Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
CFTR is a mostly <scene name='78/785332/Secondary_structure/1'>alpha helical</scene> protein. The membrane spanning segments can be clearly seen with coloring by <scene name='78/785332/Hydrophobicity/1'>hydrophobicity</scene>, which shows hydrophobic residues in gray and hydrophilic residues in purple. | CFTR is a mostly <scene name='78/785332/Secondary_structure/1'>alpha helical</scene> protein. The membrane spanning segments can be clearly seen with coloring by <scene name='78/785332/Hydrophobicity/1'>hydrophobicity</scene>, which shows hydrophobic residues in gray and hydrophilic residues in purple. | ||
| - | One feature of the CFTR is a Walker motif, which is found in ATP binding proteins.It is also known as a P (or phosphate binding) loop. | + | The extracellular end of the channel has several <scene name='78/785332/Ec_cl_selection/1'>positively charged</scene> residues that are important for recruiting chloride ions to the channel. A number of <scene name='78/785332/Plus_channel/1'>positively charged</scene> residues line the channel. One feature of the CFTR is a Walker motif, which is found in ATP binding proteins.It is also known as a P (or phosphate binding) loop. |
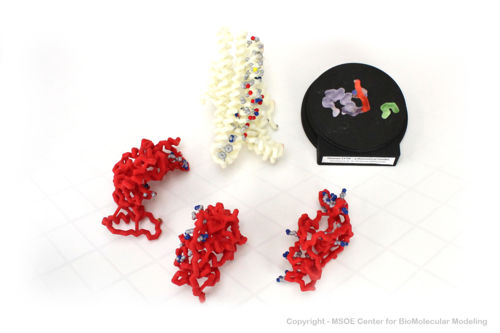
==3D Printed Physical Model of the CFTR protein== | ==3D Printed Physical Model of the CFTR protein== | ||
Revision as of 21:05, 16 October 2019
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
| |||||||||||