This is a default text for your page Isabelle A. Altieri/Sandbox 1. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Introduction
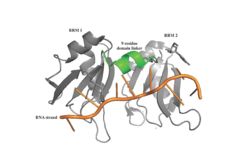
Figure 1: PABP Biological Assembly with linker highlighted.
Human Poly(A) Binding Protein (PABP) is a biopolypeptide involved in recognizing the 3' poly(A) tail that is added tomRNA processing. This recognition, as well as PABP's interaction with other proteins and initiation factors, causes it to play a significant role in translation initiation and mRNA stabilization and degradation. PABP consists of four conserved domains of RNA recognition motifs (RRMs); however, the two N-terminal RRMs (RRM1 and RRM2) and the short linker sequence that connects them support most of the function of full-length PABP. Due to this and the modular organization of the protein, it is thought that the full complement of PABP may not be essential. Thus, the published X-ray diffraction structure reveals RRM1 and RRM2 at a 2.6 Angstrom resolution. This is shown as . Both RRM 1 and 2 are needed to support biochemical function; that is, no one RRM can support biochemical function. Additionally, there is a proline rich C-terminal portion of variable length that is not well conserved and its contribution to the protein's function is unknown [3].
Function and Structure
Poly(A) Binding

Figure 2: The specific weak intermolecular interactions between RNP1 and RNP2 and adenosines. These interactions are the primary support of adenosine recognition by PABP and include mainly van der Waals interactions, hydrogen bonds, and stacking interactions.
A primary function of PABP is recognizing and interacting with the 3' Poly(A) tail created in mRNA processing. As found by EMSA competition experiments, there are a minimum of 11-12 adenosines necessary in the Poly(A) tail for the adenosine chain to bind to PABP with high affinity. However, for one biological assembly, a chain containing 9 adenosines sufficiently binds the assembly for crystallization and is shown in the biological assembly structure. The 4 RRMs that are the primary interacting sites for the adenosine recognition exist as globular domains, each having four antiparallel β-strands (labeled S1-S4) and two α-helices (labeled H1 and H2). The strands are spatially arranged as S2-S3-S1-S4, and the two inner strands create vital interactions with the Poly(A) tail. There are two conserved sequences in each RRM, called RNP1 and 2. RNP 1 consists of a conserved sequence of 8 residues, while RNP2 consists of a conserved sequence of 6 residues. Much of the weak intermolecular interactions with adenosine from the RRMs occur from the conserved sequences, which correspond to the two central β-strands, with specific interactions shown in Figure 2. The support for adenosine recognition by the RRMs occurs as a type of binding trough with the sheets, primarily forming the base of the primary binding trough, and the interstrand loop between β-strands 2 and 3 as well as the domain linker forming the . It is believed that the is disordered in the absence of RNA because it does not intramolecularly interact with either of the RRM motifs, and instead only interacts with the RNA such as with Arg 94 exhibiting pi-stacking with Adenosine-6 and side chain hydrophobic interactions with Adenosine-5. The primary binding trough is stabilized by . [3]
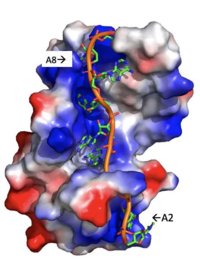
Figure 3: Basic residues of RRM 1 and 2 (shown in blue) make stabilizing electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged phosphate backbone.
