We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Frataxin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
The channel of the trimer is formed at its 3-fold axis, in a central position. It is the strure responsible for stabilizing the atom of iron for delivery, but also acts to further stabilise the trimeric form. | The channel of the trimer is formed at its 3-fold axis, in a central position. It is the strure responsible for stabilizing the atom of iron for delivery, but also acts to further stabilise the trimeric form. | ||
| - | Stabilising one side of the channel, there are some interactions between the <scene name='78/786054/151-155_144-149/1'>loops around the central channel</scene>, which form a helic structure maintened, for instance, through hydrogen bonds between the pairs <scene name='78/786054/152-147_hydrogen_bond/1'>Leu 152-Gly 147</scene> and <scene name='78/786054/146-154_hydrogen_bond/1'>Asn 146-Gln 154</scene>. | + | Stabilising one side of the channel, there are some interactions between the <scene name='78/786054/151-155_144-149/1'>loops around the central channel</scene>, which form a helic structure maintened, for instance, through hydrogen bonds between the pairs <scene name='78/786054/152-147_hydrogen_bond/1'>Leu 152-Gly 147</scene> and <scene name='78/786054/146-154_hydrogen_bond/1'>Asn 146-Gln 154</scene>. this last one also estabilizes the ASN146 interaction with the iron atom, as described in the figure below |
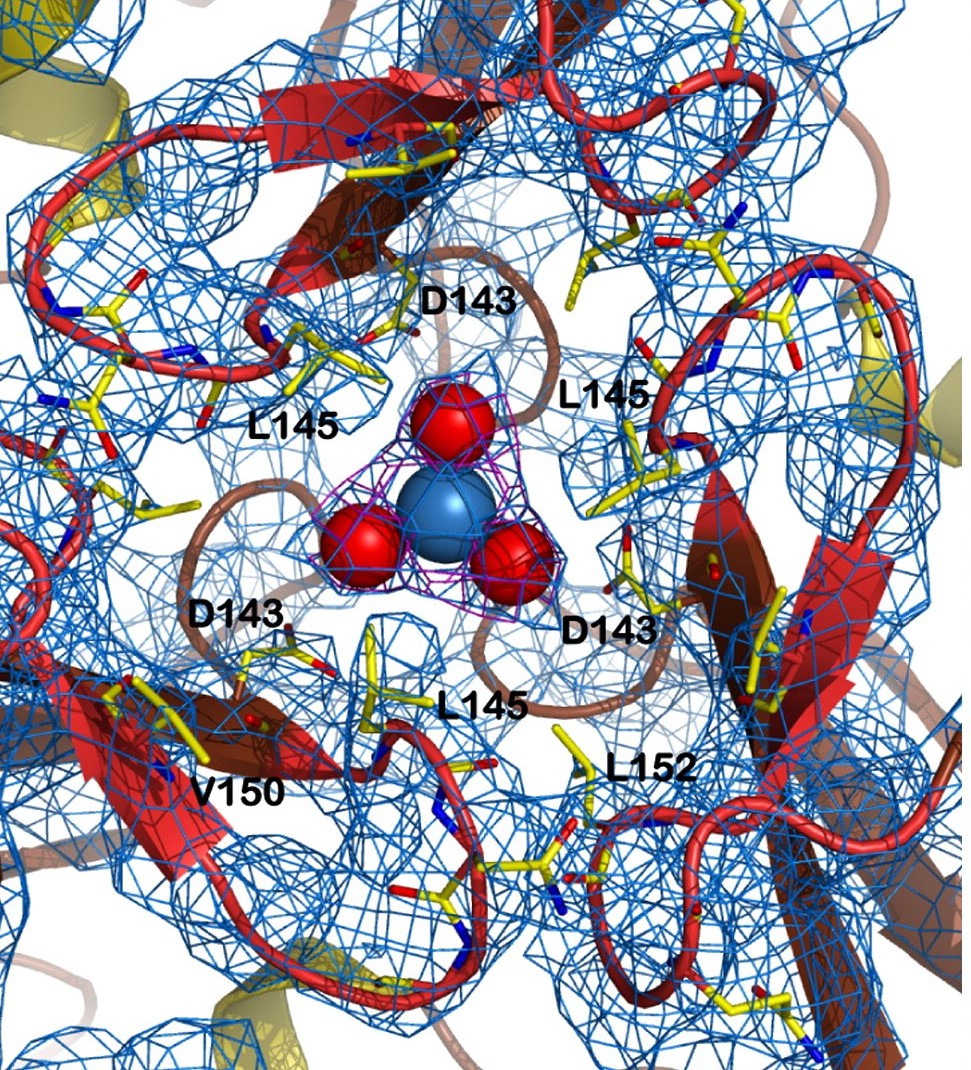
In the structure of the channel, the side chains of the hydrophobic aminoacids Leu 145, Val 150 and Leu 152 are exposed to the solvent, creating a <scene name='78/786054/Hydrophobic_lid/3'>hydrophobic lid</scene> around the channel. This hydrophobic lid isolates one of the sides of the channel core, as well as providing a hydrophobic contact surface by which other proteins can interact, hiding their hydrophobic residues from the solvent-rich environment. | In the structure of the channel, the side chains of the hydrophobic aminoacids Leu 145, Val 150 and Leu 152 are exposed to the solvent, creating a <scene name='78/786054/Hydrophobic_lid/3'>hydrophobic lid</scene> around the channel. This hydrophobic lid isolates one of the sides of the channel core, as well as providing a hydrophobic contact surface by which other proteins can interact, hiding their hydrophobic residues from the solvent-rich environment. | ||
| - | Other structure in the central channel of high importance is the loop formed by <scene name='78/786054/125-128/3'>125-128</scene>. This loop, estabilized by the hidrogen bonds between <scene name='78/786054/143-129__hydrogen_bond/1'>Asp 143-Gln 129</scene>, <scene name='78/786054/Bound_127-75/1'>127-75</scene> and <scene name='79/790348/129-126/1'>129-126</scene> | + | Other structure in the central channel of high importance is the loop formed by <scene name='78/786054/125-128/3'>125-128</scene>. This loop, estabilized by the hidrogen bonds between <scene name='78/786054/143-129__hydrogen_bond/1'>Asp 143-Gln 129</scene>, <scene name='78/786054/Bound_127-75/1'>127-75</scene> and <scene name='79/790348/129-126/1'>129-126</scene>, is present in 2 different conformations. the one just described is involved in further stabilizing the Fe atom interacting with the inside the channel |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:carregado fe.jpg]] | ||
The hydrophobic lid formed by Leu 145, Val 150 and Leu 152 fully encloses the iron atom within the channel (iron atom not shown). | The hydrophobic lid formed by Leu 145, Val 150 and Leu 152 fully encloses the iron atom within the channel (iron atom not shown). | ||
Revision as of 05:39, 18 June 2018
Frataxin
| |||||||||||
References
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
João Victor Paccini Coutinho, Michal Harel, Rebeca B. Candia