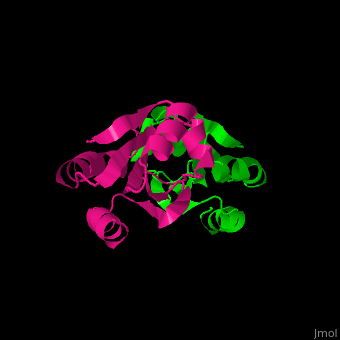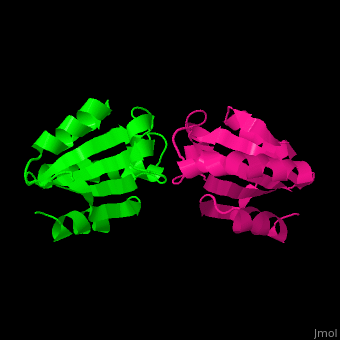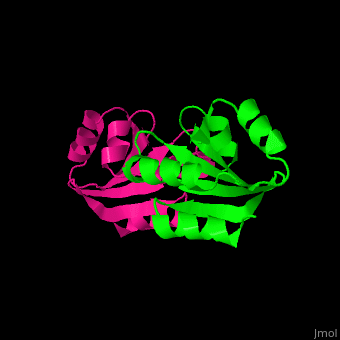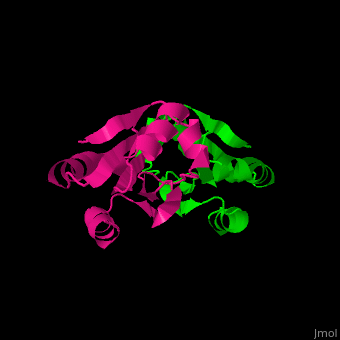We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Thioredoxin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | The <scene name='43/430885/Cv/ | + | The <scene name='43/430885/Cv/4'>active site motif Cys-Gly-Pro-Cys</scene> is involved in the reduction of disulfide bonds in proteins<ref>PMID:8805557</ref> |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 22 September 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Thioredoxin
Updated on 22-September-2019
References
- ↑ Gleason FK, Holmgren A. Thioredoxin and related proteins in procaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;4(4):271-97. PMID:3152490
- ↑ Sumida Y, Nakashima T, Yoh T, Furutani M, Hirohama A, Kakisaka Y, Nakajima Y, Ishikawa H, Mitsuyoshi H, Okanoue T, Kashima K, Nakamura H, Yodoi J. Serum thioredoxin levels as a predictor of steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2003 Jan;38(1):32-8. PMID:12480557
- ↑ Burke-Gaffney A, Callister ME, Nakamura H. Thioredoxin: friend or foe in human disease? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Aug;26(8):398-404. PMID:15990177 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2005.06.005
- ↑ Weichsel A, Gasdaska JR, Powis G, Montfort WR. Crystal structures of reduced, oxidized, and mutated human thioredoxins: evidence for a regulatory homodimer. Structure. 1996 Jun 15;4(6):735-51. PMID:8805557
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Laura Maria Batista Leal, Joel L. Sussman