Adenosine Stabilization Interaction Patterns
There are several significant interaction patterns that stabilize adenosine recognition. RRM 1 and 2 makes significant interactions with the adenosine backbone. Four of eight adenosine backbones participate in the phosphate-protein electrostatic interactions: Adenosine-2, Adenosine-3, Adenosine-6, Adenosine-8. For example, basic residues such as Lys 104 interact with the backbone of Adenosine-2 while Arg 89 interact with the phosphate backbone of Adenosine-8, shown in Figure 3. On the other hand, all adenosine nucleobases except for Adenosine-1 participate in stabilizing interactions with the protein. The Poly(A) tail stabilizes itself via intramolecular stacking interactions between adenosines. Through the extensive , the RRM specifies the position of Adenosine-2, allowing it to make strong intramolecular stacking interactions with Adenosine-1. As a result, Adenosine-1 requires less contact with the RRM. Adenosine-3 and Adenosine-6 are stabilized by stacking between aromatic and alipathic side chains. Stacking interactions also occur between nucleobases and aromatic or alipathic side chains, such as between Phe 102 and Arg 179, and it is specified by Lysine 104. Additionally, occurs similarly between Tyr 14 and Arg 94, but it is specified doubly by two residues, Trp 86 and Gln 88 [3]. Thus, the entirety of the adenosine nucleotide is stabilized within the protein through a variety of interactions.
Translation Initiation
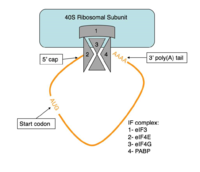
Figure 4:Closed loop model diagram required for translation initiation in eukaryotes.
The initiation of translation in eukaryotes requires many translation factors and proteins, one of which is PABP. There is evidence that PABP is critical for formation of the “closed loop” model of protein synthesis, which involves joining the 3’ poly (A) tail of mRNA to the 5’ cap to create circular RNA [4]. This process utilizes eIF4F, a protein composed of multiple translation factors that play various roles in translation. eIF4G is a scaffolding protein that binds the other subunits, eIF4E and eIF4A. eIF4E creates interactions with the 5’ cap to bring the initiation factor (IF) complex to the 5’ end of the mRNA. eIF4G also has a binding site for PABP, which is N-terminal to the binding site for eIF4F and interacts with the same RRMs that allow PABP to bind RNA. [5] All of these proteins are known to be involved in protein synthesis, but several mechanisms have been proposed for how PABP might be promoting translation.
One of the mechanisms that PABP has been shown to assist in the initiation of protein synthesis is by interaction with eIF4G. The results of Kahvejian et al. were able to show that not only might PABP be acting as a translation factor in eukaryotic cells, but it also needs to interact with eIF4G in order to have an effect [6].
PABP interactions have been shown to be critical for the formation of the 80S ribosomal subunit. PABP is essential in recruiting both the 40S and the 60S ribosomal subunit for the initiation of translation[6]. Because of this, PABP affects the formation of the 80S ribosome complex in two ways: indirectly, by allowing the 40S subunit to be available to bind, and directly, by promoting association of the 60S subunit with the 40S subunit.
In addition to these interactions, the PABP aids in this closed loop formation via interactions with Poly(A) Interacting Protein 1 (PAIP-1). In this process, PABP interacts with PAIP-1 to facilitate the complex to interact with eIF4A initiation factor. eIF4A unwinds the 5' untranslated region (UTR) of an mRNA transcript, which signals eIF4G to function as previously mentioned [3]. Thus, there are two mechanisms to initiate this loop closing pathway with eIF4G. All of these proposed interactions show that PABP stimulates translation at several points throughout the initiation process.
Structural Components of PABP Translation Initiation

Figure 5:Conserved residues that potentially bind regulatory proteins and translation initiation factors.
The RRMs support interactions with the interacting proteins such as eIF4G and PAIP-1, however, the specific ways in which PABP interacts with these proteins are not structurally proven. However, there is a convex dorsal surface present on the RRM 1 and 2 motifs formed by the two α-helices in each RRM, specified as H1 and H2 in RRM1 and H1' and H2' in RRM2. This surface contains a sequence portion of and . It is thought that this area of conservation thus produces overlapping binding sites to interact with eIF4G and PAIP-1. The conserved acidic residues may be beneficial to be used in order to interact with essential basic residues present in both eIF4G and PAIP-1 via ionic interactions [3].
