Introduction
is a protein characterized by its large size (700 kDa) and its unique tripartite structure [1][2]. Originally identified in 1989 as a desmosomal plaque protein purified from bovine muzzle epidermis called desmoyokin, AHNAK is now recognized as a scaffolding protein that has implicated in a wide range of diverse biological processes [1][2]. This includes processes from Ca2+ channel regulation and cell adhesion to cell cycle arrest [1][3][4][5]. Despite the diversity of processes that AHNAK is involved in, they’re unified in the formation of multi-protein complexes, AHNAK likely serving as a scaffolding protein for other proteins in the complex [1].
In alignment with AHNAK’s many functions, AHNAK has several identified subcellular localizations depending on cell type, intercellular contacts, and the phosphorylation state of the protein [1][6]. These include the plasma membrane, the cytoplasm and the nucleus [2][7][8][9]. There is also evidence supporting AHNAK’s export to the extracellular space [9].
Structure
AHNAK has a unique structure made up of three main domains: the N-terminal domain, the central repeated domain, and the C-terminal domain (Figure 1). These domains are 251, 4300, and 1002 amino acids in length, respectively [1][8].
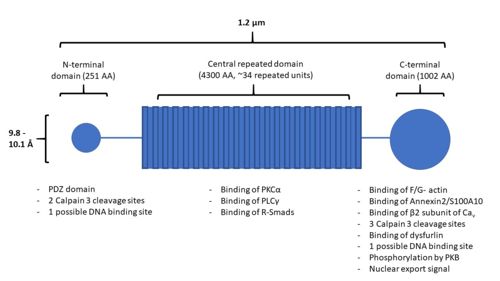
Figure 1. A structural representation of AHNAK, including sites of protein interaction. Modified from
[1] The Central Repeated Domain
The central repeated domain is comprised of many 128 amino acid repeated elements, these generally being rich in charged residues [8]. These elements are highly conserved, on average sharing an identity of 80% and maintaining both polarity and charge in their amino acid substitutions. Underlying the 128-residue repeat is a 7-residue repeat with the pattern: Φ+ΦP+Φ+, where Φ are hydrophobic residues, + are charged residues, and P is a proline residue. A molecular model of the structure resembles that of a β-strand, where intermolecular hydrogen bonding could cause the protein to adopt a seven or eight-stranded barrel structure with a diameter of 9.8 or 10.1 Å, respectively. This results in an polyionic rod structure as long as 1.2 µm.
Protein Interactions and Post-Translational Modifications
AHNAK contains many different sites for protein-protein interactions and post-translational modifications (Figure 1). The UniProt entry for human AHNAK (Q09666) shows 179 sites of post-translational modification distributed across all 3 of AHNAK’s domains. The N-terminal domain of AHNAK contains a [10]. PDZ domains are domains involved in protein interaction, typically recognizing short C-terminal amino acid sequences of their target proteins [11]. AHNAK has been demonstrated undergoing heterodimerization between its large and small isoforms, likely through interactions with their PDZ domains [12]. The small AHNAK isoform is also capable of homodimerization.
AHNAK has many different sites of interaction for the many other proteins and processes that it relates to, below is a list of some of the other molecules and proteins that AHNAK can interact with, a description of the interaction, and the location of the interaction in the AHNAK protein (Figure 2):
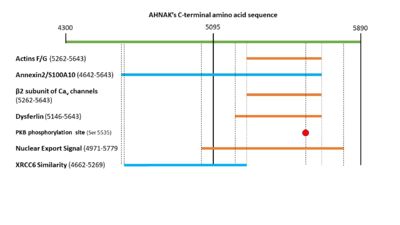
Figure 2. A visual representation of the C-terminal sequence of AHNAK and its sites of protein interaction.
Both F- and G- actin have been shown interacting with residues 5262–5643 of the C-terminal domain of AHNAK [13].
will interact with / structural scaffolding complex through residues 4642–5643 in its C-terminal domain [7].
- β2 subunit of L-type voltage-gated calcium (Cav) channels
The β2 subunit of Cav channels will interact with residues 5262-5643 of the C-terminal domain of AHNAK [13].
There are 5 cleavage sites for Calpain in AHNAK, 2 are in the N-terminus and 3 are in the C-terminus. [14]
The N-terminal region of dysfurlin will interact with the C-terminal domain of AHNAK from residues 5146 – 5643 [15].
AHNAK has been shown having weak DNA binding affinity similar to the Ku protein 16. Sequence alignment of AHNAK with Ku70 (Uniprot P13010)and Ku80 (Uniprot P12956) indicated areas of similarity from residues 1-200 and 4661-5260 respectively (Figure 3) [17]. These sites may be AHNAK’s prospective DNA binding sites.
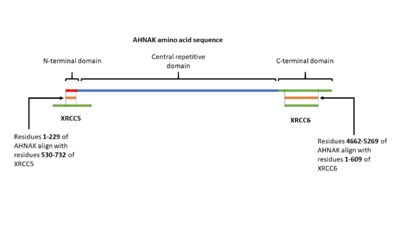
Figure 3. A visual representation of AHNAK's amino acid sequence and its sites of similarity with the proteins XRCC5 and XRCC6.
