We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Kyle Burton/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
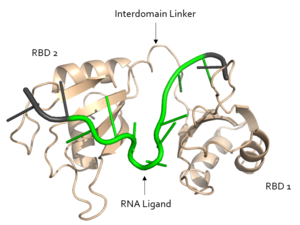
The <scene name='78/783145/Arg_252_interaction_with_u3_g4/6'>R252 interaction with U3 and G4</scene> is crucial to pre-mRNA binding; a mutation of R252 to alanine eliminated the ability of Sxl to bind RNA<ref name="original">PMID: 9398148</ref>. | The <scene name='78/783145/Arg_252_interaction_with_u3_g4/6'>R252 interaction with U3 and G4</scene> is crucial to pre-mRNA binding; a mutation of R252 to alanine eliminated the ability of Sxl to bind RNA<ref name="original">PMID: 9398148</ref>. | ||
| - | The ligand pre-mRNA sequence forms a <scene name='78/783145/U5_u6_u7_loop/5'>loop</scene> at U5, U6, and U7. This interaction is stabilized by π stacking between the G4 and <scene name='78/783145/Aromatic_stacking/4'>Y214</scene> as well as U5 and <scene name='78/783145/Aromatic_stacking/4'>F256</scene>, respectively | + | The ligand pre-mRNA sequence forms a <scene name='78/783145/U5_u6_u7_loop/5'>loop</scene> at U5, U6, and U7. This interaction is stabilized by π stacking between the G4 and <scene name='78/783145/Aromatic_stacking/4'>Y214</scene> as well as U5 and <scene name='78/783145/Aromatic_stacking/4'>F256</scene>, respectively. The nucleobases are exposed to residues on Sxl due to the 2’ endo conformation of all the nucleotides except for U8, which maintains a 3’ endo conformation. |
The U6 residue is recognized as part of the RNA <scene name='78/783145/U5_u6_u7_loop/13'>loop at U5, U6, and U7</scene> by R195. The R195 amide hydrogen-bonds to the O2' of U6 and the U6 N3H hydrogen bonds to the R195 carbonyl oxygen<ref name="Handa"/>. | The U6 residue is recognized as part of the RNA <scene name='78/783145/U5_u6_u7_loop/13'>loop at U5, U6, and U7</scene> by R195. The R195 amide hydrogen-bonds to the O2' of U6 and the U6 N3H hydrogen bonds to the R195 carbonyl oxygen<ref name="Handa"/>. | ||
| - | In the <scene name='78/783145/U5_u6_u7_loop/2'>RNA loop</scene>, the U7 and U8 bases are involved in <scene name='78/783145/U7_u8_stacking/3'>π stacking</scene>, stabilizing the 3' endo conformation of the U8 sugar | + | In the <scene name='78/783145/U5_u6_u7_loop/2'>RNA loop</scene>, the U7 and U8 bases are involved in <scene name='78/783145/U7_u8_stacking/3'>π stacking</scene>, stabilizing the 3' endo conformation of the U8 sugar. U8 is further stabilized via hydrogen bonding <scene name='78/783145/U8_with_s165_and_y166/3'>interactions with S165 and Y166</scene>. The amine group of U8 hydrogen bonds to the the carbonyl oxygens of both S165 and Y166. |
| - | <scene name='78/783145/N130_interaction_with_u9/4'>U9</scene> is recognized by the interdomain linker | + | <scene name='78/783145/N130_interaction_with_u9/4'>U9</scene> is recognized by the interdomain linker. This interaction is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge salt bridge] between the N130 side chain and a phosphate oxygen of U9. U9 is further stabilized by a second <scene name='78/783145/U9_with_interdomain_linker/1'>an ion-dipole interaction</scene> between the U9 O2' and the side chain of R202 and the U9 O4' and the K197 side chain. |
U9 facilitates the stabilization of U10, which is also recognized by the interdomain linker. <scene name='78/783145/Arg_258_interaction_w_u9_u10/3'>R258 interacts with U9 and U10</scene> to form a salt bridge. | U9 facilitates the stabilization of U10, which is also recognized by the interdomain linker. <scene name='78/783145/Arg_258_interaction_w_u9_u10/3'>R258 interacts with U9 and U10</scene> to form a salt bridge. | ||
| - | U11 is recognized by R155. The O2' of U11 <scene name='78/783145/R155_intxn_with_u11/3'>interacts with R155</scene> to form a hydrogen bond | + | U11 is recognized by R155. The O2' of U11 <scene name='78/783145/R155_intxn_with_u11/3'>interacts with R155</scene> to form a hydrogen bond. |
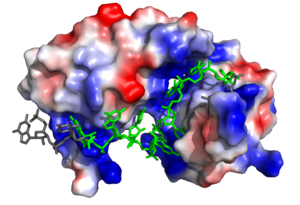
The above interactions are relevant in that Sxl recognizes the specific pre-mRNA based mostly on interactions with the sugar-phosphate backbones<ref name="Handa"/>. Many proteins with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_recognition_motif RNA recognition motifs] are specific in the interactions they form with the bases of the RNA recognized. In contrast, Sxl has a high specificity despite primarily interacting with the phosphate backbone. | The above interactions are relevant in that Sxl recognizes the specific pre-mRNA based mostly on interactions with the sugar-phosphate backbones<ref name="Handa"/>. Many proteins with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_recognition_motif RNA recognition motifs] are specific in the interactions they form with the bases of the RNA recognized. In contrast, Sxl has a high specificity despite primarily interacting with the phosphate backbone. | ||
Revision as of 21:34, 21 April 2018
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 Handa N, Nureki O, Kurimoto K, Kim I, Sakamoto H, Shimura Y, Muto Y, Yokoyama S. Structural basis for recognition of the tra mRNA precursor by the Sex-lethal protein. Nature. 1999 Apr 15;398(6728):579-85. PMID:10217141 doi:10.1038/19242
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Penalva L, Sanchez L. RNA Binding Protein Sex-Lethal (Sxl) and Control of Drosophila Sex Determination and Dosage Compensation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.;67(3):343-356. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.3.343–359.2003
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Bashaw GJ, Baker BS. The msl-2 dosage compensation gene of Drosophila encodes a putative DNA-binding protein whose expression is sex specifically regulated by Sex-lethal. Development. 1995 Oct;121(10):3245-58. PMID:7588059
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 Black DL. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:291-336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720., Epub 2003 Feb 27. PMID:12626338 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Georgiev P, Chlamydas S, Akhtar A. Drosophila dosage compensation: males are from Mars, females are from Venus. Fly (Austin). 2011 Apr-Jun;5(2):147-54. Epub 2011 Apr 1. PMID:21339706
- ↑ Lee AL, Volkman BF, Robertson SA, Rudner DZ, Barbash DA, Cline TW, Kanaar R, Rio DC, Wemmer DE. Chemical shift mapping of the RNA-binding interface of the multiple-RBD protein sex-lethal. Biochemistry. 1997 Nov 25;36(47):14306-17. doi: 10.1021/bi970830y. PMID:9398148 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi970830y