We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Jennifer Taylor/Sandbox 3
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
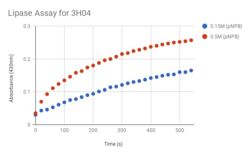
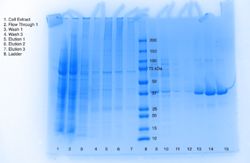
| - | This project seeks to determine the function of a protein with an identified structure. The query protein, in this case, can be identified by the Protein Data Bank Identification (PDB ID) code 3H04. 3H04 is a alpha/beta hydrolase found in Escherichia Coli, a bacterium that resides in the lower intestines of warm-blooded mammals. The more specific purpose of this study is to characterize the function of 3H04. Plasmid purification is just one method for identifying an unidentified protein. Protein purification in bacterial cells requires the plasmids, a small circular double-stranded DNA molecule, to be purified and identified. The purification of the plasmid is meant to isolate and purify the plasmid DNA. The protein in the plasmid is identified through bacterial cells, and grows against ampicillin so the bacterial cells are growing against the antibiotic; the cells that grow have AmpR (Ampicillin Resistance gene). And in efforts to characterize our protein, | + | This project seeks to determine the function of a protein with an identified structure. The query protein, in this case, can be identified by the Protein Data Bank Identification (PDB ID) code <scene name='78/787193/3h04_n_to_c_rainbow/1'>3H04</scene>. 3H04 is a alpha/beta hydrolase found in Escherichia Coli, a bacterium that resides in the lower intestines of warm-blooded mammals. The more specific purpose of this study is to characterize the function of 3H04. Plasmid purification is just one method for identifying an unidentified protein. Protein purification in bacterial cells requires the plasmids, a small circular double-stranded DNA molecule, to be purified and identified. The purification of the plasmid is meant to isolate and purify the plasmid DNA. The protein in the plasmid is identified through bacterial cells, and grows against ampicillin so the bacterial cells are growing against the antibiotic; the cells that grow have AmpR (Ampicillin Resistance gene). And in efforts to characterize our protein, 3H04, we are comparing it to other proteins with significant parts in common to hopefully help characterize the function of 3H04. The comparison of the different aspects of our protein to different aspects of other proteins also helped us determine our assay. |
==Hypothesis== | ==Hypothesis== | ||
Revision as of 14:35, 21 May 2018
3H04 Test Page
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644