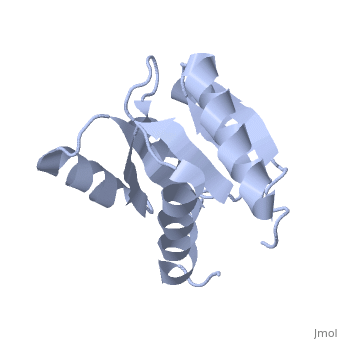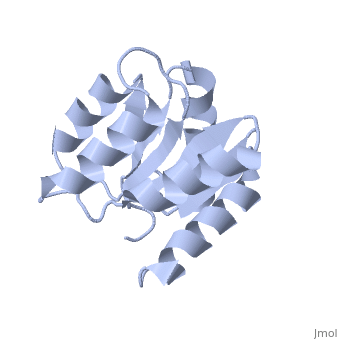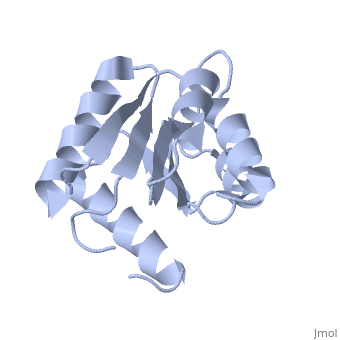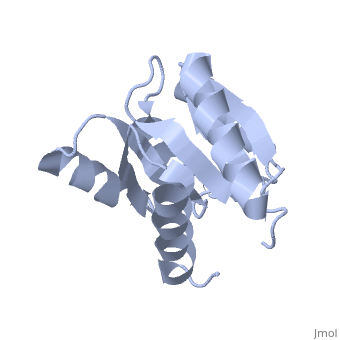
Chemotaxis protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''Chemotaxis proteins''' direct cell movement according to certain chemicals in their environment.<ref>PMID:4598187</ref> | '''Chemotaxis proteins''' direct cell movement according to certain chemicals in their environment.<ref>PMID:4598187</ref> | ||
| - | + | *'''CheY''' is a response regulator determining the swimming behaviour of the cell<ref>PMID:7623663</ref>. | |
*[[Molecular Playground/Bacterial Chemotaxis Receptors]] for '''CheW'''<br /> | *[[Molecular Playground/Bacterial Chemotaxis Receptors]] for '''CheW'''<br /> | ||
*[[Molecular Playground/Bacterial Chemotaxis Complex]] for '''CheA''' and '''CheW'''<br /> | *[[Molecular Playground/Bacterial Chemotaxis Complex]] for '''CheA''' and '''CheW'''<br /> | ||
Revision as of 07:42, 3 June 2024
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Adler J, Tso WW. "Decision"-making in bacteria: chemotactic response of Escherichia coli to conflicting stimuli. Science. 1974 Jun 21;184(4143):1292-4. PMID:4598187
- ↑ Sanna MG, Swanson RV, Bourret RB, Simon MI. Mutations in the chemotactic response regulator, CheY, that confer resistance to the phosphatase activity of CheZ. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Mar;15(6):1069-79. PMID:7623663 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02282.x
- ↑ Djordjevic S, Stock AM. Chemotaxis receptor recognition by protein methyltransferase CheR. Nat Struct Biol. 1998 Jun;5(6):446-50. PMID:9628482
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Lynmarie K Thompson, Alexander Berchansky