We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Poly(A) binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
===Poly (A)Binding=== | ===Poly (A)Binding=== | ||
| - | [[Image: Screen_Shot_2018-03-29_at_12.18.14_AM.png|250 px|left|thumb|Figure 2: The specific weak intermolecular interactions between RNP1 and RNP2 and | + | [[Image: Screen_Shot_2018-03-29_at_12.18.14_AM.png|250 px|left|thumb|Figure 2: The specific weak intermolecular interactions between RNP1 and RNP2 and adenosines. These interactions are the primary support of adenosine recognition by PABP and include mainly van der Waals interactions, hydrogen bonds, and stacking interactions. ]] |
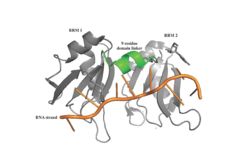
| - | A primary function of PABP is recognizing and interacting with the 3' Poly(A) tail created in mRNA processing. As found by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrophoretic_mobility_shift_assay EMSA competition experiments], there are a minimum of 11-12 adenosines necessary in the Poly(A) tail for the adenosine chain to bind to PABP with high affinity. However, for one biological assembly, a chain containing 9 adenosines sufficiently binds the assembly for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crystallization crystallization] and is shown in the biological assembly structure. The 4 RRMs that are the primary interacting sites for the adenosine recognition exist as globular domains, each having four antiparallel [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet β-strands] (labeled S1-S4) and two [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix α-helices] (labeled H1 and H2). The strands are spatially arranged as S2-S3-S1-S4, and the two inner strands create vital interactions with the Poly(A) tail. There are two [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conserved_sequence conserved sequences] in each RRM, called RNP1 and 2. RNP 1 consists of a conserved sequence of 8 [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Residue residues], while RNP2 consists of a conserved sequence of 6 residues. Much of the weak [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intermolecular_force intermolecular interactions] with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine adenosine] from the RRMs occur from the <scene name='78/781946/Rnp_1_rnp2/1'>RNP 1 and RNP 2</scene> conserved sequences, which correspond to the two central β-strands, with specific interactions shown in Figure 2. The support for adenosine recognition by the RRMs occurs as a type of binding trough with the sheets, primarily <scene name='78/781946/Rnp_1_rnp2/1'>RNP 1 and RNP 2</scene> forming the base of the primary binding trough, and the interstrand loop between β-strands 2 and 3 as well as the domain linker forming the <scene name='78/781947/Adenosine_binding_wall/1'>Adenosine Binding Wall</scene>. It is believed that the <scene name='78/781946/Pabp_linker_conserved_residues/1'>Conserved Linker Shown</scene> is disordered in the absence of RNA because it does not intramolecularly interact with either of the RRM motifs, and instead only interacts with the RNA such as with Arg 94 exhibiting pi-stacking with | + | A primary function of PABP is recognizing and interacting with the 3' Poly(A) tail created in mRNA processing. As found by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrophoretic_mobility_shift_assay EMSA competition experiments], there are a minimum of 11-12 adenosines necessary in the Poly(A) tail for the adenosine chain to bind to PABP with high affinity. However, for one biological assembly, a chain containing 9 adenosines sufficiently binds the assembly for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crystallization crystallization] and is shown in the biological assembly structure. The 4 RRMs that are the primary interacting sites for the adenosine recognition exist as globular domains, each having four antiparallel [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet β-strands] (labeled S1-S4) and two [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix α-helices] (labeled H1 and H2). The strands are spatially arranged as S2-S3-S1-S4, and the two inner strands create vital interactions with the Poly(A) tail. There are two [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conserved_sequence conserved sequences] in each RRM, called RNP1 and 2. RNP 1 consists