Polyneuridine Aldehyde Esterase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
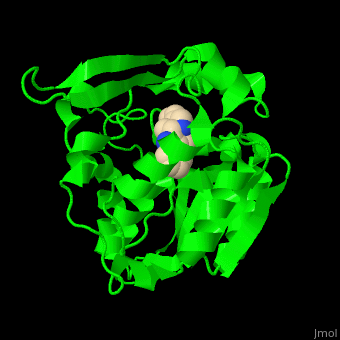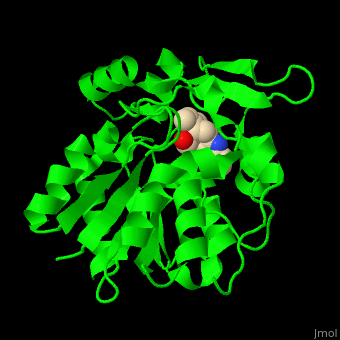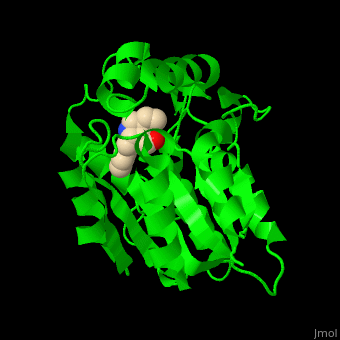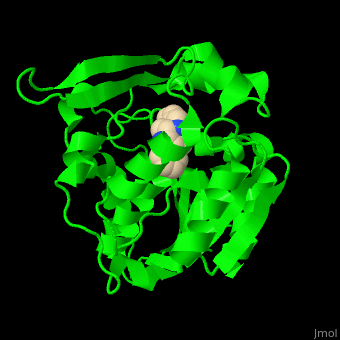
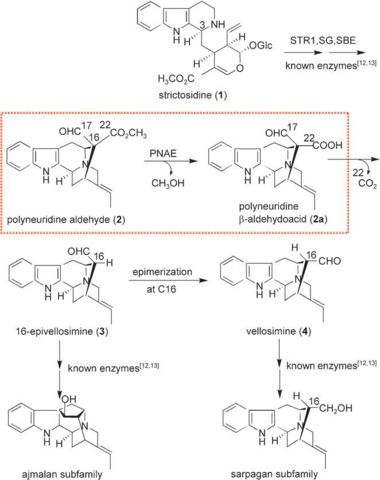
| - | PNAE overall structure is of an α/β hydrolase. | + | PNAE overall structure is of an α/β hydrolase. <scene name='37/373631/Cv/7'>PNAE active site</scene> contains the <scene name='37/373631/Cv/8'>canonical hydrolase triad of Ser, Asp and His (mutated to Ala)</scene> and the <scene name='37/373631/Cv/9'>Ser is covalently linked to the vellosimine ligand</scene><ref>PMID:19496101</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of polyneuridine aldehyde esterase== | ==3D structures of polyneuridine aldehyde esterase== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of polyneuridine aldehyde esterase
2wfm – SePAE (mutant) – Serpentwood
2wfl – SePAE
3gzj – SePAE + 16-epi-vellosimine
References
- ↑ Mattern-Dogru E, Ma X, Hartmann J, Decker H, Stockigt J. Potential active-site residues in polyneuridine aldehyde esterase, a central enzyme of indole alkaloid biosynthesis, by modelling and site-directed mutagenesis. Eur J Biochem. 2002 Jun;269(12):2889-96. PMID:12071952
- ↑ Yang L, Hill M, Wang M, Panjikar S, Stockigt J. Structural basis and enzymatic mechanism of the biosynthesis of C9- from C10-monoterpenoid indole alkaloids. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48(28):5211-3. PMID:19496101 doi:10.1002/anie.200900150
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, Liuqing Yang, Joel L. Sussman