We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Courtney Brown/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
< User:Courtney Brown(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
===Histones=== | ===Histones=== | ||
| - | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone Histones] are basic proteins that interact with nuclear DNA to help condense this DNA into [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromatin chromatin]. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleosome Nucleosomes] are chromatin beads made up of this nuclear DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins, or a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_octamer histone octamer], in order to fit into the nucleus<ref name="Histones"> Histones | Learn Science at Scitable https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/histone-histones-57</ref>. The chromatin found inside the nucleus are catagorized into [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heterochromatin heterochromatin], which are compact and transcriptionally silent, and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euchromatin euchromatin], which are less compact and transcriptionally active<ref name="Chromatin"> What is chromatin, heterochromatin and euchromatin? MBInfo https://www.mechanobio.info/genome-regulation/what-is-chromatin-heterochromatin-and-euchromatin</ref>. Modifying histones is a type of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigenetics epigenetics], where changes are made in gene expression | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone Histones] are basic proteins that interact with nuclear DNA to help condense this DNA into [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromatin chromatin]. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleosome Nucleosomes] are chromatin beads made up of this nuclear DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins, or a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_octamer histone octamer], in order to fit into the nucleus<ref name="Histones"> Histones | Learn Science at Scitable https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/histone-histones-57</ref>. The chromatin found inside the nucleus are catagorized into [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heterochromatin heterochromatin], which are compact and transcriptionally silent, and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euchromatin euchromatin], which are less compact and transcriptionally active<ref name="Chromatin"> What is chromatin, heterochromatin and euchromatin? MBInfo https://www.mechanobio.info/genome-regulation/what-is-chromatin-heterochromatin-and-euchromatin</ref>. Modifying histones is a type of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigenetics epigenetics], where changes are made in gene expression while the DNA sequence remains the same. Four different examples of histone modifications include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_acetylation_and_deacetylation histone acetylation, histone deacetylation], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_methylation histone methylation] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demethylase histone demethylation]<ref name="Histones" />. |
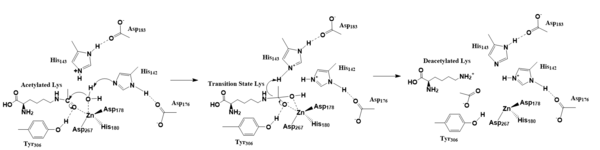
===Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)=== | ===Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)=== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
==Inhibition== | ==Inhibition== | ||
===HDAC Inhibitors=== | ===HDAC Inhibitors=== | ||
| - | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_deacetylase_inhibitor HDAC inhibitors] render histone deacetylases inactive. While a variety of these inhibitors are used to target different HDACs, common structural motifs among them include a zinc-binding moiety, a surface recognition or capping group, and a straight chain alkyl, vinyl, or aryl linker | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_deacetylase_inhibitor HDAC inhibitors] render histone deacetylases inactive. While a variety of these inhibitors are used to target different HDACs, common structural motifs among them include a zinc-binding moiety, a surface recognition or capping group, and a connecting straight chain alkyl, vinyl, or aryl linker. HDAC inhibitors bind and deactivate the HDACs through interactions with the rim amino acids at the active site of the HDAC (<scene name='81/811716/Hdac8_hydroxamicacid/6'>HDAC8 with Inhibitor</scene>)<ref name="Tabackman">PMID:27374062</ref>. The capping group is generally hydrophobic and <scene name='81/811716/Hydrophobic_intxn/1'>interacts</scene> with these residues (Figure 3)[[Image:Vorinostat_image.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 3. The anticancer agent Vorinostat is an example of an HDAC inhibitor that is currently undergoing clinical trial.]]. Binding occurs via interaction between conserved sections of HDAC active sites and the alkyl, vinyl, or aryl functional groups of the HDAC inhibitors<ref name="Marks">PMID:20594930</ref>. (<scene name='81/811715/Hdac8activesiteinhib/1'>Catalytic Pocket Bound by Inhibitor</scene>)<ref name="Vannini">PMID:15477595</ref>. |
===Clinical Application=== | ===Clinical Application=== | ||
Current revision
The Human Histone Deacetylase, HDAC8
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Histones | Learn Science at Scitable https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/histone-histones-57
- ↑ What is chromatin, heterochromatin and euchromatin? MBInfo https://www.mechanobio.info/genome-regulation/what-is-chromatin-heterochromatin-and-euchromatin
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 Vannini A, Volpari C, Gallinari P, Jones P, Mattu M, Carfi A, De Francesco R, Steinkuhler C, Di Marco S. Substrate binding to histone deacetylases as shown by the crystal structure of the HDAC8-substrate complex. EMBO Rep. 2007 Sep;8(9):879-84. Epub 2007 Aug 10. PMID:17721440
- ↑ Seto E, Yoshida M. Erasers of histone acetylation: the histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Apr 1;6(4):a018713. doi:, 10.1101/cshperspect.a018713. PMID:24691964 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a018713
- ↑ Chen K, Zhang X, Wu YD, Wiest O. Inhibition and mechanism of HDAC8 revisited. J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Aug 20;136(33):11636-43. doi: 10.1021/ja501548p. Epub 2014, Aug 7. PMID:25060069 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja501548p
- ↑ Tabackman AA, Frankson R, Marsan ES, Perry K, Cole KE. Structure of 'linkerless' hydroxamic acid inhibitor-HDAC8 complex confirms the formation of an isoform-specific subpocket. J Struct Biol. 2016 Sep;195(3):373-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2016.06.023. Epub 2016, Jun 29. PMID:27374062 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2016.06.023
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Marks PA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: a chemical genetics approach to understanding cellular functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct-Dec;1799(10-12):717-25. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.05.008. Epub 2010 Jun 8. PMID:20594930 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.05.008
- ↑ Vannini A, Volpari C, Filocamo G, Casavola EC, Brunetti M, Renzoni D, Chakravarty P, Paolini C, De Francesco R, Gallinari P, Steinkuhler C, Di Marco S. Crystal structure of a eukaryotic zinc-dependent histone deacetylase, human HDAC8, complexed with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Oct 19;101(42):15064-9. Epub 2004 Oct 11. PMID:15477595
Student Contributors
- Courtney Brown
- Cassandra Marsh
- Carolyn Hurdle