We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1480
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
==Structure of the protein LHPP== | ==Structure of the protein LHPP== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='2x4d' size='340' side='right' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='2x4d' size='340' side='right' caption='LHPP structure' scene=''> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
LHPP is a phosphatase with an in vitro activity towards inorganic pyrophosphate, imidodiphosphate, 3‑phosphohistidine and 6‑phospholysine. The enzyme acts more effectively on N-P bonds than O-P bonds. | LHPP is a phosphatase with an in vitro activity towards inorganic pyrophosphate, imidodiphosphate, 3‑phosphohistidine and 6‑phospholysine. The enzyme acts more effectively on N-P bonds than O-P bonds. | ||
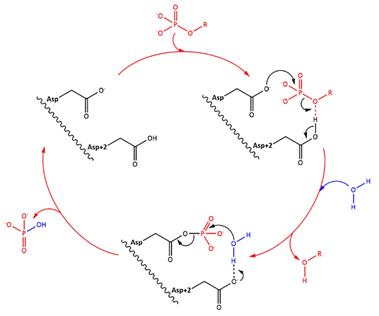
| - | + | [[Image:HAD.PNG]] | |
Fig 1. Simplified catalytic mechanism of HAD phosphatases. Asp acts a nucleophile and Asp+2 as a acid/base. The phosphorylated substrate and the respective leaving groups are shown in red, and the water nucleophile is in blue. (Source: Do metabolic HAD phosphatases moonlight as protein phosphatases?, A. Gohla, 2018). In the human LHPP, the Asp+2 is replaced by a Serine. | Fig 1. Simplified catalytic mechanism of HAD phosphatases. Asp acts a nucleophile and Asp+2 as a acid/base. The phosphorylated substrate and the respective leaving groups are shown in red, and the water nucleophile is in blue. (Source: Do metabolic HAD phosphatases moonlight as protein phosphatases?, A. Gohla, 2018). In the human LHPP, the Asp+2 is replaced by a Serine. | ||
Revision as of 12:37, 7 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Structure of the protein LHPP
| |||||||||||