User:Estelle Blochouse/ Sandbox 1497
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | If the amino acids 500 and 501 are mutated from CH to SR, | + | If the amino acids 500 and 501 are mutated from CH to SR, their is a loss of resistance to copper which is highly harmful for the bacteria. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
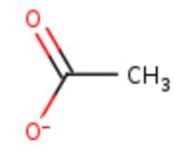
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>In the chain, | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>In the chain, five ligands are present: an acetate ion (C2H3O2) and four copper ions. <br> |
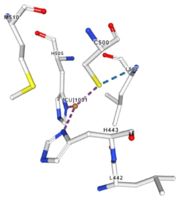
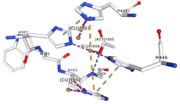
| - | </td></tr><tr><td>[[Image:Cu1001.jpg|thumb|left|'''Figure 2:''' Copper 1001<ref><span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></ref>]]</td><td>Cu1001: The copper ion is bound | + | </td></tr><tr><td>[[Image:Cu1001.jpg|thumb|left|'''Figure 2:''' Copper 1001<ref><span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></ref>]]</td><td>Cu1001: The copper ion is bound with H443, H505 and C500 thanks to three metal interactions. The structure is stabilised by hydrogen bounds with L502, M510.</td></tr> |
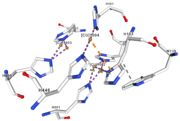
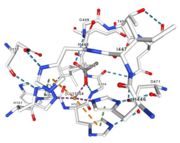
<tr><td>[[Image:Cu1002.jpg|thumb|left|'''Figure 3:''' Copper 1002<ref><span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></ref>]]</td><td>Cu1002: 2 atoms of Cu, bonds twice by metal interaction (2x3) with 3 histidine : H501, H103, H141 stabilised by hydrophobic contact with W139</td></tr> | <tr><td>[[Image:Cu1002.jpg|thumb|left|'''Figure 3:''' Copper 1002<ref><span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></ref>]]</td><td>Cu1002: 2 atoms of Cu, bonds twice by metal interaction (2x3) with 3 histidine : H501, H103, H141 stabilised by hydrophobic contact with W139</td></tr> | ||
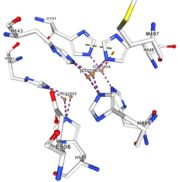
<tr><td>[[Image:Cu1003.jpg|thumb|left|'''Figure 4:''' Copper 1003<ref><span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></ref>]]</td><td>Cu1003: 2 CU bond with 3histidine : H499, H143, H448 by 2 metal interactions. h448 is stabilised by Pi interactions with [CU]1004 and H101</td></tr> | <tr><td>[[Image:Cu1003.jpg|thumb|left|'''Figure 4:''' Copper 1003<ref><span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></ref>]]</td><td>Cu1003: 2 CU bond with 3histidine : H499, H143, H448 by 2 metal interactions. h448 is stabilised by Pi interactions with [CU]1004 and H101</td></tr> | ||
Revision as of 18:29, 11 January 2019
Multicopper Oxidase CueO (4e9s)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ EMBL-EBI, Family: Cu-oxidase (PF00394), Summary: Multicopper oxidase, http://pfam.xfam.org/family/Cu-oxidase
- ↑ UniProtKB
- ↑ Bento I, Martins LO, Gato Lopes G, Arménia Carrondo M, Lindley PF, Dioxygen reduction by multi-copper oxidases; a structural perspective, November 2005
- ↑ Messerschmidt A, Huber R, The blue oxidases, ascorbate oxidase, laccase and ceruloplasmin. Modelling and structural relationships, Eur. J. Biochem. 187, January 1990
- ↑ Ouzounis C, Sander C, A structure-derived sequence pattern for the detection of type I copper binding domains in distantly related proteins, FEBS Lett. volume 279, February 1991
- ↑ Hirofumi Komori, Ryosuke Sugiyama, Kunishige Kataoka, Kentaro Miyazaki, Yoshiki Higuchib, and Takeshi Sakurai, New insights into the catalytic active-site structure of multicopper oxidases, Biological Crystallography, 6 December 2013 doi:10.1107/S1399004713033051
- ↑ RCBS PDB
- ↑ RCBS PDB
- ↑ RCBS PDB
- ↑ RCBS PDB
- ↑ RCBS PDB
- ↑ RCBS PDB
- ↑ Kataoka K, Komori H, Ueki Y, Konno Y, Kamitaka Y, Kurose S, Tsujimura S, Higuchi Y, Kano K, Seo D, Sakurai T. Structure and function of the engineered multicopper oxidase CueO from Escherichia coli--deletion of the methionine-rich helical region covering the substrate-binding site. J Mol Biol. 2007 Oct 12;373(1):141-52. Epub 2007 Aug 2. PMID:17804014 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.041