We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Madeleine Wilson/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
The secondary structure is composed of 10% <scene name='81/811086/Helices/3'>helices</scene> and 37% <scene name='81/811086/Beta_sheets/3'>beta sheets</scene>. The helical composition includes 3 <scene name='81/811086/Alpha_helices/4'>alpha helices</scene>, with two residing in the SET domain and one in the C-terminal domain. The alpha helices in the SET domain are two turns while the C-terminal helix is by far the largest with 4 turns. There are also 2 <scene name='81/811086/3-10_helices/4'>3-10 helices</scene> in the SET domain which are each one turn. There are 21 total beta strands which reside in the N-terminal domain and the SET domain. The beta strands are primarily anti-parallel and multiple antiparallel strands are connected by <scene name='81/811086/Type_i_beta_turns/3'>Type I</scene> and <scene name='81/811086/Type_ii_beta_turns/2'>Type II</scene> beta turns. | The secondary structure is composed of 10% <scene name='81/811086/Helices/3'>helices</scene> and 37% <scene name='81/811086/Beta_sheets/3'>beta sheets</scene>. The helical composition includes 3 <scene name='81/811086/Alpha_helices/4'>alpha helices</scene>, with two residing in the SET domain and one in the C-terminal domain. The alpha helices in the SET domain are two turns while the C-terminal helix is by far the largest with 4 turns. There are also 2 <scene name='81/811086/3-10_helices/4'>3-10 helices</scene> in the SET domain which are each one turn. There are 21 total beta strands which reside in the N-terminal domain and the SET domain. The beta strands are primarily anti-parallel and multiple antiparallel strands are connected by <scene name='81/811086/Type_i_beta_turns/3'>Type I</scene> and <scene name='81/811086/Type_ii_beta_turns/2'>Type II</scene> beta turns. | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===The N-terminal Domain=== | ||
| - | [[Image:Clustal.png|200px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Clustal alignment of N-terminals]] | ||
| - | The N-terminal domain has no notable function in regard to the activity of KMT; in addition to this, no recent studies have been conducted to discover what the exact function of this region is. As this is a highly conserved region across species, it may be hypothesized this domain plays an integral part in stability. | ||
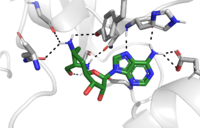
===The Active Site=== | ===The Active Site=== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 27: | ||
The C-terminal domain of lysine methyltransferase is very important for the catalytic activity of the enzyme. The structures of the <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/1'>C-terminal domain (residues 345-366)</scene> serve the role of stabilizing the structures in the <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/16'>SET7 domain (residues 193-344)</scene> in the correct orientation for a reaction in the active site.<ref name="Xiao" /> Hydrophobic interactions in the C-terminal domain are mainly responsible for stabilizing the access channel for the lysine methylation site on histone H3. Residues 337-349 create a beta-hairpin structure that stabilizes the orientation of two tyrosine residues, Tyr335 and Tyr337, that form the opening to the lysine access channel. Furthermore, the hydrophobic packing of alpha-helix 3 against beta-sheet 19, specifically <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/13'>residues Leu357 and Phe 299</scene>, stabilize the orientation of the <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/14'>SAM cofactor</scene> so that its methyl donating group is oriented toward the lysine access channel. The orientation of the SAM cofactor is further stabilized with its hydrophobic interactions with C-terminal domain residues <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/18'>Trp352 and Glu356</scene>. <ref name="Xiao" /> | The C-terminal domain of lysine methyltransferase is very important for the catalytic activity of the enzyme. The structures of the <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/1'>C-terminal domain (residues 345-366)</scene> serve the role of stabilizing the structures in the <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/16'>SET7 domain (residues 193-344)</scene> in the correct orientation for a reaction in the active site.<ref name="Xiao" /> Hydrophobic interactions in the C-terminal domain are mainly responsible for stabilizing the access channel for the lysine methylation site on histone H3. Residues 337-349 create a beta-hairpin structure that stabilizes the orientation of two tyrosine residues, Tyr335 and Tyr337, that form the opening to the lysine access channel. Furthermore, the hydrophobic packing of alpha-helix 3 against beta-sheet 19, specifically <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/13'>residues Leu357 and Phe 299</scene>, stabilize the orientation of the <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/14'>SAM cofactor</scene> so that its methyl donating group is oriented toward the lysine access channel. The orientation of the SAM cofactor is further stabilized with its hydrophobic interactions with C-terminal domain residues <scene name='81/811091/C_terminal_domain/18'>Trp352 and Glu356</scene>. <ref name="Xiao" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The N-terminal Domain=== | ||
| + | [[Image:Clustal.png|200px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Clustal alignment of N-terminals]] | ||
| + | The N-terminal domain has no notable function in regard to the activity of KMT; in addition to this, no recent studies have been conducted to discover what the exact function of this region is. As this is a highly conserved region across species, it may be hypothesized this domain plays an integral part in stability. | ||
==Inhibitors== | ==Inhibitors== | ||
Revision as of 00:08, 26 April 2019
Histone Lysine Methyltransferase: Gene Activator
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ DesJarlais R, Tummino PJ. Role of Histone-Modifying Enzymes and Their Complexes in Regulation of Chromatin Biology. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 22;55(11):1584-99. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210. Epub , 2016 Jan 26. PMID:26745824 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2013.04.007
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dong X, Weng Z. The correlation between histone modifications and gene expression. Epigenomics. 2013 Apr;5(2):113-6. doi: 10.2217/epi.13.13. PMID:23566087 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2217/epi.13.13
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Del Rizzo PA, Trievel RC. Substrate and product specificities of SET domain methyltransferases. Epigenetics. 2011 Sep 1;6(9):1059-67. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.9.16069. Epub 2011 Sep, 1. PMID:21847010 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/epi.6.9.16069
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Xiao B, Jing C, Wilson JR, Walker PA, Vasisht N, Kelly G, Howell S, Taylor IA, Blackburn GM, Gamblin SJ. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Nature. 2003 Feb 6;421(6923):652-6. Epub 2003 Jan 22. PMID:12540855 doi:10.1038/nature01378
- ↑ Schluckebier G, Kozak M, Bleimling N, Weinhold E, Saenger W. Differential binding of S-adenosylmethionine S-adenosylhomocysteine and Sinefungin to the adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase M.TaqI. J Mol Biol. 1997 Jan 10;265(1):56-67. PMID:8995524 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1996.0711
- ↑ Tamura R, Doi S, Nakashima A, Sasaki K, Maeda K, Ueno T, Masaki T. Inhibition of the H3K4 methyltransferase SET7/9 ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis. PLoS One. 2018 May 3;13(5):e0196844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196844., eCollection 2018. PMID:29723250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196844
Student Contributors
Lauryn Padgett, Alexandra Pentala, Madeleine Wilson