While there are only proposed mechanisms for how PABP promotes the initiation of translation in Homo sapiens, the mechanism is better understood in a pathogenic protozoan, Leishmania. Osvaldo P. de Melo Neto et. al found that an eIF4F-like complex phosphorylates a site on the domain linker of a PABP homolog, PABP-1, at either serine-proline or threonine-proline residues.The authors suggest that this phosphorylation is part of how PABP-1 aids the eIF4F complex in initiating translation. They supported this by removing the gene that encodes PABP-1 and the results showed that the protozoan could not initiated cell growth and therefore survive without the PABP-1 gene. The homo sapiens' PABP also contain a () site on the domain linker which could be interacting with the eIF4 complex in a similar way as in Leishmania protozoan [7].
Relevance
Medical Relevance with Rotavirus
Rotavirus, a virus of varying size, containing 11 double stranded RNA and 12 proteins (6 structural, 6 non-structural) is responsible for preventing initiation of translation in infected cells. The virus enters the cell and undergoes a non-conservative replication cycle in the cytoplasm. After a replication cycle, non-structural protein 3 (NSP3) can be found spread throughout the cytoplasm. NSP3 is responsible for releasing PABP from eIF4F and inhibiting translation initiation. In a study done by Piron et al. it has been seen that NSP3 competes with PABP in binding to the poly(A)-tail of mRNA. This competitor inhibits the proper closing of the closed loop therefore inhibiting translation and protein synthesis. The presence of translation of viral mRNA allows the virus to spread throughout an organism and lead to a greater decrease in host protein synthesis. [5]
Biological Relevance in Plants
PABP is a conserved protein in eukaryotes and has been identified in yeast, mammals, and plants. While PABP is seen among these three it is only present in yeast as a single protein. Mammalian and plant PABP is in a diverse gene family and may have isoforms which have more specific functions. In a study done by Gallie and Liu it was seen that Arabidopsis, a small flowering plant, and yeast have multiple distinct PABP proteins which perform specific functions. The various PABP proteins in yeast vary in functions including acceleration of mRNA into a degradation pathway, mRNA biogenesis and export, and protecting the 5’ cap from degradation. While different species have different specific proteins the RRMs in PABP are highly conserved. The PABP has evolved overtime form a single gene found in yeast and algae to a large family of genes found in land plants and mammalian species. When PABP is viewed among different species of plants including Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chaetosphaeridium globosum, and Klebsormidium flaccidum it has been seen that different intron patterns are conserved in different species. Gallie and Liu suggest that PABP gene families are still undergoing evolution [8].
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Deo, Rahul C, et al. “Recognition of Polyadenylate RNA by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein.” Cell, vol. 98, no. 6, 1999, pp. 835–845., doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81517-2.
- ↑ Imataka, H. “A Newly Identified N-Terminal Amino Acid Sequence of Human eIF4G Binds Poly(A)-Binding Protein and Functions in Poly(A)-Dependent Translation.” The EMBO Journal, vol. 17, no. 24, 1998, pp. 7480–7489., doi:10.1093/emboj/17.24.7480.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Piron, M. “Rotavirus RNA-Binding Protein NSP3 Interacts with eIF4GI and Evicts the Poly(A) Binding Protein from eIF4F.” The EMBO Journal, vol. 17, no. 19, 1998, pp. 5811–5821., doi:10.1093/emboj/17.19.5811.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kahvejian, A. “Mammalian Poly(A)-Binding Protein Is a Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor, Which Acts via Multiple Mechanisms.” Genes & Development, vol. 19, no. 1, 2005, pp. 104–113., doi:10.1101/gad.1262905.
- ↑ De Melo Neto, Osvaldo P., et al. “Phosphorylation and Interactions Associated with the Control of the Leishmania Poly-A Binding Protein 1 (PABP1) Function during Translation Initiation.” RNA Biology, 23 Mar. 2018, pp. 1–17., doi:10.1080/15476286.2018.1445958.
- ↑ Gallie, Daniel R, and Renyi Liu. “Phylogenetic Analysis Reveals Dynamic Evolution of the Poly(A)-Binding Protein Gene Family in Plants.” BMC Evolutionary Biology, vol. 14, no. 1, 2014, doi:10.1186/s12862-014-0238-4.





