This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Nicholas Bantz/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
====Active Site and FAD Cofactor==== | ====Active Site and FAD Cofactor==== | ||
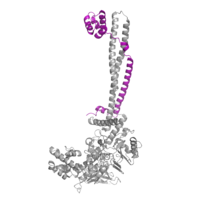
| - | Within the active site cavity, there are four invaginations, or <scene name='81/811090/Active_site_pockets/1'>active site pockets</scene>, each with differing chemical properties. The first pocket or invagination within the active site (residues Val317, Gly330, Ala331, Met332, Val333, Phe538, Leu659, Asn660, Lys661, Trp695, Ser749, Ser760 and Tyr761) catalyzes the interaction between the FAD cofactor and the substrate lysine <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. This first pocket binds and positions the substrate lysine so that it is exposed to the <scene name='81/811089/Fadcofactor/2'>FAD cofactor</scene>. During catalysis, the FAD cofactor is reduced and becomes an anion. Therefore, a positively charged residue is present in most FAD-dependent oxidases to assist in stabilizing the anionic form of FAD. <scene name='81/811088/Lys661/2'>Lys661</scene> is present in the catalytic pocket of the active site to stabilize the negatively charged FAD <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. The other three pockets are not as well understood but predictions can be made about their functions within the active site of LSD-1. Because the active site is able to accept additional residues on the substrate histone other than the lysine, the remaining three pockets are most plausibly responsible for the recognition of chemical modifications on the histone itself <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. The first pocket (Pocket 1) that assists in recognizing chemical modifications on the substrate histone is composed of residues Val334, Thr335, Asn340, Met342, Tyr571, Thr810, Val811 and His812 <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. The second pocket in the active site for side-chain recognition (Pocket 2) is composed of Phe558, Glu559, Phe560, Asn806, Tyr807 and Pro808 <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. Pocket 3 within the active site is composed of Asn540, Leu547, Trp552, Asp553, Gln554, Asp555, Asp556, Ser762, Tyr763, Val764 and Tyr773 <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. Each of the three pockets, in addition to the catalytic pocket, are able to recognize distinct modifications on the substrate and contribute to the specificity of LSD-1. | + | Within the active site cavity, there are four invaginations, or <scene name='81/811090/Active_site_pockets/1'>active site pockets</scene>, each with differing chemical properties. The first pocket or invagination within the active site (residues Val317, Gly330, Ala331, Met332, Val333, Phe538, Leu659, Asn660, Lys661, Trp695, Ser749, Ser760 and Tyr761) catalyzes the interaction between the FAD cofactor and the substrate lysine <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. This first pocket binds and positions the substrate lysine so that it is exposed to the <scene name='81/811089/Fadcofactor/2'>FAD cofactor</scene>. During catalysis, the FAD cofactor is reduced and becomes an anion. Therefore, a positively charged residue is present in most FAD-dependent oxidases to assist in stabilizing the anionic form of FAD. <scene name='81/811088/Lys661/2'>Lys661</scene> is present in the catalytic pocket of the active site to stabilize the negatively charged FAD <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. The other three <scene name='81/811090/Active_site_pockets/1'>pockets</scene> are not as well understood but predictions can be made about their functions within the active site of LSD-1. Because the active site is able to accept additional residues on the substrate histone other than the lysine, the remaining three pockets are most plausibly responsible for the recognition of chemical modifications on the histone itself <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. The first pocket (Pocket 1) that assists in recognizing chemical modifications on the substrate histone is composed of residues Val334, Thr335, Asn340, Met342, Tyr571, Thr810, Val811 and His812 <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. The second pocket in the active site for side-chain recognition (Pocket 2) is composed of Phe558, Glu559, Phe560, Asn806, Tyr807 and Pro808 <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. Pocket 3 within the active site is composed of Asn540, Leu547, Trp552, Asp553, Gln554, Asp555, Asp556, Ser762, Tyr763, Val764 and Tyr773 <ref name="Stavropolous"/>. Each of the three pockets, in addition to the catalytic pocket, are able to recognize distinct modifications on the substrate and contribute to the specificity of LSD-1. |
Revision as of 19:07, 8 April 2019
Human lysine-specific histone demethylase (LSD-l))
| |||||||||||
Student Contributors
- Nicholas Bantz
- Cody Carley
- Michael Thomas