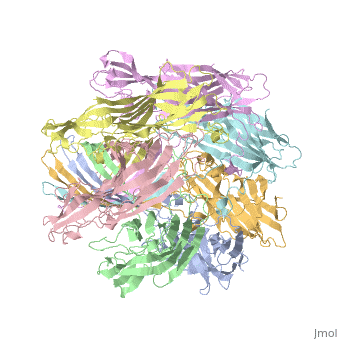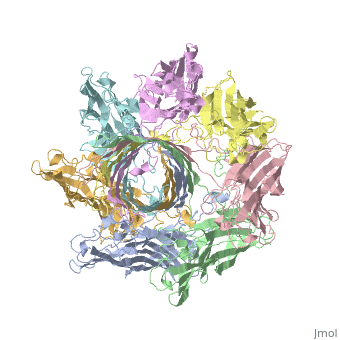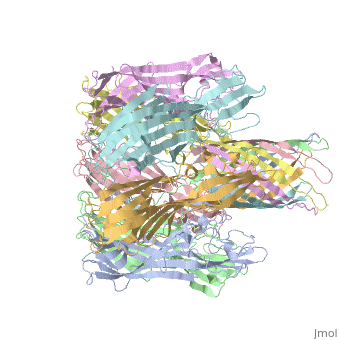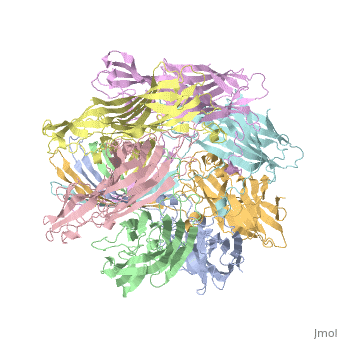Hemolysin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='7ahl' size='350' side='right' caption='α-hemolysin heptamer (PDB code [[7ahl]]).' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='7ahl' size='350' side='right' caption='α-hemolysin heptamer (PDB code [[7ahl]]).' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Hemolysin''' (HL) is exotoxin from bacteria which causes lysis of red blood cells<ref>PMID:20110774</ref>. | + | '''Hemolysin''' (HL) is exotoxin from bacteria which causes lysis of red blood cells<ref>PMID:20110774</ref>. '''α-hemolysin''' from the bacterium ''Clostridium'' are called '''alpha-toxin'''. They are zinc metalloenzymes which bind to the membrane in the presence of calcium. It acts as a phospholipase C. |
See details for α-hemolysin in [[Pore forming toxin, α-hemolysin]]. | See details for α-hemolysin in [[Pore forming toxin, α-hemolysin]]. | ||
Revision as of 08:07, 17 August 2020
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mestre MB, Fader CM, Sola C, Colombo MI. Alpha-hemolysin is required for the activation of the autophagic pathway in Staphylococcus aureus-infected cells. Autophagy. 2010 Jan;6(1):110-25. PMID:20110774
- ↑ Nizet V. Streptococcal beta-hemolysins: genetics and role in disease pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 2002 Dec;10(12):575-80. PMID:12564994
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Mark Hoelzer, Wayne Decatur, Alexander Berchansky, Marius Mihasan