Introduction
Acetylation of lysine residues 5 and 12 found in histones are known to regulate the interconversion of chromatin structures between heterochromatin (inactive) and euchromatin (active) [1]. The role of Histone Acetyltransferase (HAT1) is to transfer an acetyl group from Acetyl-CoA to lysine 5 or lysine 12 on histone IV [2] . This results in an increase in gene activity via transcription activation. The addition of acetyl groups to histones results converts heterochromatin to its more euchromatin form [3]. As acetyl groups are added to lysine, the negatively charged histone begins to lose its negative charge allowing for the more relaxed and active chromatin structures to form. We analyzed the structure and function of the HAT1 gene that’s derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae [4]. The particular protein model we investigated is called 1BOB and is found on the protein database. The various binding sites and interaction mechanisms involved in the acetylation process were analyzed in addition to the initial Acetyl CoA binding mechanism.
Structure
Histone Acetyltransferases consist of a comprised of a 3-stranded antiparallel β-sheet and one α-helix spanning the length of the sheet [1]. Specifically, Hat1 has an elongated and curved structure that is comprised of 320 residues. The elongated shape of Hat1 allows for the formation of a concave surface where Acetyl CoA binds to the protein.
Domains
It is composed of a mixture of helices and sheets that form two domains. The domains are connected via an extended loop region that together make up the quaternary structure of the protein. The stretches from residues 2-111 and the
extends from residues 122-320 [3]. Residues 112–121 are what are thought to construct the extended loop that connects the two domains. Additionally, the C-terminal domain contains the active site [3].
Active Site
The concave groove mentioned above is where Acetyl CoA binds and is known to be the active site of the enzyme. he Acetyl-CoA binding site is nearly 1100 Å of surface area where several residues interact to simultaneously bind Acetyl CoA and the lysine target of acetylation [3]. Because Acetyl CoA exhibits a bent shape it is thought that the ligand is able to wrap itself around the protein upon binding. Functional studies state that a
conformational change occurs after Acetyl CoA binds this conformational change and results in the formation of a for the target lysine residue to enter the backside of the active site to be acetylated [3]. The side chain of the Lysine to be acetylated enters the complex from the back side of the active site adjacent to the gating region. Near 60% of the Acetyl CoA molecule is found buried in a highly non-polar region of the protein surface called the hydrophobic pocket.
Hydrophobic Pocket
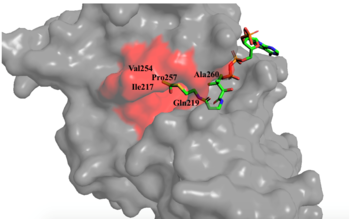
Figure 1. Image of the substrate Acetyl CoA bound in the groove of HAT1 (1BOB.pdb). The groove contains the three residues involved in the acetyltransferase mechanism.
The active site consists of the Acetyl CoA ligand bound to the enzyme in a groove on the surface of the protein. The
ligand is held in place by several bonds to protein residues that result in the formation of a . The hydrophobic pocket consists of the interacting side chains from residues in addition to further bonds resulting from residues 217-220 and 255-256
[3] (figure 1). The amide of main-chain hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl oxygen of the Acetyl group in the binding pocket. The main-chain amide of also donates a hydrogen bond from its side chain to oxygen PO5 of the pantothenic acid group
[3]. The binding within the hydrophobic pocket is further supplemented through the creation of a protein gate that establishes a bridge over the concave surface that serves to keep Acetyl CoA in place while the enzyme interacts with the histone.
Mechanism
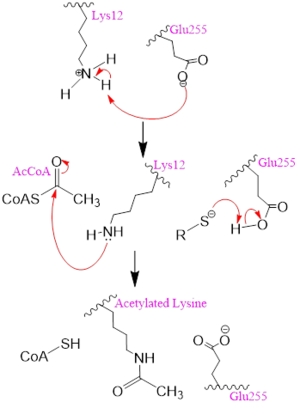
Figure 2. A possible acetylation mechanism of HAT1 (PDB: 1BOB). Mechanism consists of deptronation of Lys-12 of histone H4 and then transfer of an acetyl group from Acetyl CoA to Lys-12.
