User:Kayque Alves Telles Silva/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='1kq1' size='400' side='right' scene='78/789833/Hfq/2' caption='Host Factor for the Replication of the Qβ Phage RNA (Hfq)'> | <StructureSection load='1kq1' size='400' side='right' scene='78/789833/Hfq/2' caption='Host Factor for the Replication of the Qβ Phage RNA (Hfq)'> | ||
Hfq is a bacterial cytoplasmatic protein, first named for being a Host Factor for the Replication of the Qβ Phage RNA[1 - Schumacher 2002]. Hfq acts pleiotropically and impacts both the degradation and the translation efficiency of mRNAs [2 - Azam 2000], through the modification of sRNAs[3 - Wassarman 2001]. Besides, Hfq has a strongly conserved structure[4 - Kajitani 1994] and belongs to the LSm protein family, present in each of the three domains of life. Despite Hfq’s underscored importance, there is a wide spectrum of cellular functions, as growth rate and cell length, that are directly dependent of its chaperone function and have been discovered in the last century[5,6,7,8 - Artigos baixados], but many others remain unknown. | Hfq is a bacterial cytoplasmatic protein, first named for being a Host Factor for the Replication of the Qβ Phage RNA[1 - Schumacher 2002]. Hfq acts pleiotropically and impacts both the degradation and the translation efficiency of mRNAs [2 - Azam 2000], through the modification of sRNAs[3 - Wassarman 2001]. Besides, Hfq has a strongly conserved structure[4 - Kajitani 1994] and belongs to the LSm protein family, present in each of the three domains of life. Despite Hfq’s underscored importance, there is a wide spectrum of cellular functions, as growth rate and cell length, that are directly dependent of its chaperone function and have been discovered in the last century[5,6,7,8 - Artigos baixados], but many others remain unknown. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structure == | ||
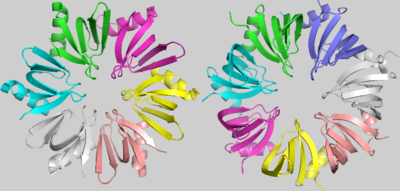
| + | <scene name='78/789833/Hfq/2'>Hfq</scene> is a doughnut shaped homohexamer of roughly 8,9kDa, ~65Å diameter and ~23Å width, as described in S.aureus[1]. The action mechanisms of Hfq as a chaperone are based in its interaction with sRNAs. The best literature described functions among them are: the sequestering of ribosome binding sites (RBS); the inhibition of RBS-blocking mRNA regions, allowing translation; the stabilization of sRNAs which would otherwise be degraded; and the degradation of mRNAs. Hfq might also contribute to the degradation of certain mRNAs directly, but rarely. [9] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:Hfq_and_SmAP1.png | thumb | right | 400px | Hfq (Left) and SmAP1 (Right)]] | [[Image:Hfq_and_SmAP1.png | thumb | right | 400px | Hfq (Left) and SmAP1 (Right)]] | ||
| - | <scene name='78/789833/Hfq/2'>Hfq</scene> | ||
<scene name='78/789833/Smap1/1'>SmAP1</scene> | <scene name='78/789833/Smap1/1'>SmAP1</scene> | ||
Revision as of 03:47, 18 June 2018
Hfq
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644