|
|
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
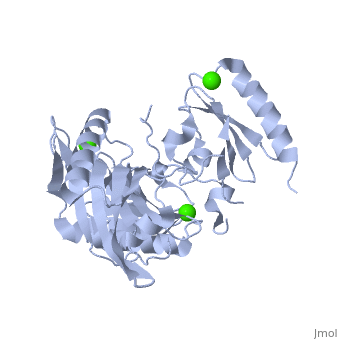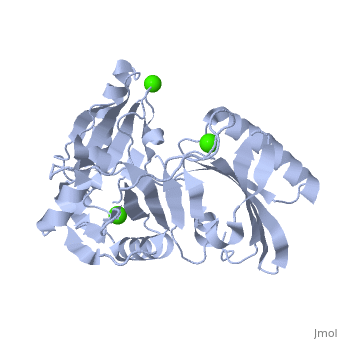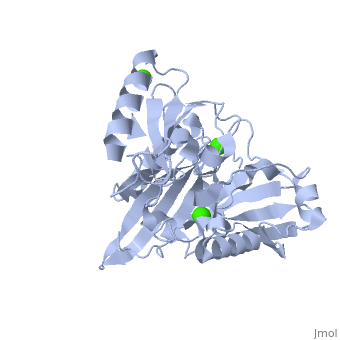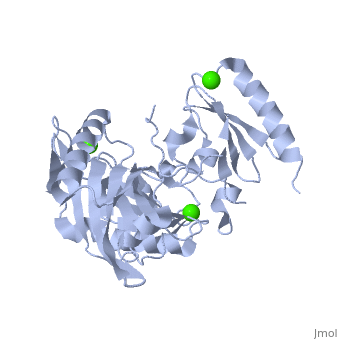
| | <StructureSection load='1p8x' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1p8x]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.00Å' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='1p8x' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1p8x]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.00Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1p8x]] is a 3 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1P8X OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1P8X FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1p8x]] is a 3 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1P8X OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1P8X FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CA:CALCIUM+ION'>CA</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1p8x FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1p8x OCA], [http://pdbe.org/1p8x PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1p8x RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1p8x PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1p8x ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CA:CALCIUM+ION'>CA</scene></td></tr> |
| | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1p8x FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1p8x OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1p8x PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1p8x RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1p8x PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1p8x ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Disease == | | == Disease == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/GELS_HUMAN GELS_HUMAN]] Defects in GSN are the cause of amyloidosis type 5 (AMYL5) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/105120 105120]]; also known as familial amyloidosis Finnish type. AMYL5 is a hereditary generalized amyloidosis due to gelsolin amyloid deposition. It is typically characterized by cranial neuropathy and lattice corneal dystrophy. Most patients have modest involvement of internal organs, but severe systemic disease can develop in some individuals causing peripheral polyneuropathy, amyloid cardiomyopathy, and nephrotic syndrome leading to renal failure.<ref>PMID:2157434</ref> <ref>PMID:2153578</ref> <ref>PMID:2176481</ref> <ref>PMID:1338910</ref> | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/GELS_HUMAN GELS_HUMAN] Defects in GSN are the cause of amyloidosis type 5 (AMYL5) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/105120 105120]; also known as familial amyloidosis Finnish type. AMYL5 is a hereditary generalized amyloidosis due to gelsolin amyloid deposition. It is typically characterized by cranial neuropathy and lattice corneal dystrophy. Most patients have modest involvement of internal organs, but severe systemic disease can develop in some individuals causing peripheral polyneuropathy, amyloid cardiomyopathy, and nephrotic syndrome leading to renal failure.<ref>PMID:2157434</ref> <ref>PMID:2153578</ref> <ref>PMID:2176481</ref> <ref>PMID:1338910</ref> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/GELS_HUMAN GELS_HUMAN]] Calcium-regulated, actin-modulating protein that binds to the plus (or barbed) ends of actin monomers or filaments, preventing monomer exchange (end-blocking or capping). It can promote the assembly of monomers into filaments (nucleation) as well as sever filaments already formed. Plays a role in ciliogenesis.<ref>PMID:20393563</ref> | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/GELS_HUMAN GELS_HUMAN] Calcium-regulated, actin-modulating protein that binds to the plus (or barbed) ends of actin monomers or filaments, preventing monomer exchange (end-blocking or capping). It can promote the assembly of monomers into filaments (nucleation) as well as sever filaments already formed. Plays a role in ciliogenesis.<ref>PMID:20393563</ref> |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| Line 32: |