Several mechanisms for the transfer of the acetyl group to the Lys-12 of the histone have been proposed. The most accurate and likely mechanism today is conserved across several HAT1 studies and consists of deprotonating the amino group on the Lys-12 of H4 (figure 2). This mechanism was proposed by Wu et al with respect to the human HAT1 protein. Analysis was done on the 1BOB model (retrieved from the protein database) and similar residues with respect to location and function were identified. The main chain carbonyl oxygen of the polar residues are predicted to deprotonate the Lys-12 reside of H4 as seen in figure 2
[5]. Structural analysis of the 4PSW protein shows that the main chain carbonyls of these three residues are found in close proximity of the amino group of Lys-12
[6]. Of those residues it is uncertain which (if any) accept the proton of Lys-12. Each main chain carbonyl oxygen belonging to these three residues falls within 2 to 3 angstroms of the target amide on Lysine 12. Deprotonation of the amino group on the Lys-12 makes the residue nucleophilic enough to directly attack the carbonyl carbon of the acetyl group to initiate the acetyl transfer. We selected Glu255 to be the proton acceptor in our proposed mechanism displayed in figure 2. The transfer mechanism is contingent on the conformational change and the formation of a functional gate that spans the concave groove over the bound Acetyl CoA. This gate holds the substrate in place while the enzymatic
deprotonation process takes place
[5].
Protein Gate
The consists of several residues that coordinate a conformational change in the protein to hold the Acetyl CoA ligand in place. cooperate to create a bridge over Acetyl CoA [3]. The main chain amide of hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl oxygen of Asn-258 which allows for proper positioning of Asn-258 to bond with other residues and Acetyl CoA itself. The side chain amide of Asn-258 also binds via a water molecule (H2O-415) to Glu-162 on its main chain amide [3]. These bonds help secure the position of so that a hydrogen bond can be established from the side-chain amide to the PO5 carbonyl oxygen. Together, the side chains of Ile-161, Glu-162, and Asn-258 form a protein gate over the Acetyl CoA binding cleft. Hydrogen bonds further fixate Acetyl CoA by connecting the main chain amide of Glu-162 to the side chain amide of Asn-258. The side chain carbonyl oxygen of Phe-261 hydrogen bonds to its main chain amide to bridge the binding cleft over Acetyl-CoA. The gate allows for correct binding of Acetyl CoA. Once the ligand is bound, subsequent conformational changes of HAT1 take place allowing for Lys-12 to act as a nucleophile.
Medical Relevance
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kleff S, Andrulis ED, Anderson CW, Sternglanz R. Identification of a gene encoding a yeast histone H4 acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):24674-7. PMID:7559580
- ↑ DesJarlais R, Tummino PJ. Role of Histone-Modifying Enzymes and Their Complexes in Regulation of Chromatin Biology. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 22;55(11):1584-99. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210. Epub , 2016 Jan 26. PMID:26745824 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Kleff S, Andrulis ED, Anderson CW, Sternglanz R. Identification of a gene encoding a yeast histone H4 acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):24674-7. PMID:7559580
- ↑ Agudelo Garcia PA, Hoover ME, Zhang P, Nagarajan P, Freitas MA, Parthun MR. Identification of multiple roles for histone acetyltransferase 1 in replication-coupled chromatin assembly. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Sep 19;45(16):9319-9335. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx545. PMID:28666361 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx545
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Wu H, Moshkina N, Min J, Zeng H, Joshua J, Zhou MM, Plotnikov AN. Structural basis for substrate specificity and catalysis of human histone acetyltransferase 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 5;109(23):8925-30. Epub 2012 May 21. PMID:22615379 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114117109
- ↑ Li Y, Zhang L, Liu T, Chai C, Fang Q, Wu H, Agudelo Garcia PA, Han Z, Zong S, Yu Y, Zhang X, Parthun MR, Chai J, Xu RM, Yang M. Hat2p recognizes the histone H3 tail to specify the acetylation of the newly synthesized H3/H4 heterodimer by the Hat1p/Hat2p complex. Genes Dev. 2014 Jun 1;28(11):1217-27. doi: 10.1101/gad.240531.114. Epub 2014 May , 16. PMID:24835250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.240531.114
Student Contributors
Kiran Kaur, Emily Leiderman, Benjamin Nick


