Nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Hrp1-RNA Interactions== | ==Hrp1-RNA Interactions== | ||
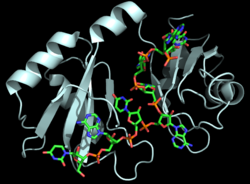
| - | The interface between Hrp1 and its target RNA sequence is dominated by interactions between key aromatic residues and RNA nucleobases <ref name="GM3H"/>. Only six RNA bases, an <scene name='78/781952/Ua_repeats/ | + | The interface between Hrp1 and its target RNA sequence is dominated by interactions between key aromatic residues and RNA nucleobases <ref name="GM3H"/>. Only six RNA bases, an <scene name='78/781952/Ua_repeats/2'>(AU)3</scene> repeat, act as the PEE and form specific contacts with Hrp1 <ref name="GM3H"/>. The kinked conformation around Ade4 is uncommon for RNA alone, and may be adopted by the RNA for specific interactions with Hrp1. Ade4 is part of a crucial interaction with Trp168 which will be discussed later, and could explain the adoption of the kinked conformation. Hydrophilic residues of Hrp1 provide base specificity through hydrogen bonding <ref name="GM3H"/>. Most of the key residues that interact with the RNA can be found in the ß-sheet region of Hrp1; however, loops and the interdomain linker are also essential for Hrp1-RNA recognition <ref name="GM3H"/>. Perhaps the most important Hrp1-RNA interaction is the <scene name='78/783765/Ade4-trp168/4'>interaction between Ade4 and Trp168</scene> <ref name="GM3H"/>. In this case, Trp168 stacks on Ade4 and forms crucial base-specific hydrogen bonds such as the H-bond between N7 of Ade4 and amide hydrogren of Trp168 <ref name="GM3H"/>. This interaction is a unique feature of the Hrp1-PEE complex and has not been found in any other single-stranded RNA-binding proteins with two canonical RBDs <ref name="GM3H"/>. It is also worth noting that a second Hrp1 residue is critical to holding Ade4 in place, <scene name='78/781945/Lys226-ade4-trp168/3'>Lys226</scene>, which stabilizes Ade4 likely via a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cation%E2%80%93pi_interaction cation–π interaction]. As displayed in the structure, the lysine cationic nitrogen is approximately 4Å away from the pi system, which is within the 6Å range associated with cation-pi interactions. A third contributor, <scene name='78/783765/Phe204_and_u7_interaction/2'>Phe204</scene>, also stacks with Ura7 to aid in RNA recognition and binding <ref name="GM3H"/>. |
==RBD-RBD Interactions and the Linker Region== | ==RBD-RBD Interactions and the Linker Region== | ||
Revision as of 15:15, 24 April 2018
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 Perez-Canadillas JM. Grabbing the message: structural basis of mRNA 3'UTR recognition by Hrp1. EMBO J. 2006 Jul 12;25(13):3167-78. Epub 2006 Jun 22. PMID:16794580
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Leeper TC, Qu X, Lu C, Moore C, Varani G. Novel protein-protein contacts facilitate mRNA 3'-processing signal recognition by Rna15 and Hrp1. J Mol Biol. 2010 Aug 20;401(3):334-49. Epub 2010 Jun 19. PMID:20600122 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.06.032
- ↑ Kessler MM, Henry MF, Shen E, Zhao J, Gross S, Silver PA, Moore CL. Hrp1, a sequence-specific RNA-binding protein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, is required for mRNA 3'-end formation in yeast. Genes Dev. 1997 Oct 1;11(19):2545-56. PMID:9334319
- ↑ Clery A, Blatter M, Allain FH. RNA recognition motifs: boring? Not quite. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Jun;18(3):290-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002. PMID:18515081 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Cory A. Wuerch, Matthew Douglas Moore, Savannah Davis, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky