it might be involved in aiding protein-protein interactions in the spliceosome. It contains 164 amino acids, half belonging to the RRM and other half to the RS domain (Figure 1). SRp20 has a molecular weight of 19 kDA
[1].
Poor Solubility Problem
The SRp20 protein has poor
solubility in its free state.
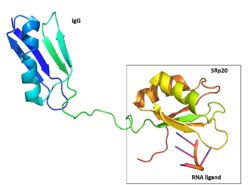
Figure 2: SRp20 with the solubility IgG tag and the RNA ligand are shown. The solubility tag is at the N' terminus, in front of the RRM. While in the actual protein, the RRM is at the N'terminus, in front of the RS domain. Image created using
PymolThis made it impossible to determine the structure of SRp20 using HSQC Spectroscopy without a modification to the free state protein. This problem was resolved by studying the proteins after fusing the RRM (RNA-recognition motif) with the immunoglobulin G-binding domain 1 of Streptococcal
Protein G GB1 solubility tag (Figure 2)
[2].
RNA Interactions
1H-15N HSQC results showed a large hydrophobic β-sheet on the RRM binding to the RNA with all four bases interacting with one of the four aromatic residues via hydrophobic interactions [2]. β-hairpin amino acids are hydrogen bonded to bases on nucleic acid targets [11]. This suggests that the β-hairpin plays a role in SRp20 selectivity for specific ligands. The researchers used a smaller peptide chain to reduce the NMR broadening seen with longer peptides (allowing for structure determination), with the consequence of reduced binding affinity. The ligand used was . The conformation of U3 and C4 shows that U3 bulges out while C4 partially stacks over A2. Interactions with the RRM that the researchers saw were that in β1 and in β3. These aromatic side chains form hydrophobic interactions with the ligand when stacked (Figure 3). Also, the residue . <C1 is recognized definitively by the RRM</scene>. The C1 amino proton hydrogen bonds with the Leu 80 carbonyl oxygen and the Glu 79 side-chain carbonyl oxygen in SRp20. The C1 N3 hydrogen bonds with the Asn 82 amide. The C1 O2 hydrogen bonds with the Ser 81 hydroxyl group [2].
It was also noted that adopts an unusual syn conformation. U3 interacts with and with the β2-3 loop of the RRM. These residues are all hydrophobic, offering a large hydrophobic surface that helps bind the ligand, as well as prevents the solvent from binding. Additionally, C4 is maintained in its position by a
[2].

Figure 3: C1 and A2 on the RNA ligand interacting with hydrophobic residues (Tyr 13, Phe 50, Phe 48) in the RRM domain of the SRp20 protein. Image created using
Pymol RRM Stability
SRp20 has a , which may contribute to the stability of the protein. A previous study, looking at the RRM in TDP-43 has suggested that the hydrophobic core may be a strong contributing factor to the protein’s stability [12]. In a different study, it was determined that, in the U11/U12-65K protein, the β-sheet packs against the two α-helices by way of hydrophobic interactions and that the resulting stabilization could be critical for the proper folding and orientation of elements for RNA binding [13]. Due to the conservative nature of RRMs, it could be speculated that the hydrophobic core found in SRp20, between the β-sheet and two α-helices, could contribute to the stability of its RRM in a similar fashion. However, additional studies done specifically on SRp20 need to be done to confirm this supposition.
RRM Specificity
4 nucleotides can be accommodated by the SRp20 RRM β-sheet, but its recognition is only partially sequence specific. A study was done showing that C1 was more specific, while A2 and U3 were less specific. When the RNA ligand was changed to GAUC, the affinity of the SRp20 RRM for the RNA ligand decreased 10-fold. It is uncertain whether C4 is specifically recognized by the RRM. It was also seen that A was preferred over G at the 2 position, but there was no indication of a preference over U or C. U3 is even less specific, as it could also be C, G or A. The recognition of C1 is functionally necessary because a C to G mutation within the histone mRNA can impair RNA export [2].
Advantages of low specificity
One advantage of low specificity is that it puts less evolutionary pressure on bound RNA, which would be prefered for exonic sequences [11]. With lower specificity, a larger array of RNA sequences can be targeted. Additionally, SRp20 can associate/disassociate with RNA more easily, which is important for highly dynamic RNA metabolism processes. RNA binding affinity can be modulated by protein-protein interactions (which are dependent on the level of phosphorylation) [2]. This can be used to tune post-transcriptional gene expression.
Comparing RRMs
Other RRM-containing proteins typically contain RRMs that specifically recognize anywhere from 2-8 nucleotides of the RNA ligand. Aromatic residues in the β-sheets and the loops between β-strands and α-helices are the residues that specifically recognize the nucleotides. The SR protein ASF/SF2 has a histidine in the α2/β1 loop that is crucial for RNA binding and specificity. When this histidine is mutated to alanine (His183Ala) ASF/SF2 loses much of its ability to crosslink RNA. The location and type of residues that binds the RNA ligand is what gives different RRM-containing proteins different specificities. The number of RRMs present in a protein also affects the proteins specificity. In general, the more RRMs a protein contains, the more specific it is to binding its RNA ligand [11]. Mutating an RRM disrupts the specificity of the protein so it can no longer recognize the correct RNA sequence and ultimately leads to incorrect gene splicing or no mRNA export. Specifically, looking at how mutations in the RRM of ASF/SF2 is relevant to our understanding of SRp20 because they are both operate as alternative splicing factors in Homo Sapians. While these specific point mutations have not been done in the RRM of SRp20, it can be speculated that related mutations in the SRp20 RRM might have a similar effect on its specificity and ability to bind a ligand.
