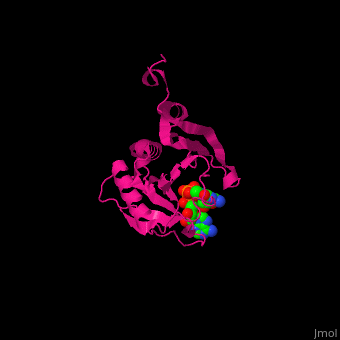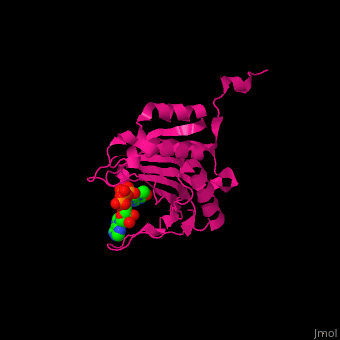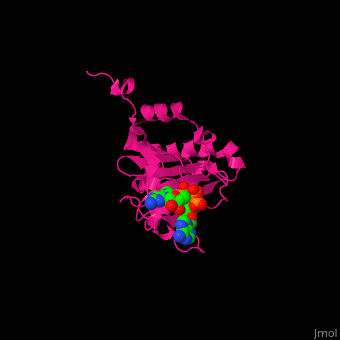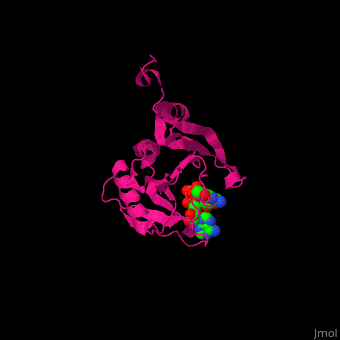This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Eukaryotic initiation factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
EIF domains include the N terminal domain (NTD), C terminal domain (CTD), RNA recognition domain, middle domain, PAZ domain of EIF2C and a protein-protein interaction domain (PCI) of EIF3. | EIF domains include the N terminal domain (NTD), C terminal domain (CTD), RNA recognition domain, middle domain, PAZ domain of EIF2C and a protein-protein interaction domain (PCI) of EIF3. | ||
| - | *<scene name='50/507723/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='50/507723/Cv/4'>P1-7-METHYLGUANOSINE-P3-ADENOSINE-5',5'-TRIPHOSPHATE (7-methyl GPPPA) binding site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 11:04, 14 March 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of eukaryotic initiation factor
Updated on 14-March-2019
References
- ↑ Jivotovskaya AV, Valasek L, Hinnebusch AG, Nielsen KH. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 (eIF3) and eIF2 can promote mRNA binding to 40S subunits independently of eIF4G in yeast. Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;26(4):1355-72. PMID:16449648 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/MCB.26.4.1355-1372.2006
- ↑ Hershey JW. The role of eIF3 and its individual subunits in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1849(7):792-800. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Nov 1. PMID:25450521 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.10.005