This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Kayque Alves Telles Silva/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
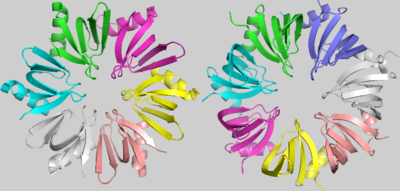
<scene name='78/789833/Hfq/2'>Hfq</scene> is a doughnut shaped homohexamer of roughly 8,9kDa, ~65Å diameter and ~23Å width, as described in S.aureus[1]. The action mechanisms of Hfq as a chaperone are based in its interaction with sRNAs. The best literature described functions among them are: the sequestering of ribosome binding sites (RBS); the inhibition of RBS-blocking mRNA regions, allowing translation; the stabilization of sRNAs which would otherwise be degraded; and the degradation of mRNAs. Hfq might also contribute to the degradation of certain mRNAs directly, but rarely. [9] | <scene name='78/789833/Hfq/2'>Hfq</scene> is a doughnut shaped homohexamer of roughly 8,9kDa, ~65Å diameter and ~23Å width, as described in S.aureus[1]. The action mechanisms of Hfq as a chaperone are based in its interaction with sRNAs. The best literature described functions among them are: the sequestering of ribosome binding sites (RBS); the inhibition of RBS-blocking mRNA regions, allowing translation; the stabilization of sRNAs which would otherwise be degraded; and the degradation of mRNAs. Hfq might also contribute to the degradation of certain mRNAs directly, but rarely. [9] | ||
| - | The '' | + | The <scene name='78/789833/Subunit/1'>basic subunit</scene> which forms the homo-hexamer of Hfq has 77 residues[1] comprising one N-terminal α helix (α1), five beta sheets (β1-β5) and one variable region. An unstructured carboxy-terminal region, which may have >100 residues in certain species is also present[10 -Updegrove]. The fold of the beta sheets is characterized by two important <scene name='78/789833/Motifs/5'>motifs</scene>, Sm1 and Sm2, used to clusterize the LSm protein family components considering their highlighted conservation throughout Life’s domains. |
The most conserved amino acids of Sm and LSm proteins, including Hfq, are the aspartic acid 40 and the glycine 34, determining hydrophobic residues present in the Sm1 motif which maintain the highly distorted Sm1 fold. Tyr56 and Tyr63, highly conserved in the Sm2 motif, are fundamental for the interaction between subunits. The glutamine 8 and tyrosine 42 are highly conserved in Hfq proteins due to their role in uracil binding[1]. The highly variable C-terminus of Hfq proteins has no defined structure and its function is not clearly understood yet[10]. | The most conserved amino acids of Sm and LSm proteins, including Hfq, are the aspartic acid 40 and the glycine 34, determining hydrophobic residues present in the Sm1 motif which maintain the highly distorted Sm1 fold. Tyr56 and Tyr63, highly conserved in the Sm2 motif, are fundamental for the interaction between subunits. The glutamine 8 and tyrosine 42 are highly conserved in Hfq proteins due to their role in uracil binding[1]. The highly variable C-terminus of Hfq proteins has no defined structure and its function is not clearly understood yet[10]. | ||
Revision as of 04:18, 18 June 2018
Hfq
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644