Relationship to 9G8
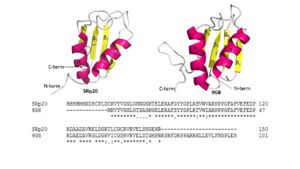
Figure 4: Comparing SRp20 and 9G8 RRMs and sequence alignments. Structural images created using
Pymol and splicing factor are both sequence specific RNA binding proteins (Figure 4). They are the smallest members of the Serine-and-Arginine Rich (SR) protein family. Both RNA Recognition Motifs (RRMs) have a similar βαββαβ topology. SRp20 and 9G8 are 80% identical. The sequence alignment shows the alignment of the RRMs of SRp20 and 9G8
[2]. SRp20 binds pyrimidine rich areas while 9G8 binds purine rich areas.This difference in binding comes from the fact that 9G8 has a
zinc knuckle that recognizes GAC triplets
[14]. 9G8s RRM is followed by a zinc knuckle and then the SR domain whereas SRp20s RRM is followed directly by the SR domain. When 9G8 lacks a zinc knuckle, it binds pyrimidine-rich sequences like SRp20
[2]. The zinc knuckle of 9G8 contains glycine residues at positions 5 and 8 and charged residues at positions 6 and 13 that are highly conserved
[14]. Due to the poor solubility problem, a structure for the zinc knuckle of 9G8 is not available to show in an image.
A study by Huang and Steitz showed that 9G8 and SRp20 promote the export of mRNA from the nucleus[15]. There is a 101-nt sequence in the coding region of mouse histone H2a mRNA that promotes the the export of intronless human β-globin cDNA transcripts [16]. Of this 101-nt sequence, there is specifically a 22-nt sequence that is necessary for export activity. UV cross-linking and immunoprecipitation experiments determined SRp20 and 9G8 specifically associating with the 22-nt sequence. SR proteins were associating with the 22-nt sequence by adding antibodies specific for SRp20 then 9G8. SRp20 antibodies inhibited mRNA export 3-fold while 9G8 antibodies inhibited mRNA export at least 10-fold showing that SRp20 and 9G8 are active factors that promote mRNA export. It was shown that SRp20 and 9G8 are cross-linked to polyadenylated RNA in the nucleus and cytoplasm showing that both proteins play a direct role in mRNA export from the nucleus [15].
Disease
Cancer
There have been findings that support SRp20s role in cellular proliferation/maturation. It was discovered that there was an over expression of SRp20 in breast cancer tissues, and when SRp20 was reduced in the cancer cells via siRNA targeting SRp20 mRNA, there was reduction in cell proliferation and increase in cellular apoptosis. For example, it was speculated that SRp20 might be involved in alternative splicing of FoxM1, a transcription factor involved in cellular proliferation, by either the inclusion or exclusion of exon 9 in FoxM1 transcript. If exon 9 was excluded from the FoxM1 mRNA via SRp20 then there was an increase in FoxM1 expression, cellular proliferation, and reduction in cell apoptosis[3]. Another noteworthy interaction occurs between SRp20 and Caspase-2, where SRp20 promotes exon 9 skipping on caspase-2 through an interaction with exon 8. When SRp20 is overexpressed, exon 9 is skipped and caspase-2 produces the pro-apoptotic Casp-2L protein. When SRp20 is under-expressed, exon 9 is included and caspase-2 produces an anti-apoptotic Casp-2S protein [17]. Apoptosis is a necessary function to maintain homeostasis, and an imbalance in the regulation in apoptosis can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumor development. Due to the alternative splicing functionality of SRp20, it effects many other genes involved in cancer other than the ones discussed above such as CD44 gene, pyruvate kinase M (PK-M) gene, TAU gene, TP53 gene, and involved in WnT signaling pathway[1]. Although it has been understood the SRp20 plays a crucial role in cancer cells, it is still unclear about the mechanism of SRp20 in the genes it effects and how its structure contributes to the development of oncogenic genes[3][17].
Relevance and Conclusions
Understanding and recognizing the mechanisms that SRp20 is involved in can help find treatment and management of cancer patients
The use of SR proteins (such as SRp20) may in the future be used for targeted therapy
Because there is no known structure for the C-term domain, due to an inability to obtain a structural image for it, most of the focus has been on the RRM domain. Little is understood about how the RS domain might recognize structures or other proteins.
