The protein we are focusing one is a protein kinase receptor to a family of ligands called angiopoietins. This receptor is a Tyrosine Kinase TIE2. We are going to analyze the kinase domain of this protein
It acts as cell-surface receptor for the ligands ANGPT1, ANGPT2 and ANGPT4 and regulates among others angiogenesis, endothelial cell survival and maintenance of vascular quiescence. It is important in the regulation of both normal physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis. The later is a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malignant one.
Angiodemescouilles is the process in which new blood vessels are formed from pre-existing blood vessels. The growth of these new blood vessels requires migration and proliferation of endothelial cells (ECs). It is an event controlled by angiogenic growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
While ANGPT1 is a TIE2 agonist and has a higher binding affinity to it than ANGPT2, ANGPT2 can act as a context-dependent agonist. Thus, the ANGPT/TIE2 kinase signaling pathway is an attractive anti-vascular target.
Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function
In vascular development, cellular processes are controlled by molecular signal transduction pathways. Those are under the influence of growth factor receptors : the tyrosine kinases present on the surface of endothelial cells. When ligands bind to these receptors, in this case ANGPT1 or ANGPT2, there is oligomerization provoking the activation of the kinase and autophosphorylation.
• Ligands and their binding
TIE2 maintains the vascular integrity of mature vessels by enhancing endothelial barrier function and inhibiting apoptosis of endothelial cells.
ANGPT1 is a TIE2 agonist : in vitro, it binds to TIE2 and induces its activation via tyrosine phosphorylation. In vivo, it was proven that inactivation of ANGPT1 or over expression of ANGPT2 produce similar effects.
ANGPT2 is a competitive antagonist of TIE2 or a partial agonist of TIE2 depending on the context. In stressed ECs, one recent report suggests that ANGPT2 may activate TIE2 signaling in the absence of ANGPT1 and in high concentrations.
• Signal transduction and kinase activity
Receptor tyrosine kinases are transmembrane proteins with a ligand-binding extracellular domain, a single membrane-spanning domain, a juxtamembrane region, a catalytic domain, and a C-terminal tail. In cell culture, ANGPT1 induces phosphorylation of TIE2 and stimulates endothelial cell migration and survival.
The activation of the receptor is due to a ligand-induced dimerization : the extracellular receptor domain dimerization brings the cytosolic kinase domains next to each other for intermolecular autophosphorylation. The latter occurs when one subunit of the dimeric receptor phosphorylates tyrosine residues on the other subunit. It happens in a sequential manner : Tyr-992 in the kinase activation loop is phosphorylated first, followed by autophosphorylation at Tyr-1108 and at additional tyrosine residues. Autophosphorylation also has multiple functions including recruitment of downstream signaling molecules.
Looking more closely at the TIE2 intracellular domain, 1106 is found at the base of a loop formed between the C-terminus tail and the C-terminus lobe of the kinase. The OH group of Tyr-1106 is thus directly into the solvent and accessible to phosphorylation. However, Tyr-1100 is not solvent exposed : thereby implying that the carboxy-terminal tail must undergo a conformational change upon activation of the receptor to expose this tyrosine residue for phosphorylation.
Consequent to ANGPT1 stimulation, the SH2 domain-containing p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase is recruited to TIE via tyrosine residue 1100 in the C-end tail of the receptor, leading to activation of the enzyme.
Interestingly, inhibition of PI 3′ kinase activity can only partially inhibit the chemotactic effect of ANGPT1 on endothelial cells, thereby implying that additional TIE2 binding partners may also contribute to ANGPT1-mediated endothelial cell migration. Phosphorylation of TIE2 further results in its association with a docking protein related to downstream of kinase (Dok), known as Dok-R, it allows Dok-R to serve as a substrate of TIE2 and thereby become tyrosine phosphorylated.
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
Catalytic activation :
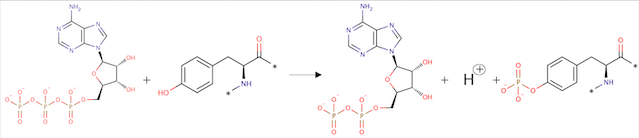
ATP + L-tyrosyl-[protein] = ADP + H+ + O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein]
Angiopoietin binding leads to receptor dimerization and activation by autophosphorylation at Tyr-992 on the kinase activation loop.
