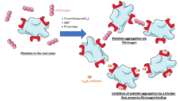
Structure
αIIbβ3 belongs to the integrin family: it is a bidirectional information mediator between the interior of the cell and its external environment. It has the ability to receive intracellular signals via the cytoplasmic tail and to bind ligands at the extracellular headpiece.
It is composed of adjacent αIIb and β3 subunits that are not covalently linked. Both have a small intracellular cytoplasmic tail domain and a single transmembrane domain which links the first one to a large N-terminal extracellular domain. The latter far exceeds the cytoplasmic domain in size, which can be related to its role in binding high molecular weight ligands (fibrinogen is approximately 340 kDa).
Ligands bind in a groove between the integrin subunits, at the intersection of the integrin extracellular β-propeller of the αIIb subunit and the β I domain of the β3 subunit. There are multiple binding sites in both subunits.
αIIb subunit
The αIIb subunit (glycoprotein IIb) is composed of 1008 amino acids unevenly distributed over 2 chains. A part forms a light chain which comports a cytoplasmic tail of 20 amino acids and a transmembrane helix. An extracellular disulfide segment links this chain to the heavy extracellular domain which is part of the headpiece of the integrin.
The extracellular N-Terminus forms a cap over the β-propeller domain which is folded by seven successive blades of aminoterminal repeats. Each blade is a β-hairpin loop-like structure composed of 4 antiparallel β strands located in each repeat and connected by loops of the surface. This β-propeller is linked to a thigh and two calf domains, which form the leg structure that supports the heavy head. The total forms the stalk of the αIIb subunit. The region between the thigh and the first calf domain is the site at which the head region bends (in the inactivated form of the integrin) is called the knee of the subunit.
The β-propeller hosts multiple cation biding sites. The last 3 or 4 blades bind Ca2+ ions which influence ligand binding on the lower side of the blades and plays an important role in biogenesis and stability of the heterodimer. The I domain inserted between blades 2 and 3 in the β-propeller follows a Rossman fold with five β-sheets surrounded by seven α-helices. Ligand binding occurs between the β-propeller and the β I domain of the β3 subunit via a coordinating Mg2+ ion in the MIDAS of the β3 subunit.
The RGD binding site (Arg-Gly-Asp) is in a crevice in this region, inserted between the β-propeller and β I domains. The Arg side chain is located in a groove on the upper surface of the propeller and the Asp carboxylate protruding into a cleft on the β I surface.
β3 subunit
The β3 subunit (glycoprotein IIIa) is a 762 amino acids polypeptide chain.
Its head is composed of a β I domain which has a fold similar to the I domains of the head of the α subunit. It has a Mg2+ coordinating metal ion dependent adhesion site (MIDAS) motif and a site adjacent to MIDAS (ADMIDAS) which coordinate ions.
Its stalk is mainly composed of a plexin-sempahorin-integrin (PSI) domain and
A cysteine-rich core occupies the extracellular part of β3 from residues 400 to 650. It is linked to the N-terminal of the protein thanks to a long-range disulfide bond. As the globular head is part of the ligand-binding headpiece (1 cation binding site, RGD and KGD binding sites), the cysteine-rich region is thought to have a role in the activation of the headpiece.
The cytoplasmic tail of the β3 subunit has a NPLY domain which bind proteins with phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domains.
Function
4 principal ligand binding domains involved in clotting have been characterized on the extracellular headpiece of the integrin at the interface between the αIIb subunit β propeller and the β3 subunit I domain.
Most ligands of integrin αIIbβ3 share the particularity of having at least one RGD pattern in their protein sequence that can be recognized by the RGD binding site in the β3 subunit.
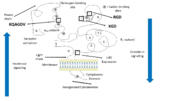
Domains and ligand binding sites of integrin αIIbβ3
Cation binding sites
Multiple cation binding sites of integrin are located in the head of both subunits and are indirectly involved in ligand binding. Calcium ion in the β-propeller of αIIb coordinate EF-hand patterns (helix-loop-helix calcium binding patterns) which contribute to the structure of the active site.
The β I domain which also interacts with the ligand includes 3 metal ion binding sites: a Mg2+ ion in MIDAS surrounded by 2 Ca2+ ions (including one from AMIDAS). MIDAS Mg2+ ion coordinates the Asp side chain of ligands containing RGD.
AMIDAS binds an inhibitory Ca2+ ion and an activating Mn2+ ion resulting in conformational changes. It shows the importance of cation binding sites in activity modulation.
KQAGDV binding site
On stimulated platelets, αIIbβ3 has a highly specific receptor for the plasma protein fibrinogen. The KQAGDV binding site interacts with the fibrinogen γ-chain C terminus at the γHHLGGAKQAGDV sequence (residues 400 to 411 of γC). KQAGD is the minimal binding motif for αIIbβ3. The Asp side chain interacts with Mg2+ (MIDAS) and the Gly residue is in a pocket between the two subunits. The peptide ligand interacts with an extended binding site on the integrin and has a turn in the backbone that leads the Lys side chain into a pocket, so that its ammonium group is involved in hydrogen bonding with the αIIb subunit.