of a conserved sequence of 8 [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Residue residues], while RNP2 consists of a conserved sequence of 6 residues. Much of the weak [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intermolecular_force intermolecular interactions] with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine adenosine] from the RRMs occur from the <scene name='78/781946/Rnp_1_rnp2/1'>RNP 1 and RNP 2</scene> conserved sequences, which correspond to the two central β-strands, with specific interactions shown in Figure 2. The support for adenosine recognition by the RRMs occurs as a type of binding trough with the sheets, primarily <scene name='78/781946/Rnp_1_rnp2/1'>RNP 1 and RNP 2</scene> forming the base of the primary binding trough, and the interstrand loop between β-strands 2 and 3 as well as the domain linker forming the <scene name='78/781947/Adenosine_binding_wall/1'>Adenosine Binding Wall</scene>. It is believed that the <scene name='78/781946/Pabp_linker_conserved_residues/1'>Conserved Linker Shown</scene> is disordered in the absence of RNA because it does not intramolecularly interact with either of the RRM motifs, and instead only interacts with the RNA such as with Arg 94 exhibiting pi-stacking with Adenosine-6 and side chain hydrophobic interactions with Adenosine-5. The primary binding trough is stabilized by <scene name='78/781947/Rrm1_2_packing_intxn/3'>Stabilizing Packing Interactions of RRM1 RRM2 Binding Trough</scene>. <ref name= "PABP"/> |
[[Image: Adenosine_backbone.png |200 px|right|thumb|Figure 3: Basic residues of RRM 1 and 2 (shown in blue) make stabilizing electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged phosphate backbone. ]] | [[Image: Adenosine_backbone.png |200 px|right|thumb|Figure 3: Basic residues of RRM 1 and 2 (shown in blue) make stabilizing electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged phosphate backbone. ]] | ||
====Adenosine Stabilization Interaction Patterns==== | ====Adenosine Stabilization Interaction Patterns==== | ||
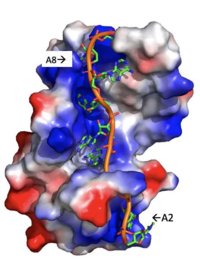
| - | There are several significant interaction patterns that stabilize adenosine recognition. RRM 1 and 2 makes significant interactions with the adenosine backbone. Four of eight | + | There are several significant interaction patterns that stabilize adenosine recognition. RRM 1 and 2 makes significant interactions with the adenosine backbone. Four of eight adenosine backbones participate in the phosphate-protein electrostatic interactions: Adenosine-2, Adenosine-3, Adenosine-6, Adenosine-8. For example, basic residues such as Lys 104 interact with the backbone of Adenosine-2 while Arg 89 interact with the phosphate backbone of Adenosine-8, shown in Figure 3. On the other hand, all adenosine nucleobases except for Adenosine-1 participate in stabilizing interactions with the protein. The Poly(A) tail stabilizes itself via intramolecular stacking interactions between adenosines. Through the extensive <scene name='78/781947/Interactions_with_a2/1'>interactions with Adenosine-2</scene>, the RRM specifies the position of Adenosine-2, allowing it to make strong intramolecular stacking interactions with Adenosine-1. As a result, Adenosine-1 requires less contact with the RRM. Adenosine-3 and Adenosine-6 are stabilized by being sandwiched between [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aromatic_amino_acid aromatic] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aliphatic_compound alipathic] side chains. Stacking interactions also occur between nucleobases and aromatic or alipathic side chains, such as <scene name='78/781947/Stacking_interactions_a3/1'>Adenosine-3 stacking interactions</scene> occur between Phe 102 and Arg 179, and it is specified by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lysine Lysine] 104. Additionally, <scene name='78/781947/Residues_interacting_with_a6/3'>Adenosine-6 stacking interactions</scene> occurs similarly between Tyr 14 and Arg 94, but it is specified doubly by two residues, Trp 86 and Gln 88 <ref name= "PABP"/>. Thus, the entirety of the adenosine nucleotide is stabilized within the protein through a variety of interactions. |
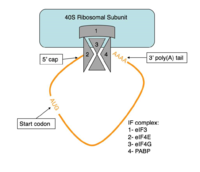
===Translation Initiation=== | ===Translation Initiation=== | ||
Revision as of 23:52, 23 April 2018
Poly(A) binding protein
| |||||||||||