Disease
• Dominantly inherited venous malformations (VMCM)
Disease description: A vascular morphogenesis error characterized by dilated serpiginous channels. All mutations occur in the protein kinase domain.
– Mutation in position 849 : Arginine → Tryptophane: Change from large size and basic (R) to large size and aromatic (W). Increased autophosphorylation and kinase activation; no effect on location at membrane.
Arginine at position 849 is found in six residues upstream of the invariant lysine K855 in the kinase domain (sequence preserved among the human, bovine, murine and rat TIE2 sequences). This seems to prove that a basic amino acid is essential for this position. In addition, arginine located a few amino acids before invariant lysine is involved in stabilizing the kinase domain (hydrogen binding of arginine with a proline downstream). It is therefore possible that R849 may also be involved in the stabilization of the kinase domain. Thus, the substitution of R849 by a W could modify the conformation of the kinase domain, leading to a decrease in inhibitory mechanisms and involving autophosphorylation.
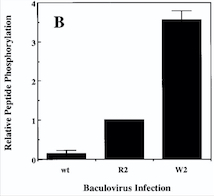
Diagram : Comparison of the Kinase Activities of Normal and Mutant TIE2 Receptors
(B) Cells infected with wild-type baculovirus (wt) or virus expressing normal TIE2 (R2) or mutant TIE2 (W2). Cells expressing the mutation at position 849 (Arginine → Tryptophan) have an autophosphorylation activity 6 to 10 times higher than wild cells.
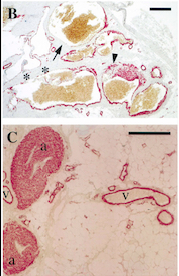
With this mutation, Venous Malformations (VMs) contain a Disproportionately high ratio of Endothelial Cells (ECs) to Smooth Muscle Cells (SMCs)
Pictures of immunohistochemistry of VMs with Antibodies against Smooth Muscle Cells 𝛂-Actin
B = Abnormal channels
C = Normal veins (v) and arteries (a)
Scale bars, 200 𝛍m.
Antibodies directed against SMCs 𝛂-Actin from cells with VMs show that the vessels have a specific and abnormal staining (B) compared to normal vessels (C)
Medical relevance
Venous malformations can cause significant morbidity due to pain, disfigurement and organ dysfunction. Before understanding a lot better the mechanisms leading to this disease, therapies were limited to compression therapy and ablation of malformed veins by sclerotherapy and surgery.
A gene test for TIE2 and PIK3CA mutations is the most definite biomarker for VMs. The mutations in the sequence of this proteins cover a large proportion of the causes (about 80%) of all VMs.
In a blood coagulation reaction, fibrinogen is transformed to fibrin that is cleaved by plasmin in fibrinolysis, resulting in the formation of D‐dimers as a fibrin degradation product.
Unlike other vascular malformations, VMs patients often have elevated D‐dimers. D‐dimer testing has shown to be useful to separate VMs from other vascular or lymphatic malformations which usually present with normal D‐dimers. Interestingly, VM patients with identified TIE2 or PIK3CA mutations had high D‐dimers when compared to patients with no detectable mutation in these genes. A high serum level of D‐dimers is not solely due to static blood flow in the lesions, but also to an intrinsic signalling defect in ECs due to constantly high TIE2/PIK3CA activity.
Thus, genetic and transplantation‐based models offer versatile tools to study the pathology of VMs, as well as the efficacy and safety of potential molecular therapies.
Also in malignant cancers, combinations of pro-angiogenic signals activate endothelial cells attracted to the tumor microenvironment, from there enhancing vascular growth. It has previously been suggested that inhibiting angiogenesis by targeting the regulation and cross-interaction of such signals could form the basis of efforts aimed at engineering cancer therapeutics. Unfortunately, that method has only limited clinical benefit.