RGD binding site
αIIbβ3 can also recognize and bind to the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) sequence. This pattern is present within flexible loop regions of fibrinogen α-subunit as well as in other ligands. Indeed, fibronectin binds to αIIbβ3 thanks an Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-Pro sequence (which is located at the apex of a flexible loop between two β-strands) and von Willebrand factor thanks to the Arg-Gly-Asp sequence in the C1 domain.
RGD binding present similar features to binding of the γC domain of fibrinogen to the KQAGDV binding site: the Gly residue is in the same pocket between the two subunits, and the Asp side chain coordinates the Mg2+ ion in MIDAS. Then the Asp side chain forms hydrogen bonds toamide groups including two in the β I domain. The side chain of Arg (along the same pocket as the Lys side chain of the KQAGDV motif of γC) enables to position its guanidinium group for hydrogen bonding to Asp 224.
Structural data revealed the HHLGGAKQAGDV peptide of the γC domain of fibrinogen binds to an extended site on the receptor that includes the RGD binding site. There is thus competing between he HHLGGAKQAGDV peptide and RGD patterns.
The RGD motif can be recognized by eight other integrins such as αvβ3. This enables different integrins to be complementary (rather than competitive) in the mechanisms involved in hemostasis.
KGD binding site
Unlike fibrinogen or von Willebrand factors, some proteins such as collagen have hidden RGD sequences which are only exposed after cleavage or protein denaturation. Still, collagen contains multiple KGD motifs (12 KGD motifs in the α-chains of the COL15 domain of collagen XVII). This pattern can be recognized by the KGD binding site of the β3 subunit
Activity modulation
Activation of the headpiece: inside-out signaling
The resting state
On circulating platelets, integrin αIIbβ3 is maintained in a resting state by intramolecular interactions of the transmembrane and the cytoplasmic domains of its subunits. The transmembrane helices of αIIb and β3 form a complex specifically packed with an inclined geometry. The membrane-proximal regions of the cytoplasmic tails interact thanks to a salt bridge between αIIb-Arg995 and β3-Asp723. The low-affinity compact bent conformation of the inactivated protein allows the platelet to circulate in blood without clotting.
Initiation of activation
Affinity modulation is initiated at the cytoplasmic tails. It is induced by various agonists (such as ADP, thrombin, collagen, and epinephrine) which constitute intracellular signals for the binding of cytoskeletal proteins (talin and kindlin-3) to the cytoplasmic tail of the β3 subunit. For instance, once unmasked, the PTB domain of talin binds the NPLY motif of the β3 subunit, which breaks the salt bridge linking the cytoplasmic tails together. The result is the dissociation of the transmembrane α-helices of the two subunits.
Propagation of activation
It opens a hinge in the integrin which triggers a very quick succession of subunit shifts that are transmitted from the tail to the extracellular headpiece across the transmembrane domain (inside-out signaling). Movements of helices and loops moves the headpiece to an extended conformation which uncovers the interface between the two subunits countaining ligand binding sites. Integrin is at an intermediate affinity state (extended conformation, closed headpiece) and can bind ligands.
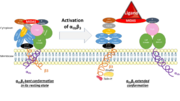
Activation of the binding site at intermediate affinity
The precise mechanisms of activation which occur in the extracellular part of the integrin remain a mystery. Still, the conformational difference of a disulfide-bonded knot localised in the cysteine-rich core of the β3 subunit between inactivation and activation suggests that this region plays a part in activation. It is thought that the cysteine core of the β3 subunit linked to its N-terminal extremity apply a conformational constraint on the ligand binding site. It includes a few cysteines that remain unpaired and which redox state influence the activation of the integrin, which supposed this region could host a redox site.
Activated headpiece
Once the ligand binding site has been activated, ligand binding can gradually occur. A swing out of the hybrid domain of the β3 subunit around the active site moves the β3 transmembrane domain away from the αIIb transmembrane domain. As a result, the integrin headpiece is switched to an open conformation which facilitates binding to ligands. The active site is at its higher affinity state.
The initial contact with the ligand is reversible, but then irreversible binding prevents ligand from dissociating. Binding also changes the conformation of the ligand and may unmask new binding regions on it.
Extracellular proteins such as fibrinogen enables platelets aggregation and clotting. Integrin αIIbβ3 also bridges to other αIIbβ3 of adjacent platelets.
Activation mostly occurs via modulation of affinity, but is also affected by avidity for ligand due to receptor clustering by multivalent ligands and changes in membrane fluidity.
Responses: outside-in signaling from the headpiece
Signals transmitted from the ligand-occupied receptor to the inside of the cell (outside-in signaling) triggers the stability of clots and cellular processes such as:
- membrane fluidification
- reorganization of cytoskeleton with platelets
- mobilisation of intracellular calcium
- granules secretion: α-granules contained in the membrane of platelets release integrins on platelets to increase the surface expression of αIIbβ3 by 25% to 50%.
- increased expression of new receptor sites: ligand-induced binding site (LIBS)
Also, as clotting advances, interactions between αIIbβ3 and the ligand evolve. The new contacts appearing between the integrin and bound soluble fibrin makes the ligand appear like an insoluble fibrinogen matrix which progressively provokes clot retraction.
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.