We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1491
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | == | + | ==2xml - KDM4C catalytic domain== |
==Preview== | ==Preview== | ||
'''2xml''' is a 2 chain structure. This domain belongs to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human] '''KDM4C''' protein. | '''2xml''' is a 2 chain structure. This domain belongs to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human] '''KDM4C''' protein. | ||
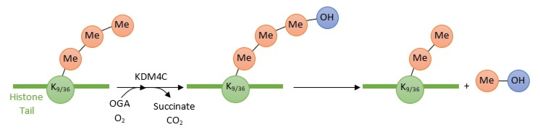
| - | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KDM4C KDM4C] is a '''histone demethylase''' involved in the specific demethylation of trimethylated residues (Lys 9 and Lys 36 of histone 3) | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KDM4C KDM4C] is a '''histone demethylase''' involved in the specific demethylation of trimethylated residues (Lys 9 and Lys 36 of histone 3)<ref></ref> |
| - | These marks are specific tags for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | These marks are specific tags for the activation and repression of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_expression genes expression]. |
KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cancer_cell tumoral cells]. | KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cancer_cell tumoral cells]. | ||
<StructureSection load='2xml' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of 2xml - monomeric domain of KDM4C' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2xml' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of 2xml - monomeric domain of KDM4C' scene=''> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | 2xml is a | + | 2xml is a monomeric domain composed of 348 amino acids. It is made up of two chains A and B. They are asymmetric, i.e. their sequence identities are below 95%. This domain is connected by a beta-hairpin to the rest of the protein. |
| - | This domain of KDM4C can bind to 5 ligands: | + | This domain of KDM4C can bind to 5 ligands: Zn2+, Ni2+, N-Oxalylglycine (or OGA), Cl- (interaction only with chain A) and 1,2-ethanediol (or EDO; only with chain A) : |
| - | + | OGA: two binding sites (chains A and B). | |
| - | + | EDO: three binding sites, only in chain A. They are linked to 2xml by hydrogen bond. | |
| - | + | Zn2+: two binding sites (chains A and B). It makes four coordination bonds : with three cysteines and one histidine. | |
| - | + | Ni2+ : two binding sites (chains A and B). It makes five coordination bonds : two with OGA, two with two histidine and a last one with a glutamic acid. | |
| - | + | Cl- : one binding site, only in chain A. | |
| - | + | 2xml presents, in each of the two chains, parallel β sheets around OGA, forming an hydrophobic (mainly made of aromatic acid) pocket. OGA interacts with 2xml amino acids through hydrogen bonds and coordination bonds with Ni2+. | |
| - | 2xml presents, in each of the two chains, parallel | + | The sequence of the domain has been particularly preserved around OGA (when the protein is folded). Thus, the 3D structure has been very preserved as well, indicating us that the structure. |
| - | The sequence of the domain has been particularly preserved around OGA (when the protein is folded) | + | |
== Epigenetic == | == Epigenetic == | ||
| - | + | Specific enzymes are directly involved in the modification of genes expression without altering the nucleotide sequence. They can modify the chromatin structure by '''adding''' (writers), '''reading''' (readers) or '''removing''' (erasers) marks : acetyl, methyl, phosphoryl groups, ubiquitin... These [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigenetics epigenetic] marks can either make the gene sequence more or less accessible for transcription factors depending on their nature, histones and labelled amino acids. All combinations of the nature and the localization of these epigenetic marks form the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_code histone code]. | |
| - | + | KDM4C is a histone demethylase. This newly discovered class of proteins plays a central role in the histone modifications : it removes the methyl group (which is very stable) from the epigenetically modified amino acid. Its actions has directed consequences on gene expression. By removing one methyl group from a trimethylated Lysine 9 of histone 3 (H3K9me3), KDM4C promotes the formation of euchromatin and therefore '''transcriptional activation'''. However, KDM4C indirectly condenses chromatin by removing one methyl group from a trimethylated Lysine 36 of histone 3 (H3K36me3) leading to the '''repression of target genes expression'''. | |
| - | KDM4C is a histone demethylase which plays a central role in the regulation of histone proteins modifications by removing methyl groups from epigenetic marks. Its actions has directed consequences on gene expression and therefore on heritable phenotype. By removing repressive histone marks (H3K9me3 and H3K36me3) from target genes KDM4C promotes the formation of euchromatin and therefore transcriptional activation. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 15:01, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
2xml - KDM4C catalytic domain
Preview
2xml is a 2 chain structure. This domain belongs to the Human KDM4C protein.
KDM4C is a histone demethylase involved in the specific demethylation of trimethylated residues (Lys 9 and Lys 36 of histone 3)Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
refs with no name must have content
These marks are specific tags for the activation and repression of genes expression.
KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of tumoral cells.
| |||||||||||