We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Metallothiol transferase FosB
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==INTRODUCTION== | ==INTRODUCTION== | ||
| - | The '''transcription factor''', DeltaFosB, is known to be involved in some of the physiological mechanisms linked to addiction and compulsive behaviors. Levels of DeltaFosB have been shown to increase in multiple regions of the brain in response to repeated drug exposure as well as stress, certain antipsychotic or antidepressant medications, electroconvulsive seizures, and certain lesions. DeltaFosB is a truncated, highly stable splice variant of the FosB transcription factor whose expression is regulated by alternative splicing of the FosB gene. Due to this splicing, DeltaFosB is known to have a half life five times that of FosB, which is thought to be a basis for addiction <ref name ="James">PMID:25083822</ref>. | + | The '''transcription factor''', '''DeltaFosB''', is known to be involved in some of the physiological mechanisms linked to addiction and compulsive behaviors. Levels of DeltaFosB have been shown to increase in multiple regions of the brain in response to repeated drug exposure as well as stress, certain antipsychotic or antidepressant medications, electroconvulsive seizures, and certain lesions. DeltaFosB is a truncated, highly stable splice variant of the FosB transcription factor whose expression is regulated by alternative splicing of the FosB gene. Due to this splicing, DeltaFosB is known to have a half life five times that of FosB, which is thought to be a basis for addiction <ref name ="James">PMID:25083822</ref>. |
==STRUCTURE== | ==STRUCTURE== | ||
Revision as of 09:14, 6 September 2020
| |||||||||||
3D structure of FosB
Updated on 06-September-2020
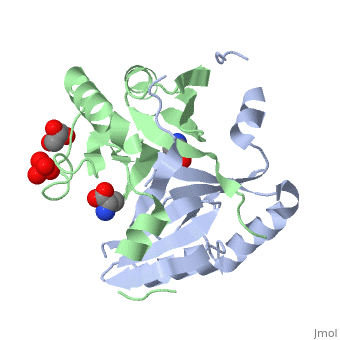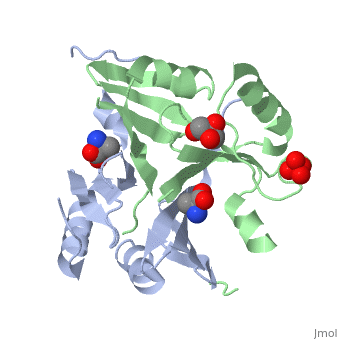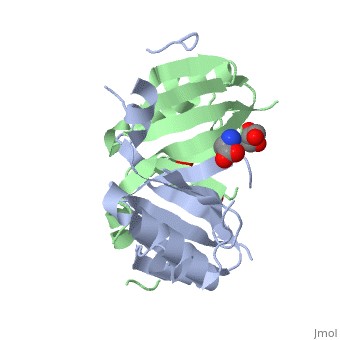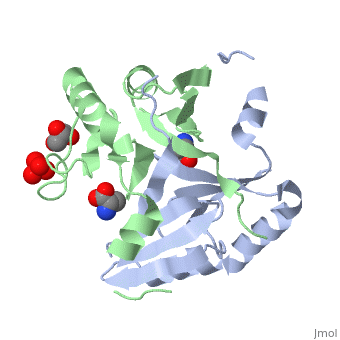
4ir0, 4jd1, 5f6q – FosB2 – Bacillus anthracis
4nay, 4naz, 4nb2 – SaFosB – Staphylococcus aureus
4jh1, 4jh2 – BcFosB – Bacillus cereus
4jh3, 4jh4, 4jh5, 4jh6 – BcFosB + fosfomycin
4jh7, 4jh8, 4jh9 – BcFosB + fosfomycin derivative
4nb0, 4nb1 – SaFosB + cysteine
5vpa, 5vpb, 5vpc, 5vpd – hFosB + Jun-D - human
5vpe, 5vpf – hFosB + Jun-D + DNA
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ruffle JK. Molecular neurobiology of addiction: what's all the (Delta)FosB about? Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2014 Nov;40(6):428-37. doi:, 10.3109/00952990.2014.933840. Epub 2014 Aug 1. PMID:25083822 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00952990.2014.933840
- ↑ Carle, T. L., Ohnishi, Y. N., Ohnishi, Y. H., Alibhai, I. N., Wilkinson, M. B., Kumar, A. and Nestler, E. J. (2007) Proteasome-dependent and -independent mechanisms for FosB destabilization: identification of FosB degron domains and implications for ΔFosB stability. European Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 3009–3019. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05575.x
- ↑ Jorissen, H. J., Ulery, P. G., Henry, L., Gourneni, S., Nestler, E. J., & Rudenko, G. (2007) Dimerization and DNA-binding properties of the transcription factor ΔFosB. Biochemistry, 46(28), 8360-8372.x
- ↑ Nestler, E. J. (2008). Transcriptional mechanisms of addiction: role of ΔFosB.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 363(1507), 3245-3255.x
- ↑ Kelz, M. B., Chen, J., Carlezon, W. A., Whisler, K., Gilden, L., Beckmann, A. M., ... & Nestler, E. J. (1999). Expression of the transcription factor ΔFosB in the brain controls sensitivity to cocaine. Nature, 401(6750), 272-276.x
- ↑ Pitchers, K. K., Vialou, V., Nestler, E. J., Laviolette, S. R., Lehman, M. N., & Coolen, L. M. (2013). Natural and drug rewards act on common neural plasticity mechanisms with ΔFosB as a key mediator. The Journal of Neuroscience,33(8), 3434-3442.x
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Naina Mangalmurti, Jaime Prilusky, Joel L. Sussman