Sandbox Reserved 1496
From Proteopedia
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Catalyzes the head-to-head condensation of two molecules of farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) into the colorless C(30) carotenoid 4,4'-diapophytoene (dehydrosqualene). | Catalyzes the head-to-head condensation of two molecules of farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) into the colorless C(30) carotenoid 4,4'-diapophytoene (dehydrosqualene). | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:CrtMcatalysa.png]] |
Transferase Activity : Transferring alkyl or aryl groups, other than methyl groups | Transferase Activity : Transferring alkyl or aryl groups, other than methyl groups | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 8 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
|
Contents |
Presentation of dehydrosqualene Synthase
The C30 carotene synthase CrtM enzyme is a bacterial carotenoid synthases and is involved in the first step of the subpathway that synthesizes staphyloxanthin from farnesyl diphosphate.
This subpathway is part of the pathway staphyloxanthin biosynthesis, which is itself part of carotenoid biosynthesis. Carotenoid pathways are branches of the general isoprenoid pathway.
Staphyloxanthin is a carotenoid, which is responsible for the golden color of S. aureus, and also play the role of virulence factor : it has an antioxidant action that helps the microbe evade death by reactive oxygen species produced by the host immune system. Having a better comprehension of the synthesis of this carotenoid will help to find a cure to S. aureus related diseases.
Function
Catalyzes the head-to-head condensation of two molecules of farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) into the colorless C(30) carotenoid 4,4'-diapophytoene (dehydrosqualene).
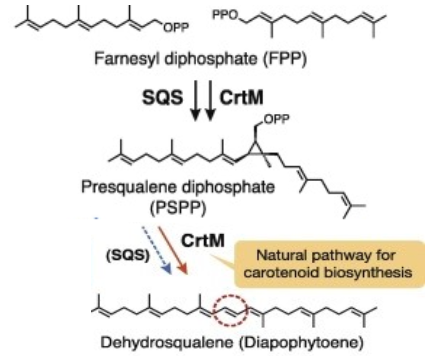
Transferase Activity : Transferring alkyl or aryl groups, other than methyl groups
Metal Ion Binding : requires Mn2+ as cofactor (2 ions per subunit).
Structure
This protein consists of 2 sequence-identical polypeptide chains of 287 amino acids. It has 6 Magnesium ions, 2 Pyrophosphate 2-, 1 L(+)-tartaric acid and 2 (3r)-3-biphenyl-4-yl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-ol as ligands (substrate or inhibitors, prosthetic groups, cofactors, carbohydrate, metal ions, regardless of whether these are covalently or non-covalently bound to the protein or nucleic acid chains).
Biological process
CrtM catalyses the first step of the synthesis of staphyloxanthin (with a 2-step mechanism). The catalysed reaction is : 2 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate <=> 15-cis-4,4'-diapophytoene + 2 diphosphate Pathogenesis
Carotenoid Biosynthetic Process
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
</StructureSection>
