|
|
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
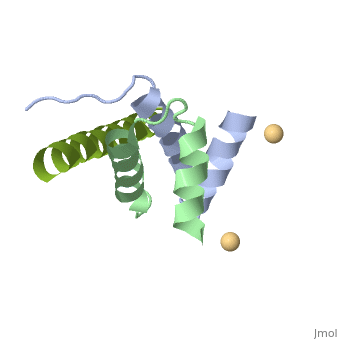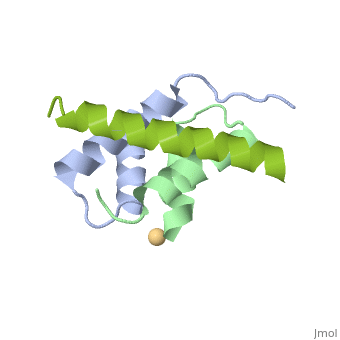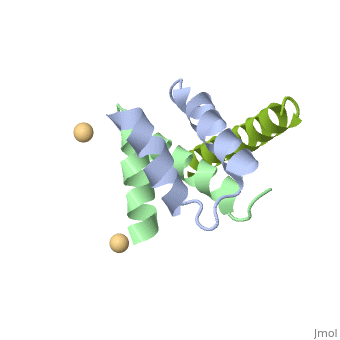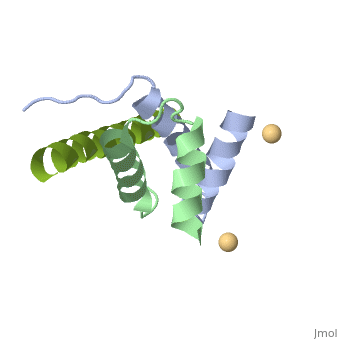
| | <StructureSection load='4zp3' size='340' side='right'caption='[[4zp3]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.63Å' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='4zp3' size='340' side='right'caption='[[4zp3]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.63Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4zp3]] is a 18 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4ZP3 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4ZP3 FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4zp3]] is a 18 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4ZP3 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4ZP3 FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CD:CADMIUM+ION'>CD</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CD:CADMIUM+ION'>CD</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">PRKAR2A, PKR2, PRKAR2 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN]), AKAP7, AKAP15, AKAP18 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN])</td></tr>
| + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4zp3 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4zp3 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/4zp3 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4zp3 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4zp3 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4zp3 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4zp3 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4zp3 OCA], [http://pdbe.org/4zp3 PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4zp3 RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4zp3 PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4zp3 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/KAP2_HUMAN KAP2_HUMAN]] Regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinases involved in cAMP signaling in cells. Type II regulatory chains mediate membrane association by binding to anchoring proteins, including the MAP2 kinase. [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/AKA7A_HUMAN AKA7A_HUMAN]] Targets the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) to the plasma membrane, and permits functional coupling to the L-type calcium channel. The membrane-associated form reduces epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity, whereas the free cytoplasmic form may negatively regulate ENaC channel feedback inhibition by intracellular sodium.<ref>PMID:10613906</ref> <ref>PMID:17244820</ref> <ref>PMID:9545239</ref> | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/AKA7G_HUMAN AKA7G_HUMAN] Probably targets cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) to the cellular membrane or cytoskeletal structures. The membrane-associated form reduces epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity, whereas the free cytoplasmic form may negatively regulate ENaC channel feedback inhibition by intracellular sodium.<ref>PMID:10613906</ref> <ref>PMID:17244820</ref> |
| | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> |
| | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == |
| Line 28: |
Line 27: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Autenrieth, K]] | + | [[Category: Autenrieth K]] |
| - | [[Category: Daumke, O]] | + | [[Category: Daumke O]] |
| - | [[Category: Faelber, K]] | + | [[Category: Faelber K]] |
| - | [[Category: Goetz, F]] | + | [[Category: Goetz F]] |
| - | [[Category: Heinemann, U]] | + | [[Category: Heinemann U]] |
| - | [[Category: Herberg, F W]] | + | [[Category: Herberg FW]] |
| - | [[Category: Klussmann, E]] | + | [[Category: Klussmann E]] |
| - | [[Category: Krause, G]] | + | [[Category: Krause G]] |
| - | [[Category: Kreuchwig, A]] | + | [[Category: Kreuchwig A]] |
| - | [[Category: Roske, Y]] | + | [[Category: Roske Y]] |
| - | [[Category: Zuehlke, K]] | + | [[Category: Zuehlke K]] |
| - | [[Category: Akap]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Amphiphathic helix]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Anchor point]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Dd-domain]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Signaling protein]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Function
AKA7G_HUMAN Probably targets cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) to the cellular membrane or cytoskeletal structures. The membrane-associated form reduces epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity, whereas the free cytoplasmic form may negatively regulate ENaC channel feedback inhibition by intracellular sodium.[1] [2]
Publication Abstract from PubMed
A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) interact with the dimerization/docking (D/D) domains of regulatory subunits of the ubiquitous protein kinase A (PKA). AKAPs tether PKA to defined cellular compartments establishing distinct pools to increase the specificity of PKA signalling. Here, we elucidated the structure of an extended PKA-binding domain of AKAP18beta bound to the D/D domain of the regulatory RIIalpha subunits of PKA. We identified three hydrophilic anchor points in AKAP18beta outside the core PKA-binding domain, which mediate contacts with the D/D domain. Such anchor points are conserved within AKAPs that bind regulatory RII subunits of PKA. We derived a different set of anchor points in AKAPs binding regulatory RI subunits of PKA. <em>In vitro</em> and cell-based experiments confirm the relevance of these sites for the interaction of RII subunits with AKAP18 and of RI subunits with the RI-specific smAKAP. Thus we report a novel mechanism governing interactions of AKAPs with PKA. The sequence specificity of each AKAP around the anchor points and the requirement of these points for the tight binding of PKA allow the development of selective inhibitors to unequivocally ascribe cellular functions to the AKAP18-PKA and other AKAP-PKA interactions.
AKAP18:PKA-RIIalpha structure reveals crucial anchor points for recognition of regulatory subunits of PKA.,Gotz F, Roske Y, Schulz MS, Autenrieth K, Bertinetti D, Faelber K, Zuhlke K, Kreuchwig A, Kennedy E, Krause G, Daumke O, Herberg FW, Heinemann U, Klussmann E Biochem J. 2016 Apr 21. pii: BCJ20160242. PMID:27102985[3]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Trotter KW, Fraser ID, Scott GK, Stutts MJ, Scott JD, Milgram SL. Alternative splicing regulates the subcellular localization of A-kinase anchoring protein 18 isoforms. J Cell Biol. 1999 Dec 27;147(7):1481-92. PMID:10613906
- ↑ Bengrine A, Li J, Awayda MS. The A-kinase anchoring protein 15 regulates feedback inhibition of the epithelial Na+ channel. FASEB J. 2007 Apr;21(4):1189-201. Epub 2007 Jan 23. PMID:17244820 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-6046com
- ↑ Gotz F, Roske Y, Schulz MS, Autenrieth K, Bertinetti D, Faelber K, Zuhlke K, Kreuchwig A, Kennedy E, Krause G, Daumke O, Herberg FW, Heinemann U, Klussmann E. AKAP18:PKA-RIIalpha structure reveals crucial anchor points for recognition of regulatory subunits of PKA. Biochem J. 2016 Apr 21. pii: BCJ20160242. PMID:27102985 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160242
|