This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Jennifer Taylor/Sandbox 4
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
4Q7Q is composed of two chains; one chain can be seen <scene name='78/787192/4q7q_chain_a/9'>here</scene>. The colors indicate the translation direction of the peptide sequence from the N to C terminus; red represents the N-terminus while dark blue represents the C-terminus. Based on this structural model, we can see that 4Q7Q is an alpha-beta superfold; there are beta sheets (represented by the straighter strands) sandwiched between the alpha helices (represented by the coiled strands). | 4Q7Q is composed of two chains; one chain can be seen <scene name='78/787192/4q7q_chain_a/9'>here</scene>. The colors indicate the translation direction of the peptide sequence from the N to C terminus; red represents the N-terminus while dark blue represents the C-terminus. Based on this structural model, we can see that 4Q7Q is an alpha-beta superfold; there are beta sheets (represented by the straighter strands) sandwiched between the alpha helices (represented by the coiled strands). | ||
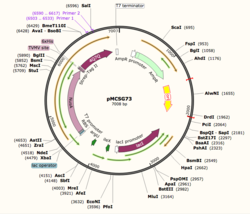
| - | Using SnapGene, we analyzed the plasmid pMCSG73, which is the expression vector used to produce 4Q7Q. We found that | + | Using SnapGene, we analyzed the plasmid pMCSG73, which is the expression vector used to produce 4Q7Q. We found that the plasmid's open reading frame (ORF), the sequence of DNA that will be eventually translated, is 2237 base pairs in length. The size of 4Q7Q is 87.1 kDa. |
| - | Overall, as seen in Figure 1, | + | Overall, as seen in Figure 1, the ORF is composed of NusA (a transcription elongation factor, two tags- 6XHis and Strep-Tag II, and a TVMV and TEV site. The plasmid map indicates the presence of a lac operon composed of three genes (lacZ, lacY, and lacA), a promoter (region that initiates transcription), terminator (region that marks the end of transcription), regulator (which codes for a repressor), and operator (repressor binds to it to prevent gene expression). |
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
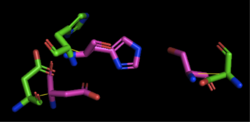
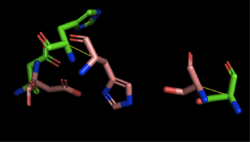
[[Image:4Q7Q_3LIP_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 2: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 3LIP's catalytic triad (shown in blue). The RMS is 2.257.]][[Image:4Q7Q_1TAH_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 3: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 1TAH's catalytic triad (shown in pink). The RMS is 2.205.]][[Image:4Q7Q_1BWR_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 4: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 1BWR's catalytic triad (shown in pink). The RMS is 2.049.]] | [[Image:4Q7Q_3LIP_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 2: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 3LIP's catalytic triad (shown in blue). The RMS is 2.257.]][[Image:4Q7Q_1TAH_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 3: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 1TAH's catalytic triad (shown in pink). The RMS is 2.205.]][[Image:4Q7Q_1BWR_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 4: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 1BWR's catalytic triad (shown in pink). The RMS is 2.049.]] | ||
| - | We initially analyzed 4Q7Q through the protein structure databases BLAST, Pfam, and Dali. | + | We initially analyzed 4Q7Q through the protein structure databases BLAST, Pfam, and Dali. The top hit was 4M8K, a GDSL-like lipase, a type of a lipase that has a flexible active site and therefore broad substrate specificity. Through BLAST, we found that 4M8K and 4Q7Q had a 36% sequence identity, with an E value of 0.002, indicating that it is a significant match. Since we can use the principle of homology to predict the function of an unknown protein, we first hypothesized that 4Q7Q was too a lipase. |
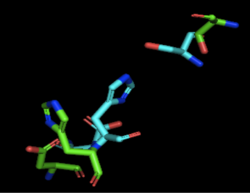
| - | Through analyzing the sequence of 4Q7Q in SnapGene and then analyzing the 3D structure in PyMOL, we hypothesized that a possible catalytic triad of 4Q7Q is Ser164, Asp193, and His196. We believe that this group of amino acids | + | Through analyzing the sequence of 4Q7Q in SnapGene and then analyzing the 3D structure in PyMOL, we hypothesized that a possible catalytic triad of 4Q7Q is Ser164, Asp193, and His196. We believe that this group of amino acids are involved in the active site of 4Q7Q and therefore affects how the protein works. As seen in this <scene name='78/787192/4q7q_active_site/8'>image</scene>, all three amino acids are close in proximity to one another and are brought together in a single orientation. |
| - | We also performed further analysis in PyMOL and ProMOL which involved the homology of active sites. Top hits included 3LIP, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia cepacia'', 1TAH, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia glumae'', and 1BWR, a hydrolase found in ''Bos taurus''. We aligned putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q with each of the catalytic triads of these known proteins. | + | We also performed further analysis in PyMOL and ProMOL which involved the homology of active sites. Top hits included 3LIP, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia cepacia'' (a human pathogen that can cause pneumonia), 1TAH, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia glumae'' (a soil bacterium), and 1BWR, a hydrolase found in ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). We aligned putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q with each of the catalytic triads of these known proteins. |
3LIP has two chains. As seen in Figure 2, when aligning the catalytic triad of 3LIP (Asp264, Ser87, His286) to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.257. | 3LIP has two chains. As seen in Figure 2, when aligning the catalytic triad of 3LIP (Asp264, Ser87, His286) to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.257. | ||
Revision as of 02:59, 23 May 2018
4Q7Q
| |||||||||||