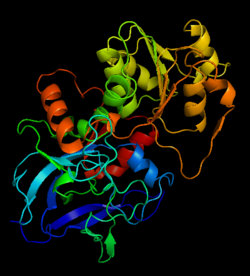
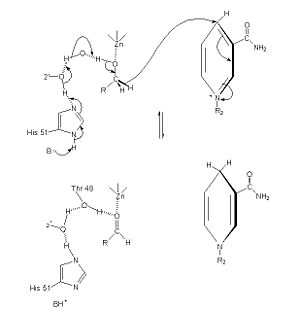
Alcohol dehydrogenase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of alcohol dehydrogenase== | ||
| + | [[Alcohol dehydrogenase 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 92: | Line 96: | ||
**[[2xaa]] – RrADH I + NAD + alcohol<br /> | **[[2xaa]] – RrADH I + NAD + alcohol<br /> | ||
**[[6ffx]] – RrADH I + Zn + NAD<br /> | **[[6ffx]] – RrADH I + Zn + NAD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[6ffz]], [[5o8h]], [[5o8q]], [[5o9d]], [[5o9f]] – RrADH I (mutant) + Zn + NAD<br /> | + | **[[6ffz]], [[5o8h]], [[5o8q]], [[5o9d]], [[5o9f]], [[6fg0]], [[5od3]] – RrADH I (mutant) + Zn + NAD<br /> |
**[[3fx4]] – pADH I + NADP + inhibitor – pig<br /> | **[[3fx4]] – pADH I + NADP + inhibitor – pig<br /> | ||
**[[4w6z]] – yADH I + Zn + NAD derivative<br /> | **[[4w6z]] – yADH I + Zn + NAD derivative<br /> | ||
| Line 107: | Line 111: | ||
**[[3owo]] – ZmADH II iron-dependent – ''Zymomonas mobilis'' | **[[3owo]] – ZmADH II iron-dependent – ''Zymomonas mobilis'' | ||
| - | *ADH II | + | *ADH II complex |
**[[3ox4]] - ZmADH II iron-dependent + NAD<br /> | **[[3ox4]] - ZmADH II iron-dependent + NAD<br /> | ||
| Line 113: | Line 117: | ||
**[[1e3e]] – mADH II + NADH – mouse<br /> | **[[1e3e]] – mADH II + NADH – mouse<br /> | ||
**[[1e3l]] - mADH II (mutant) + NADH<br /> | **[[1e3l]] - mADH II (mutant) + NADH<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1e3i]] - mADH II + NADH + inhibitor | + | **[[1e3i]] - mADH II + NADH + inhibitor<br /> |
| + | **[[5yln]] – ADH II + Zn – ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''<br /> | ||
*ADH III | *ADH III | ||
| Line 126: | Line 131: | ||
**[[4dla]] – tADH III<br /> | **[[4dla]] – tADH III<br /> | ||
**[[5mln]] – ADH III + NADPH – ''Candida magnoliae''<br /> | **[[5mln]] – ADH III + NADPH – ''Candida magnoliae''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5yat]] – ADH III + Zn – ''Komagsaataella phaffii''<br /> | ||
*ADH IV | *ADH IV | ||
| Line 154: | Line 160: | ||
**[[5vkr]] - hoADH IV e chain + Zn + ADPR<br /> | **[[5vkr]] - hoADH IV e chain + Zn + ADPR<br /> | ||
**[[5vl0]] - hoADH IV e chain + Zn + formamide derivative <br /> | **[[5vl0]] - hoADH IV e chain + Zn + formamide derivative <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6cy3]], [[6cxx]] - hoADH IV e chain (mutant) + Zn + dephosphoCoA<br /> | ||
**[[5cdu]] - hoADH IV e chain (mutant) + Zn + NAD + pyrazole<br /> | **[[5cdu]] - hoADH IV e chain (mutant) + Zn + NAD + pyrazole<br /> | ||
| Line 207: | Line 214: | ||
**[[4l0q]] - AtADH III (mutant) + NAD + Zn <br /> | **[[4l0q]] - AtADH III (mutant) + NAD + Zn <br /> | ||
**[[4cpd]] – TtADH + NAD + Zn<br /> | **[[4cpd]] – TtADH + NAD + Zn<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6n7l]] – ADH + NAD + Zn – ''Elizabethkingia anophelis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6c76]] – TthADH + NADP + Fe – ''Thermococcus thioreducens''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6c7l]] – TthADH + monophosphoadenosine diphosphate <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6c75]] – TthADH + NADP + Fe + monophosphoadenosine diphosphate <br /> | ||
*NADP-dependent ADH | *NADP-dependent ADH | ||
| Line 237: | Line 248: | ||
**[[5yvm]] – bspADH + Mn + NADP derivative – brine sea pool<br /> | **[[5yvm]] – bspADH + Mn + NADP derivative – brine sea pool<br /> | ||
**[[5yvr]], [[5yvs]] – bspADH (mutant) + Mn + NADP <br /> | **[[5yvr]], [[5yvs]] – bspADH (mutant) + Mn + NADP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5z2x]] – ADH + NADP – ''Kluyveromyces polyspora''<br /> | ||
*R-specific ADH | *R-specific ADH | ||
| - | **[[1nxq]] - LbRADH – ''Lactobacillus brevis''<br /> | + | **[[1nxq]], [[6h07]], [[6h1m]] - LbRADH – ''Lactobacillus brevis''<br /> |
