We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Actin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
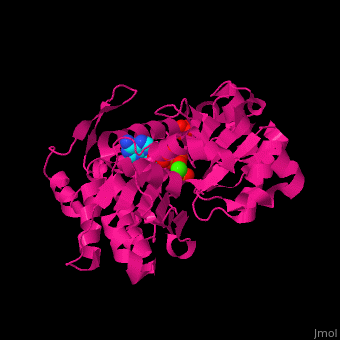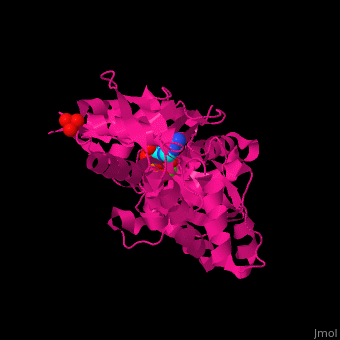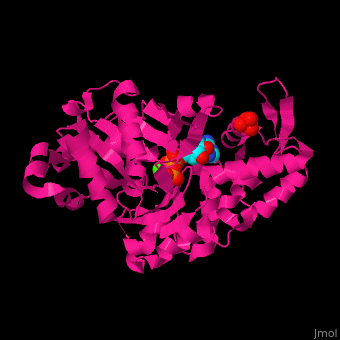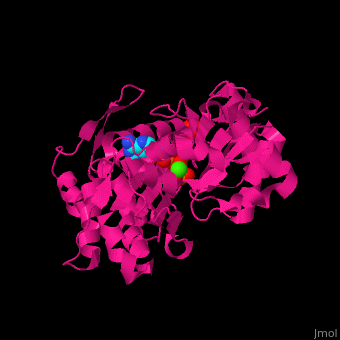
| - | <scene name='43/430015/Cv/10'>Actin binds ATP</scene> in a cleft. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='43/430015/Cv/11'>Click here to see Ca2+ ion coordination site</scene>.<ref>PMID:20540085</ref> It changes its conformation upon hydrolysis of its bound ATP to ADP. Actin filaments are polar. They are formed with all monomers having their clefts pointing in the same direction. | + | <scene name='43/430015/Cv/10'>Actin binds ATP</scene> in a cleft. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='43/430015/Cv/13'>ATP and Ca2+ ion are located in cleft</scene>. <scene name='43/430015/Cv/11'>Click here to see Ca2+ ion coordination site</scene>.<ref>PMID:20540085</ref> It changes its conformation upon hydrolysis of its bound ATP to ADP. Actin filaments are polar. They are formed with all monomers having their clefts pointing in the same direction. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D Structures of Actin == | == 3D Structures of Actin == | ||
Revision as of 10:35, 18 December 2018
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Actin
Updated on 18-December-2018
Reference
- ↑ Otterbein LR, Graceffa P, Dominguez R. The crystal structure of uncomplexed actin in the ADP state. Science. 2001 Jul 27;293(5530):708-11. PMID:11474115 doi:10.1126/science.1059700
- ↑ Wang H, Robinson RC, Burtnick LD. The structure of native G-actin. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010 Jul;67(7):456-65. PMID:20540085 doi:10.1002/cm.20458