Future Directions
Recent structural studies emphasize that not only the β-sheet surface but also the loops connecting β-strands and a-helices can be crucial for nucleic acid recognition, so a future research could look more closely at this possibility. Ideally, a structural image of the RS domain would be obtained so that farther research could be done investigating the process of RS domain phosphorylation and how it controls splicing. Research could also look farther into the specificity or lack of specificity of SR proteins to different ligands. There are not genetic studies looking at SRp20 with specific residue mutations, which would be a beneficial future direction in order to determine the mechanism function by which SRp20 participates in RNA alternative splicing and other functions. Because specific residue mutations have not been done on SRp20, it is difficult to determine exactly which residues are essential to its functionality.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Corbo C, Orru S, Salvatore F. SRp20: an overview of its role in human diseases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jun 21;436(1):1-5. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.027. Epub 2013 May 16. PMID:23685143 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.027
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Hargous Y, Hautbergue GM, Tintaru AM, Skrisovska L, Golovanov AP, Stevenin J, Lian LY, Wilson SA, Allain FH. Molecular basis of RNA recognition and TAP binding by the SR proteins SRp20 and 9G8. EMBO J. 2006 Nov 1;25(21):5126-37. Epub 2006 Oct 12. PMID:17036044
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Jia R, Li C, McCoy JP, Deng CX, Zheng ZM. SRp20 is a proto-oncogene critical for cell proliferation and tumor induction and maintenance. Int J Biol Sci. 2010 Dec 15;6(7):806-26. PMID:21179588
- ↑ Jia R, Liu X, Tao M, Kruhlak M, Guo M, Meyers C, Baker CC, Zheng ZM. Control of the papillomavirus early-to-late switch by differentially expressed SRp20. J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(1):167-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01719-08. Epub 2008 Oct 22. PMID:18945760 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01719-08
- ↑ Jumaa H, Guenet JL, Nielsen PJ. Regulated expression and RNA processing of transcripts from the Srp20 splicing factor gene during the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jun;17(6):3116-24. PMID:9154810
- ↑ Jumaa H, Nielsen PJ. Regulation of SRp20 exon 4 splicing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Nov 15;1494(1-2):137-43. PMID:11072076
- ↑ Jumaa H, Nielsen PJ. The splicing factor SRp20 modifies splicing of its own mRNA and ASF/SF2 antagonizes this regulation. EMBO J. 1997 Aug 15;16(16):5077-85. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.16.5077. PMID:9305649 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.16.5077
- ↑ Cui M, Allen MA, Larsen A, Macmorris M, Han M, Blumenthal T. Genes involved in pre-mRNA 3'-end formation and transcription termination revealed by a lin-15 operon Muv suppressor screen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Oct 28;105(43):16665-70. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0807104105. Epub 2008 Oct 22. PMID:18946043 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0807104105
- ↑ Bedard KM, Daijogo S, Semler BL. A nucleo-cytoplasmic SR protein functions in viral IRES-mediated translation initiation. EMBO J. 2007 Jan 24;26(2):459-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601494. Epub 2006 Dec, 21. PMID:17183366 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601494
- ↑ Lou H, Neugebauer KM, Gagel RF, Berget SM. Regulation of alternative polyadenylation by U1 snRNPs and SRp20. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Sep;18(9):4977-85. PMID:9710581
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Clery A, Blatter M, Allain FH. RNA recognition motifs: boring? Not quite. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Jun;18(3):290-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002. PMID:18515081 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002
- ↑ Mackness BC, Tran MT, McClain SP, Matthews CR, Zitzewitz JA. Folding of the RNA recognition motif (RRM) domains of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-linked protein TDP-43 reveals an intermediate state. J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 21;289(12):8264-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.542779. Epub 2014, Feb 4. PMID:24497641 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.542779
- ↑ Netter C, Weber G, Benecke H, Wahl MC. Functional stabilization of an RNA recognition motif by a noncanonical N-terminal expansion. RNA. 2009 Jul;15(7):1305-13. Epub 2009 May 15. PMID:19447915 doi:10.1261/rna.1359909
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Cavaloc Y, Bourgeois CF, Kister L, Stevenin J. The splicing factors 9G8 and SRp20 transactivate splicing through different and specific enhancers. RNA. 1999 Mar;5(3):468-83. PMID:10094314
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Huang Y, Steitz JA. Splicing factors SRp20 and 9G8 promote the nucleocytoplasmic export of mRNA. Mol Cell. 2001 Apr;7(4):899-905. PMID:11336712
- ↑ Huang Y, Carmichael GG. The mouse histone H2a gene contains a small element that facilitates cytoplasmic accumulation of intronless gene transcripts and of unspliced HIV-1-related mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Sep 16;94(19):10104-9. PMID:9294170
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Jang HN, Lee M, Loh TJ, Choi SW, Oh HK, Moon H, Cho S, Hong SE, Kim DH, Sheng Z, Green MR, Park D, Zheng X, Shen H. Exon 9 skipping of apoptotic caspase-2 pre-mRNA is promoted by SRSF3 through interaction with exon 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1839(1):25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.11.006. , Epub 2013 Dec 7. PMID:24321384 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.11.006