PKB will phosphorylate serine 5535 in AHNAK’s C-terminal domain [6]. This will activate AHNAK’s nuclear export signal, allowing it to move out of the nucleus. AHNAK’s nuclear export signal is made up of 5 different motifs in the C-terminal domain: (4971-4979), (5019-5027), (5034-5039), (5706-5716), and (5772-5779) [18].
- Protein Kinase C α (PKCα)
PKCα will bind to and is activated by AHNAK [19]. This interaction occurs in AHNAK’s central repeated domain (3859-4412).
PLCγ will bind AHNAK in its central repeated domain in residues 3740-3882 and 3859-4412 [20]. AHNAK also activated bound PLCγ.
- Regulatory Samds (R-Smads)
The MH2 domain of Smad2 will bind to the central repetitive domain of AHNAK from residues 4105-4633 [21].
It is also of not that AHNAK does not have a calcium binding domain, despite it responding to calcium signaling. Calcium sensing might be facilitated by AHNAK’s interaction with annexin 2, which is calcium sensitive [1][22,23].
Function
AHNAK has a diverse list of biological processes that is has been implicated in, including cell signaling and cell contacts, regulation of calcium channels, membrane repair, and interaction with DNA ligase (Figure 4) [1]. AHNAK has been implicated in each of these biological processes, each with a description of its role:
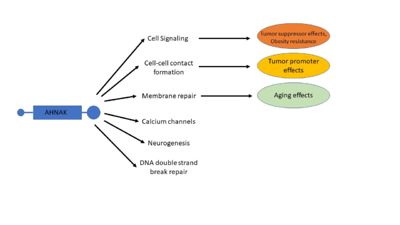
Figure 4. A visual representation of many of AHNAK's functions and how those functions relate to disease. Modified from
[1] Cell signaling
The central repetitive domain of AHNAK has been shown binding and activating the signaling proteins PKCα and PLCγ [19,20]. This activation has been demonstrated as having a downstream activating effect on the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, which in turn regulates gene expression [19,20,24]. The central repetitive domain of AHNAK has also been shown to play a role in the TGFβ and Smad signaling pathway [21]. AHNAK can interact with and translocate regulatory-Smad proteins 1-3 to the nucleus. This translocation increases the binding of phosphor-Smad3 to the c-Myc promoter, resulting in decreased c-Myc expression and in turn less cell proliferation. AHNAK overexpression in mouse fibroblast cells resulted in an accumulation of cells in the G0 and G1 phases of the cell cycle, indicating cell cycle arrest [21].
Neurogenesis
AHNAK has been associated with several different processes involving neurogenesis. In the peripheral nervous system AHNAK might play a role in myelination [25,26]. AHNAK is expressed during the period of laminin deposition and myelination in Schwann cells, and AHNAK knockdown showed detachment from laminin substrates. In the central nervous system AHNAK was implicated in the formation of the blood brain barrier, as endothelial cells forming the blood brain barrier had increased AHNAK expression levels compared to those not forming the blood brain barrier [27]. AHNAK null mice displayed increased levels of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mice, indicating that AHNAK might be involved in modulating the differentiation of new cells to neuronal or non-neuronal cells [28].
Cell-Cell contact formation
In addition to phosphorylation by PKB, AHNAK localization in epithelial cells depends on cell confluency, where sub-confluent cells displayed a nuclear localization while confluent cells displayed a cytoplasmic or plasma membrane localization [6]. When AHNAK re-localizes to the plasma membrane it complexes with actin and heterotetrameric annexin2/S100A10 [7]. A structural analysis of this complex reveals that both annexin2 and S100A10 are necessary for the complex to form [29]. A possible mechanism for calcium dependent cell-cell contact formation is that PKB phosphorylation of AHNAK will cause its translocation to the plasma membrane where it complexes with actin and annexin2/S100A10 [1][6,7].
Calcium channels
AHNAK can bind the β2 subunit of L-type voltage gated calcium (Cav ) channels in cardiomyocytes [13]. AHNAK seems to have different effects on calcium channels and from calcium across the cited studies. This may be due to different calcium channel isoforms, or different cell types (and thus different responses to calcium) [1]. One hypothesis of AHNAK function with the β2 subunit is that following β-adrenergic stimulation and phosphorylation of AHNAK by PKA, AHNAK will release the β2 subunit of the Cav channel and allow normal calcium influx [31]. AHNAK was also implicated in calcium influx in CD4+ T cells and cytotoxic CD8+ effector T-cells [32,33]. Here, AHNAK null mice showed decreased calcium influx, leading experts to hypothesize that the underlying mechanism involved AHNAK assisting the β2-subunit in membrane localization [34].
