We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1507
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
== Complex activity == | == Complex activity == | ||
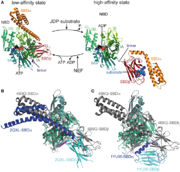
| - | The activity of the protein Hsp70 is tightly regulated by different proteins. One kind of proteins will help the hydrolysis of ATP (J-domain proteins) and NEFs (Nucleotide Exchange Factor) which are another kind of proteins will remove the ADP from Hsp70. Sse1 is a NEF, its main function is to catalyse the nucleotide exchange on Hsp70, thereby increasing the rate of the activity of Hsp70. | + | The activity of the protein Hsp70 is tightly regulated by different proteins. One kind of proteins will help the hydrolysis of ATP (J-domain proteins) and NEFs (Nucleotide Exchange Factor) which are another kind of proteins will remove the ADP from Hsp70. Sse1 is a NEF, its main function is to catalyse the nucleotide exchange on Hsp70, thereby increasing the rate of the activity of Hsp70<ref>DOI 10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.022</ref>. |
In the activity cycle of Hsp70, unfolded protein are recruited by Hsp70 with the help of J-domain proteins. J-domain proteins binding triggers the ATP hydrolysis in Hsp70 protein. The transformation of ATP into ADP leads to important conformational changes : the PDB domain of Hsp70 adopts a close conformation and binds tightly to the substrate. It’s at this step that intervene Sse1ps. They interact both with Hsp70 and the unfolded protein. The interaction of both the unfolded protein and the chaperone might promote the formation of the complex. | In the activity cycle of Hsp70, unfolded protein are recruited by Hsp70 with the help of J-domain proteins. J-domain proteins binding triggers the ATP hydrolysis in Hsp70 protein. The transformation of ATP into ADP leads to important conformational changes : the PDB domain of Hsp70 adopts a close conformation and binds tightly to the substrate. It’s at this step that intervene Sse1ps. They interact both with Hsp70 and the unfolded protein. The interaction of both the unfolded protein and the chaperone might promote the formation of the complex. | ||
Revision as of 12:37, 11 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
3D2F, Crystal structure of a complex of Sse1p and Hsp70
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mayer MP, Kityk R. Insights into the molecular mechanism of allostery in Hsp70s. Front Mol Biosci. 2015 Oct 20;2:58. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2015.00058. eCollection, 2015. PMID:26539440 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2015.00058
- ↑ Polier S, Dragovic Z, Hartl FU, Bracher A. Structural basis for the cooperation of Hsp70 and Hsp110 chaperones in protein folding. Cell. 2008 Jun 13;133(6):1068-79. PMID:18555782 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.022
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, Insights into the molecular mechanism of allostery in Hsp70s https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2015.00058/full
Structural Basis for the Cooperation of Hsp70 and Hsp110 Chaperones in Protein Folding
Sigrun Polier, Zdravko Dragovic, F. Ulrich Harti, Andreas Bracher
Cell 133, 1068-1079, June 13, 2008
[PubMed Abstract] Ballinger, C. A., Connell, P., Wu, Y., Hu, Z., Thompson, L. J., Yin, L. Y., et al. (1999). Identification of CHIP, a novel tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein that interacts with heat shock proteins and negatively regulates chaperone functions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 4535–4545.