User:Ethan Kitt/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | =Human Poly(A) Binding Protein | + | ==Discussion of Human Poly(A) Binding Protein== |
== Background == | == Background == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1cvj' size='340' side='right' caption='PABP' scene='78/782614/Structure_scene_color_scheme/1'>__NoTOC__ | + | <StructureSection load='1cvj' size='340' side='right' caption='PABP' scene='78/782614/Structure_scene_color_scheme/1'> __NoTOC__ |
| - | The crystal structure PABP was derived from X-ray Diffraction at 2.6Å (R-value: 23%). The subunits of PABP, RRM1 and RRM2, are examined in this article as the ''in vivo'' form seen in biological assembly 1 (via PDB). The protein has a homopolymeric structure, containing four RNA recognition motifs (RRMs), which are conserved. <ref name="Structure and Function">Kühn, Uwe and Elmar, Wahle. “Structure and Function of Poly(a) Binding Proteins.” Bba - Gene Structure & Expression, vol. 1678, no. 2/3, 2004. </ref> <scene name='78/782616/Rrm1_only/ | + | The crystal structure PABP was derived from X-ray Diffraction at 2.6Å (R-value: 23%). The subunits of PABP, RRM1 and RRM2, are examined in this article as the ''in vivo'' form seen in biological assembly 1 (via PDB). The protein has a homopolymeric structure, containing four RNA recognition motifs (RRMs), which are conserved. <ref name="Structure and Function">Kühn, Uwe and Elmar, Wahle. “Structure and Function of Poly(a) Binding Proteins.” Bba - Gene Structure & Expression, vol. 1678, no. 2/3, 2004. </ref> <scene name='78/782616/Rrm1_only/3'>RRM1</scene> and <scene name='78/782616/Rrm2_only/3'>RRM2</scene> are N-terminal domains that are connected by a <scene name='78/782616/Linker/4'>linker</scene>.<ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> Opposed to their counterparts, RRM3 and RRM4 bind Poly (A) RNA less tightly than RRM1 and RRM2.<ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> |
===RNA Recognition Motifs (RRMs)=== | ===RNA Recognition Motifs (RRMs)=== | ||
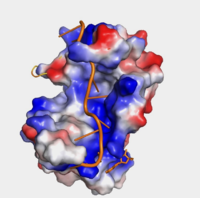
| - | The <scene name='78/782616/Subunits_of_pabp/ | + | The <scene name='78/782616/Subunits_of_pabp/4'>components of PABP</scene> are categorized into two RRMs: the n-terminus RRM1 (red) and c-terminus RRM2 (blue) are shown accordingly. The two RRMs are linked via an alpha-helix linker (green) that maintains the RRM1/2 complex that is the biological assembly and active form of PABP. Each RRM has a four-stranded antiparallel beta sheet backed by two corresponding alpha helices. <ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> mRNA poly-adenosine recognition is due to the presence of the conserved residues within the beta-sheet surface <ref name="The Poly(A)-Binding Protein and an mRNA Stability Protein Jointly Regulate an Endoribonuclease Activity.">Wang, Zuoren and Kiledjian, Megerditch. “The Poly(A)-Binding Protein and an mRNA Stability Protein Jointly Regulate an Endoribonuclease Activity.” Molecular and Cellular Biology 20.17 (2000): 6334–6341. Print.</ref> , which forms a <scene name='78/782616/Trough2/3'>trough</scene>-like pocket for the mRNA to bind. The beta-sheet flooring present in PABP interacts with the 3’ mRNA tail via a combination of van der Waals, aromatic stacking, and Hydrogen bonding. Through these interactions, PABP binds to 3’ Poly (A) tail with a KD of 2-7 nM. <ref name="Roles of Cytoplasmic Poly(A)-Binding Proteins">Gorgoni, Barbra, and Gray, Nicola. “The Roles of Cytoplasmic Poly(A)-Binding Proteins in Regulating Gene Expression: A Developmental Perspective.” Briefings in Functional Genomics and Proteomics, vol. 3, no. 2, 1 Aug. 2004, pp. 125–141., doi:10.1093/bfgp/3.2.125.</ref> [[Image:Hydrophobicity (1).png|200px|right|thumb| "Figure 1:" Surface hydrophobicity shown in presence of mRNA]] |
| - | Further, the RRM1/2 complex interacts with the mRNA's sugar-phosphate backbone, where 4 of the 8 mRNA adenosines interact electrostatically.<ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> Upon closer examination of the PABP structure, the protein contains loop-like domains that form the walls of the beta-sheet trough. Although these <scene name='78/782616/Walls_of_trough/ | + | Further, the RRM1/2 complex interacts with the mRNA's sugar-phosphate backbone, where 4 of the 8 mRNA adenosines interact electrostatically.<ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> Upon closer examination of the PABP structure, the protein contains loop-like domains that form the walls of the beta-sheet trough. Although these <scene name='78/782616/Walls_of_trough/4'>loop walls</scene> are present, no interaction occurs between the mRNA and these regions. We propose that these loops only keep unwanted cellular elements out of the binding pocket via hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions, maintaining the protein's selectivity for mRNA (Figure 1). The structural elements highlighted consist of the RRM1/2 subunits, the linker domain, and the Poly(A) mRNA binding trough. |
