UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase''' (LpxA) initiates lipid A biosynthesis. It catalyzes the transfer of 3-hydroxymyristic acid from acyl carrier protein to the 3'-hydroxyl group of UDP-GlcNAc<ref>PMID:10480918</ref>. | + | '''UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase''' or |
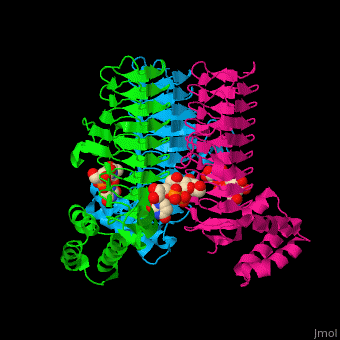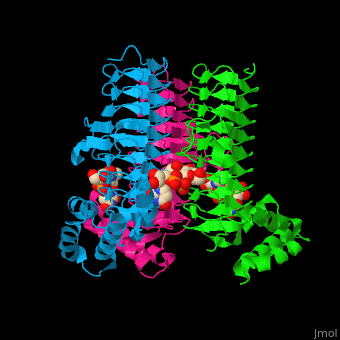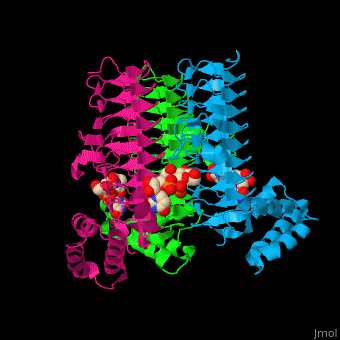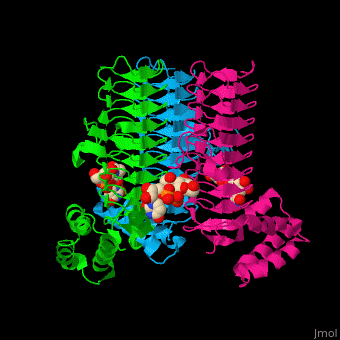
| + | '''Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]--UDP-N-acetylglucosamine O-acyltransferase''' (LpxA) initiates lipid A biosynthesis. It catalyzes the transfer of 3-hydroxymyristic acid from acyl carrier protein to the 3'-hydroxyl group of UDP-GlcNAc<ref>PMID:10480918</ref>. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 11:05, 19 March 2020
| |||||||||||
3D structures of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase
Updated on 19-March-2020
References
- ↑ Wyckoff TJ, Raetz CR. The active site of Escherichia coli UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase. Chemical modification and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 17;274(38):27047-55. PMID:10480918
- ↑ Ulaganathan V, Buetow L, Hunter WN. Nucleotide substrate recognition by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase (LpxA) in the first step of lipid A biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 2007 Jun 1;369(2):305-12. Epub 2007 Mar 21. PMID:17434525 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.03.039