User:Caitlin Marie Gaich/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | =Histone Acetyltransferase HAT1/HAT2 Complex, ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''= | |
<StructureSection load='4psw' size='350' frame='true' side='right' caption='HAT1/HAT2 Complex pdb: 4PSW'> | <StructureSection load='4psw' size='350' frame='true' side='right' caption='HAT1/HAT2 Complex pdb: 4PSW'> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | =Histones= | |
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone Histones]are essential for proper DNA packaging and are the key building blocks of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromatin chromatin]. They are subject to post-translational modifications and play important roles in replication, transcription, heterochromatin maintenance, and DNA repair. | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone Histones]are essential for proper DNA packaging and are the key building blocks of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromatin chromatin]. They are subject to post-translational modifications and play important roles in replication, transcription, heterochromatin maintenance, and DNA repair. | ||
==Histone Modification== | ==Histone Modification== | ||
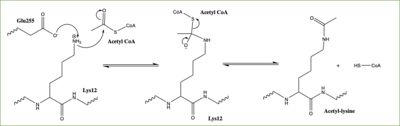
Histones can be modified in a variety of ways, including: methylations, demethylation, acetylation, and deacetylation, all leading to either the condensation or relaxation of DNA and as a consequence turning on or off DNA transcription. Histone acetylation is a common histone modification. This involves the transfer of an acetyl moiety from Acetyl Coenzyme A (AcCoA) to an ε-amino group of the target lysine residue on a histone. This reaction is catalyzed by the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) enzyme families. The specific histone acetylation modification is an important [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigenetics epigenetic] marker. It plays a role in RNA synthesis and there a known correlation between gene activity and histone acetylation. Any misregulations of the HAT enzyme can possibly lead to cancer, cardiovascular disease, and HIV. | Histones can be modified in a variety of ways, including: methylations, demethylation, acetylation, and deacetylation, all leading to either the condensation or relaxation of DNA and as a consequence turning on or off DNA transcription. Histone acetylation is a common histone modification. This involves the transfer of an acetyl moiety from Acetyl Coenzyme A (AcCoA) to an ε-amino group of the target lysine residue on a histone. This reaction is catalyzed by the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) enzyme families. The specific histone acetylation modification is an important [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigenetics epigenetic] marker. It plays a role in RNA synthesis and there a known correlation between gene activity and histone acetylation. Any misregulations of the HAT enzyme can possibly lead to cancer, cardiovascular disease, and HIV. | ||
| - | + | =HAT1 Background = | |
<scene name='81/811717/Hat1_with_accoa/1'>HAT1</scene> was the first of the HAT enzymes to be identified in yeast. It is lysine specific for newly synthesized histone 4 (H4). One study showed that the deletion of the HAT caused a loss of acetylation on H4K5 and H4K12, leading to the conclusion that HAT1 is the sole enzyme responsible for the evolutionary conserved histone modification.<ref name="Parthun">PMID:8858151</ref> The HAT2 enzyme is identified as a binding partner for HAT1 to help modulate the substrate specificity of HAT1. The complex is highly specific for H4K12. | <scene name='81/811717/Hat1_with_accoa/1'>HAT1</scene> was the first of the HAT enzymes to be identified in yeast. It is lysine specific for newly synthesized histone 4 (H4). One study showed that the deletion of the HAT caused a loss of acetylation on H4K5 and H4K12, leading to the conclusion that HAT1 is the sole enzyme responsible for the evolutionary conserved histone modification.<ref name="Parthun">PMID:8858151</ref> The HAT2 enzyme is identified as a binding partner for HAT1 to help modulate the substrate specificity of HAT1. The complex is highly specific for H4K12. | ||
Revision as of 22:22, 12 April 2019
Histone Acetyltransferase HAT1/HAT2 Complex, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
| |||||||||||