==Interactions== | ==Interactions== | ||
| - | [[Image:Dorsal side.jpg|200px|right|thumb| "Figure 3:"Dorsal side with green conserved residues that interact with eIF4 ]] | ||
| - | ===Adenosine Recognition Interactions | + | ===Adenosine Recognition Interactions (table left) and mRNA Stabilization via Aromatic Stacking (table right)=== |
| - | + | <table align='right'><tr><td colspan='2'> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'> | + | |
<tr id='Adenosine Number'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Adenosine Number</b></td><td class="sblockDat">PABP residue</td><tr> | <tr id='Adenosine Number'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Adenosine Number</b></td><td class="sblockDat">PABP residue</td><tr> | ||
<tr id='A3'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A3</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/A3-phe102_fd/1'>Phe102</scene></td><tr> | <tr id='A3'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A3</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/A3-phe102_fd/1'>Phe102</scene></td><tr> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 28: | ||
<tr id='A8'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A8</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Tyr56-a8/1'>Tyr56</scene></td></tr> | <tr id='A8'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A8</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Tyr56-a8/1'>Tyr56</scene></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'> | ||
| + | <tr id='Nucleotide'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Nucleotide</b></td><td class="sblockDat">PABP residue</td><td class="sblockDat">Atom on PABP residue</td><td class="sblockDat">Atom on RNA</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A2'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A2</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Asn105_a2/2'>Asn105</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">side chain amine</td><td class="sblockDat">N6</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A3'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A3</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Lys174-a3/2'>Lys174</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">amine</td><td class="sblockDat">N3</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A4'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A4</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Asn100-a4/2'>Asn100</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">side chain amine and carbonyl</td><td class="sblockDat">N7</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A4'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A4</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Ser127-a4/2'>Ser127</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">side chain and N-term amine</td><td class="sblockDat">N1</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A5'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A5</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/His144-a5/2'>His144</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">pyrimidine π-amine </td><td class="sblockDat">N6</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A6'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A6</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Gln88-a6/2'>Gln88</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">N-term amine and C-term OH</td><td class="sblockDat">N1</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A6'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A6</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Trp86-a6/2'>Trp86</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">N-term amine</td><td class="sblockDat">N6</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A6'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A6</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/A6-tyr14_fd/1'>Tyr14</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">phenol OH</td><td class="sblockDat">phosphate OH</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A7'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A7</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Tyr54-ribose_a7/1'>Trp54</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">side chain OH</td><td class="sblockDat">ribose 2 OH</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A7'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A7</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Asp45-a7/2'>Asn45</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">side chain OH</td><td class="sblockDat">N6</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A7'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A7</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Met46-a7/2'>Met46</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">C-term