Line 33: |
| | | | |
| | ==See Also== | | ==See Also== |
| - | *[[3D Structures of gelsolin|3D Structures of gelsolin]] | + | *[[Gelsolin 3D structures|Gelsolin 3D structures]] |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Burtnick, L D]] | + | [[Category: Burtnick LD]] |
| - | [[Category: Narayan, K]] | + | [[Category: Narayan K]] |
| - | [[Category: Robinson, R C]] | + | [[Category: Robinson RC]] |
| - | [[Category: Calcium-binding]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Structural protein]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Disease
GELS_HUMAN Defects in GSN are the cause of amyloidosis type 5 (AMYL5) [MIM:105120; also known as familial amyloidosis Finnish type. AMYL5 is a hereditary generalized amyloidosis due to gelsolin amyloid deposition. It is typically characterized by cranial neuropathy and lattice corneal dystrophy. Most patients have modest involvement of internal organs, but severe systemic disease can develop in some individuals causing peripheral polyneuropathy, amyloid cardiomyopathy, and nephrotic syndrome leading to renal failure.[1] [2] [3] [4]
Function
GELS_HUMAN Calcium-regulated, actin-modulating protein that binds to the plus (or barbed) ends of actin monomers or filaments, preventing monomer exchange (end-blocking or capping). It can promote the assembly of monomers into filaments (nucleation) as well as sever filaments already formed. Plays a role in ciliogenesis.[5]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Gelsolin requires activation to carry out its severing and capping activities on F-actin. Here, we present the structure of the isolated C-terminal half of gelsolin (G4-G6) at 2.0 A resolution in the presence of Ca(2+) ions. This structure completes a triptych of the states of activation of G4-G6 that illuminates its role in the function of gelsolin. Activated G4-G6 displays an open conformation, with the actin-binding site on G4 fully exposed and all three type-2 Ca(2+) sites occupied. Neither actin nor the type-l Ca(2+), which normally is sandwiched between actin and G4, is required to achieve this conformation.
Activation in isolation: exposure of the actin-binding site in the C-terminal half of gelsolin does not require actin.,Narayan K, Chumnarnsilpa S, Choe H, Irobi E, Urosev D, Lindberg U, Schutt CE, Burtnick LD, Robinson RC FEBS Lett. 2003 Sep 25;552(2-3):82-5. PMID:14527664[6]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Haltia M, Prelli F, Ghiso J, Kiuru S, Somer H, Palo J, Frangione B. Amyloid protein in familial amyloidosis (Finnish type) is homologous to gelsolin, an actin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):927-32. PMID:2157434
- ↑ Maury CP, Alli K, Baumann M. Finnish hereditary amyloidosis. Amino acid sequence homology between the amyloid fibril protein and human plasma gelsoline. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 15;260(1):85-7. PMID:2153578
- ↑ Ghiso J, Haltia M, Prelli F, Novello J, Frangione B. Gelsolin variant (Asn-187) in familial amyloidosis, Finnish type. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):827-30. PMID:2176481
- ↑ de la Chapelle A, Tolvanen R, Boysen G, Santavy J, Bleeker-Wagemakers L, Maury CP, Kere J. Gelsolin-derived familial amyloidosis caused by asparagine or tyrosine substitution for aspartic acid at residue 187. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):157-60. PMID:1338910 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng1092-157
- ↑ Kim J, Lee JE, Heynen-Genel S, Suyama E, Ono K, Lee K, Ideker T, Aza-Blanc P, Gleeson JG. Functional genomic screen for modulators of ciliogenesis and cilium length. Nature. 2010 Apr 15;464(7291):1048-51. doi: 10.1038/nature08895. PMID:20393563 doi:10.1038/nature08895
- ↑ Narayan K, Chumnarnsilpa S, Choe H, Irobi E, Urosev D, Lindberg U, Schutt CE, Burtnick LD, Robinson RC. Activation in isolation: exposure of the actin-binding site in the C-terminal half of gelsolin does not require actin. FEBS Lett. 2003 Sep 25;552(2-3):82-5. PMID:14527664
|