Membrane repair
AHNAK is involved in the process of membrane repair through its presence in enlargeosomes, vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane for differentiation and membrane repair [35]. AHNAK typically marks these enlargeosomes just below the plasma membrane. When stimulated with ionomycin AHNAK will label the plasma membrane, as would be expected from a membrane fusion event [35]. AHNAK co-localizes and interacts with a membrane repair protein dysferlin, which also interacts with the annexin2/S100A10 complex [15,36]. AHNAK’s interaction with S100A10 is small enough to allow it to still interact with dysferlin [23,29]. This complex may be regulated by calpain 3, a protease that has been implicated in limb girdle muscular dystrophy A2 along with dysferlin and was experimentally shown to cleave AHNAK [14].
Repair of double strand breaks
In 2004, AHNAK was published interacting specifically with the DNA ligase IB-XRCC4 complex, which is involved in non-homologous end joining [16]. This interaction is not observed with AHNAK and other DNA ligases. AHNAK was shown having a weak DNA-binding affinity by itself, but formed a more stable complex when complexed with DNA and DNA ligase.
AHNAK in Disease
Despite initial mouse models that showed no phenotypic defects in AHNAK-null mice, AHNAK has been related to several different diseases [10,37]. These include but are not limited to: cancer, obesity, and aging [1][38-40].
Cancer
AHNAK’s roles in cancer and tumor metastasis have recently become a large part of the research being done with AHNAK. Due to AHNAK’s implications in many different biological processes, AHNAK seems to promote cancer in some contexts [30,41], and serve as a tumor suppressor in others [3,4,21]. Due to its functionality in cytoskeletal stabilization and interaction with actin filaments, AHNAK was found to be essential in actin-rich pseudopod protrusion across several different metastatic human tumor cell lines [30]. AHNAK knockdown caused these cells to retract their pseudopods and reverse the epithelial to mesenchymal transition that is necessary for cancer metastasis [30]. Similarly, significantly higher levels of AHNAK expression were detected in mesotheliomal cell lines, and migration and invasion were both decreased following AHNAK knockdown [41].
AHNAK can also act as a tumor suppressor because of its role in the TFGβ/Smad pathway [21]. Overexpression of AHNAK in mouse fibroblast cell resulted in increased cell-cycle arrest. Analysis of AHNAK mRNA levels in glioma demonstrated that AHNAK was down-regulated in some cell lines, and was a statistically significant prognostic factor for poor survival of glioma patients [4]. Similar results were shown in a study of AHNAK in triple-negative breast cancer, also associating AHNAK with the AMK/MAPK signaling pathway and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway [3]. These differing effects of AHNAK in cancer may involve its regulation via TGFβ, which has both tumor suppressor and tumor promotor roles [1][42].
Obesity
In a 2010 study, AHNAK knock out mice were found to have a resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity [43]. The authors indicated that the mechanism of resistance likely was related to changes in amino acid levels related to fat metabolism, but did not elucidate a direct mechanism for the effect that they saw. Similarly, impaired adipogenesis has been observed in AHNAK null mice [44]. Adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis relies on the expression of Pparγ2, which in turn relies on Smad signaling. By potentiating Pparγ2 signaling, AHNAK serves as a regulator of metabolic homeostasis and might be useful in future metabolic disorder studies related to obesity [44].
Aging
AHNAK has also been implicated in the aging process. In an analysis of gene expression analysis of human skeletal muscle biopsies, AHNAK displayed increased expression with increased age [38,39]. Similarly, in an analysis of gene expression profiles of multiple male age groups, high AHNAK expression levels were correlated with low maximal oxygen uptake and poor muscle fitness [40].
Evolutionarily Related Proteins
AHNAK is ubiquitously expressed in most tissues throughout the body, and the AHNAK family of proteins is specific to vertebrates [9,12,45]. There are 3 AHNAK-like genes, AHNAK1, AHNAK2, and Periaxin. AHNAK2 is a 600-kDa protein that is hypothesized to have a similar localization and function to AHNAK1 [10]. Periaxin is a 155-kDa protein that is important in the myelination of the peripheral nervous system [46].
All 3 of these proteins have similar genetic structure (several small exons that are upstream of a single large exon), tripartite repeat protein structure, and conserved N-terminal [12]. Both AHNAK and Periaxin have large and small isoforms [47]. Phylogenetic analysis of the 3 AHNAK family members and their isoforms indicates that the AHNAK protein family is derived from a common ancestor and that and are more similar than AHNAK [12].
AHNAK has previously been reported dimerizing, and the PDZ domains of AHNAK2 and Periaxin have been crystallized as homodimers (sources of AHNAK dimer and PDZ dimerization). This dimerization may be an important piece of the scaffolding functions of the proteins in the AHNAK family [48].
Links to Available AHNAK Structures
AHNAK Structures
- 4ftg - An in complex with the / heterotetramer [49].
- 4drw - The ternary complex between S100A10, an Annexin A2 N-terminal peptide and an [29].
- 4hrg - p11-Annexin A2(N-terminal) Fusion protein complexed with [50].
AHNAK Homolog Structures
- 4cn0 - An intertwined homodimer of the [48].
- 4cmz - An intertwined homodimer of the [48].