carbonyl</td><td class="sblockDat">N1</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A8'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A8</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Tyr54-a8/2'>Tyr54</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">side chain OH</td><td class="sblockDat">phosphate OH</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A8'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A8</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Tyr56-a8_fd/2'>Tyr56</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">side chain OH</td><td class="sblockDat">phosphate OH</td> | ||
| + | <tr id='A9'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>A9</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='78/782616/Arg44-a9/2'>Arg44</scene></td><td class="sblockDat">side chain τ-amine</td><td class="sblockDat">N1</td> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 62: | Line 60: | ||
===Eukaryotic Translation Initiation=== | ===Eukaryotic Translation Initiation=== | ||
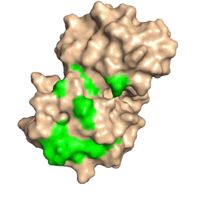
| - | Upon mRNA Poly(A) recognition, PABP and the bound mRNA stimulate the initiation of translation by interacting with initiation factor eIF4G. Protein eIF4G actually interacts with PABP's dorsal side (under the trough) hydrophobic and acidic residues that stimulate the interaction between the two proteins. These specific residues are phylogenetically conserved among all PABPs, and therefore significant in the protein's function and interaction with eIF4G. | + | Upon mRNA Poly(A) recognition, PABP and the bound mRNA stimulate the initiation of translation by interacting with initiation factor eIF4G. Protein eIF4G actually interacts with PABP's dorsal side (Figure2) (under the trough) hydrophobic and acidic residues that stimulate the interaction between the two proteins. These specific residues are phylogenetically conserved among all PABPs, and therefore significant in the protein's function and interaction with eIF4G. [[Image:Dorsal side.jpg|200px|right|thumb| "Figure 2:"Dorsal side with green conserved residues that interact with eIF4.]] |
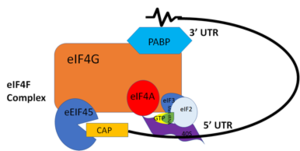
| - | PABP and mRNA complex aids in translation initiation under two proposed mechanisms. Within the two mechanisms, studies have highlighted the presence The “Closed Loop” Model entails the recognition of the 5’ 7-methyl-Guanosine cap by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eukaryotic_initiation_factor_4F eIF4F], which is a ternary complex made up of a cap-binding protein [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EIF4E (eIF4E)] and RNA helicase [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EIF4A (eIF4A)] connected by the bridging protein (eIF4G) (Figure | + | PABP and mRNA complex aids in translation initiation under two proposed mechanisms. Within the two mechanisms, studies have highlighted the presence The “Closed Loop” Model entails the recognition of the 5’ 7-methyl-Guanosine cap by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eukaryotic_initiation_factor_4F eIF4F], which is a ternary complex made up of a cap-binding protein [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EIF4E (eIF4E)] and RNA helicase [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EIF4A (eIF4A)] connected by the bridging protein (eIF4G) (Figure 3).¹ Translation initiation is stimulated by the PABP bound to the poly(A) tail and its association with eIF4G.<ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> The 5’ UTR is unwound by the elF4F complex, and ribosomes are recruited to create the initiation complex. The eIF4G protein then guides the 40S subunit to the start codon (AUG), which is followed by the binding 60S ribosomal subunit, creating the 80S initiation complex.<ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> The association of the PABP and eIF4G gave rise to the name “closed loop.”<ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> Mutations of Arg→Ala and Lys→Ala in human eIF4G and in yeast extracts decrease the rate of translation initiation and destabilizing the interactions with PABP, indicating that basic residues are essential to the interaction with PABP.<ref name="Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein">Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print. </ref> |
| - | [[Image:closedlooper.png|300px|right|thumb| "Figure | + | [[Image:closedlooper.png|300px|right|thumb| "Figure 3:" Closed loop model of the eIF4F complex and PABP creating a loop out of the mRNA ]] |
