This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Jennifer Taylor/Sandbox 4
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== ''In silico'' Analysis == | == ''In silico'' Analysis == | ||
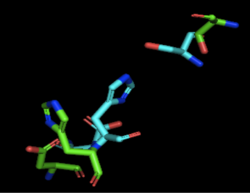
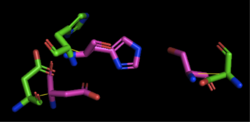
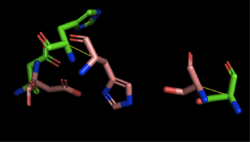
| - | [[Image:4Q7Q_3LIP_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 1: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 3LIP's catalytic triad (shown in blue) | + | [[Image:4Q7Q_3LIP_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 1: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 3LIP's catalytic triad (shown in blue). The RMS is 2.257.]][[Image:4Q7Q_1TAH_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 2: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 1TAH's catalytic triad (shown in pink). The RMS is 2.205.]][[Image:4Q7Q_1BWR_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 3: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 1BWR's catalytic triad (shown in pink). The RMS is 2.049.]] |
We initially analyzed 4Q7Q through the protein structure databases BLAST, Pfam, and Dali. Our top hit was 4M8K, a GDSL-like lipase. Through BLAST, we found that 4M8K and 4Q7Q had a 36% sequence identity, with an E value of 0.002, indicating that it is a significant match. Since we can use the principle of homology to predict the function of an unknown protein, we first hypothesized that 4Q7Q was too a lipase. | We initially analyzed 4Q7Q through the protein structure databases BLAST, Pfam, and Dali. Our top hit was 4M8K, a GDSL-like lipase. Through BLAST, we found that 4M8K and 4Q7Q had a 36% sequence identity, with an E value of 0.002, indicating that it is a significant match. Since we can use the principle of homology to predict the function of an unknown protein, we first hypothesized that 4Q7Q was too a lipase. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
We also performed further analysis in PyMOL and ProMOL which involved the homology of active sites. Top hits included 3LIP, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia cepacia'', 1TAH, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia glumae'', and 1BWR, a hydrolase found in ''Bos taurus''. We aligned putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q with each of the catalytic triads of these known proteins. | We also performed further analysis in PyMOL and ProMOL which involved the homology of active sites. Top hits included 3LIP, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia cepacia'', 1TAH, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia glumae'', and 1BWR, a hydrolase found in ''Bos taurus''. We aligned putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q with each of the catalytic triads of these known proteins. | ||
| - | 3LIP is a two chained protein. When aligning the catalytic triad of 3LIP | + | 3LIP is a two chained protein. When aligning the catalytic triad of 3LIP (Asp264, Ser87, His286) to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.257. |
| - | 1TAH has four chains. When aligning the catalytic triad of 1TAH to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.205. | + | 1TAH has four chains. When aligning the catalytic triad of 1TAH (Asp263, Ser87, His285) to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.205. |
| - | 1BWR has one chain. When aligning the catalytic triad of 1BWR to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.049. | + | 1BWR has one chain. When aligning the catalytic triad of 1BWR (Asp192, Ser47, His195) to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.049. |
Compiling all of the data together, we can see that 1BWR is most structurally similar to 4Q7Q due to the low RMS values calculated when aligning both protein structures and catalytic triads. Therefore, we hypothesized that 4Q7Q is most likely a hydrolase; through experiments, we can investigate further if 4Q7Q is specifically a lipase. | Compiling all of the data together, we can see that 1BWR is most structurally similar to 4Q7Q due to the low RMS values calculated when aligning both protein structures and catalytic triads. Therefore, we hypothesized that 4Q7Q is most likely a hydrolase; through experiments, we can investigate further if 4Q7Q is specifically a lipase. | ||
Revision as of 20:56, 22 May 2018
4Q7Q
| |||||||||||