| - | **[[1zk2]], [[1zk3]] - LbRADH (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[1zk2]], [[1zk3]], [[6hlf]] - LbRADH (mutant)<br /> |
**[[1zjy]], [[1zjz]], [[1zk0]], [[1zk1]] – LbRADH (mutant) + NADH + alcohol<br /> | **[[1zjy]], [[1zjz]], [[1zk0]], [[1zk1]] – LbRADH (mutant) + NADH + alcohol<br /> | ||
**[[1zk4]] - LbRADH (mutant) + NADH + acetophenone<br /> | **[[1zk4]] - LbRADH (mutant) + NADH + acetophenone<br /> | ||
Revision as of 08:29, 4 March 2019
| |||||||||||
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
3D Structures of Alcohol dehydrogenase
Updated on 04-March-2019
References
- ↑ Voet, et. al. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: 3rd Edition. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008.
- ↑ Voet, et. al. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: 3rd Edition. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008.
- ↑ Protein: Alcohol Dehydrogenase. The College of Saint Benedict and Saint John's University. 1 March 2010 < http://web.archive.org/web/20080307193453/http://www.users.csbsju.edu/~hjakubow/classes/rasmolchime/99ch331proj/alcoholdehydro/index.htm>
- ↑ Protein: Alcohol Dehydrogenase. The College of Saint Benedict and Saint John's University. 1 March 2010 < http://web.archive.org/web/20080307193453/http://www.users.csbsju.edu/~hjakubow/classes/rasmolchime/99ch331proj/alcoholdehydro/index.htm>
- ↑ Voet, et. al. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: 3rd Edition. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008.
- ↑ Dickinson FM, Monger GP. A study of the kinetics and mechanism of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase with a variety of substrates. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):261-70. PMID:4352908
- ↑ Dickinson FM, Monger GP. A study of the kinetics and mechanism of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase with a variety of substrates. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):261-70. PMID:4352908
- ↑ Bille V, Remacle J. Simple-kinetic descriptions of alcohol dehydrogenase after immobilization on tresyl-chloride-activated agarose. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):343-8. PMID:3769934
- ↑ Dickinson FM, Monger GP. A study of the kinetics and mechanism of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase with a variety of substrates. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):261-70. PMID:4352908
- ↑ Blomstrand R, Ostling-Wintzell H, Lof A, McMartin K, Tolf BR, Hedstrom KG. Pyrazoles as inhibitors of alcohol oxidation and as important tools in alcohol research: an approach to therapy against methanol poisoning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3499-503. PMID:115004
- ↑ Alcohol Dehydrogenase. Worthington Biochemical Corporation . 31 March 2010 < http://http://www.worthington-biochem.com/ADH/default.html>
- ↑ Alcohol Dehydrogenase.Worthington Biochemical Corporation . 31 March 2010 < http://http://www.worthington-biochem.com/ADH/default.html>
- ↑ Goihberg E, Dym O, Tel-Or S, Levin I, Peretz M, Burstein Y. A single proline substitution is critical for the thermostabilization of Clostridium beijerinckii alcohol dehydrogenase. Proteins. 2007 Jan 1;66(1):196-204. PMID:17063493 doi:10.1002/prot.21170
- ↑ Goihberg E, Dym O, Tel-Or S, Shimon L, Frolow F, Peretz M, Burstein Y. Thermal stabilization of the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica alcohol dehydrogenase by a single proline substitution. Proteins. 2008 Feb 7;. PMID:18260103 doi:10.1002/prot.21946
- ↑ Goihberg E, Peretz M, Tel-Or S, Dym O, Shimon L, Frolow F, Burstein Y. Biochemical and Structural Properties of Chimeras Constructed by Exchange of Cofactor-Binding Domains in Alcohol Dehydrogenases from Thermophilic and Mesophilic Microorganisms. Biochemistry. 2010 Feb 9. PMID:20102159 doi:10.1021/bi901730x
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, David Birrer