In more complex eukaryotic organisms, PABP indirectly stimulates translation via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PAIP1 PAIP-1] (PABP interacting protein). A higher presence of PAIP-1 increases the rate of translation initiation, indicating another way to “close the loop.”¹ | In more complex eukaryotic organisms, PABP indirectly stimulates translation via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PAIP1 PAIP-1] (PABP interacting protein). A higher presence of PAIP-1 increases the rate of translation initiation, indicating another way to “close the loop.”¹ | ||
Current revision
Contents |
Discussion of Human Poly(A) Binding Protein
Background
The Human Poly(A) Binding Protein (PABP) was discovered in 1973 by the use of a sedimentation profile detailing the RNase digestion differentiated the PABP protein. [1] Attempts to purify the 75 kDa protein then followed. In 1983, then considered “poly(A)-organizing protein,” was determined and purified by molecular weight, ligand-binding affinity, and amounts found in cytoplasmic portions of cell with ability to bind to free poly(A). [2]
PABP is a mRNA binding protein that binds to the 3’ Poly(A) tail on mRNA. It is comprised of four RNA recognition motifs (RRMs), which are highly conserved RNA-binding domains.[3] The RRM in PABP is found in over two hundred families of proteins across species, indicating that it is ancient.[3] Through extensive Adenosine recognition by the RRMs of PABP, the protein is involved in three main functions: recognition of the 3’ Poly(A) tail, mRNA stabilization, and eukaryotic translation initiation. The contributions of controlling gene expression via different families of PABPs is not yet fully understood. PABP families are divided into nuclear and cytoplasmic. [4] PABP1, which is predominantly cytoplasmic, is often referred to as PABP because it is the only form of PABP that has been extensively studied in its role with mRNA translation and stability. [4]
Structure
| |||||||||||
Disease and Medical Relevance
Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy, or OPMD, is an autosomal dominant late-onset disease. [7] It’s characterized by the myopathy of the eyelids and the throat. The symptoms entail eye-drooping and difficulty swallowing. There are two types of OPMD: autosomal dominant and recessive, both originating from the mutation of the PABP nuclear 1 (PABPN1) gene located on the long arm of chromosome 14. [7] This mutation results in an abnormally long polyalanine tract, 11-18 alanines, opposed to the normal 10. [7] Patients with longer PABPN1 expansion (more alanines) are on average diagnosed at an earlier in life than patients with a shorter expansion; therefore, expansion size plays a role in OPMD severity and progression. [8]
The mutation results in PABPN1 forming clumps in muscle cells that can’t be degraded. [7] It’s suspected that this is a source of cell death for effected cells, however, it has not been concluded why this mutation only affects certain muscle cells.
Studies on Mutations
Studies conducted on Drosophila are common due to 75% conservation between human and Drosophila genomes. Drosophila only encode one cytoplasmic PABP, and its deletion results in embryonic lethality. [4] Similarly, in Caenorhabditis elegans, which have two cytoplasmic PABPs, display 50-80% embryonic lethality with the introduction of an RNAi to one of these PABPs. [4]
References
- ↑ Blobel, Gunter. “A Protein of Molecular Weight 78,000 Bound to the Polyadenylate Region of Eukaryotic Messenger Rnas.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 70, no. 3, 1973, pp. 924–8.
- ↑ Baer, Bradford W. and Kornberg, Roger D. "The Protein Responsible for the Repeating Structure of Cytoplasmic Poly(A)-Ribonucleoprotein." The Journal of Cell Biology, vol. 96, no. 3, Mar. 1983, pp. 717-721. EBSCOhost.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell 98:6. (1999) 835-845. Print.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Gorgoni, Barbra, and Gray, Nicola. “The Roles of Cytoplasmic Poly(A)-Binding Proteins in Regulating Gene Expression: A Developmental Perspective.” Briefings in Functional Genomics and Proteomics, vol. 3, no. 2, 1 Aug. 2004, pp. 125–141., doi:10.1093/bfgp/3.2.125.
- ↑ Kühn, Uwe and Elmar, Wahle. “Structure and Function of Poly(a) Binding Proteins.” Bba - Gene Structure & Expression, vol. 1678, no. 2/3, 2004.
- ↑ Wang, Zuoren and Kiledjian, Megerditch. “The Poly(A)-Binding Protein and an mRNA Stability Protein Jointly Regulate an Endoribonuclease Activity.” Molecular and Cellular Biology 20.17 (2000): 6334–6341. Print.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 “Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy.” NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders), rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/oculopharyngeal-muscular-dystrophy/.
- ↑ Richard, Pascale, et al. “Correlation between PABPN1 Genotype and Disease Severity in Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy.” Neurology, vol. 88, no. 4, 2016, pp. 359–365., doi:10.1212/wnl.0000000000003554.